
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union, it adopts European legislation, following a proposal by the European Commission. The Parliament is composed of 705 members (MEPs). It represents the second-largest democratic electorate in the world, with an electorate of 375 million eligible voters in 2009.

A local area network (LAN) is a computer network that interconnects computers within a limited area such as a residence, school, laboratory, university campus or office building. By contrast, a wide area network (WAN) not only covers a larger geographic distance, but also generally involves leased telecommunication circuits.

A minicomputer, or colloquially mini, is a type of smaller general-purpose computer developed in the mid-1960s and sold at a much lower price than mainframe and mid-size computers from IBM and its direct competitors. In a 1970 survey, The New York Times suggested a consensus definition of a minicomputer as a machine costing less than US$25,000, with an input-output device such as a teleprinter and at least four thousand words of memory, that is capable of running programs in a higher level language, such as Fortran or BASIC.

A microcomputer is a small, relatively inexpensive computer having a central processing unit (CPU) made out of a microprocessor. The computer also includes memory and input/output (I/O) circuitry together mounted on a printed circuit board (PCB). Microcomputers became popular in the 1970s and 1980s with the advent of increasingly powerful microprocessors. The predecessors to these computers, mainframes and minicomputers, were comparatively much larger and more expensive. Many microcomputers are also personal computers. An early use of the term "personal computer" in 1962 predates microprocessor-based designs. (See "Personal Computer: Computers at Companies" reference below). A "microcomputer" used as an embedded control system may have no human-readable input and output devices. "Personal computer" may be used generically or may denote an IBM PC compatible machine.

Wang Laboratories was a US computer company founded in 1951 by An Wang and G. Y. Chu. The company was successively headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts (1954–1963), Tewksbury, Massachusetts (1963–1976), and finally in Lowell, Massachusetts (1976–1997). At its peak in the 1980s, Wang Laboratories had annual revenues of US$3 billion and employed over 33,000 people. It was one of the leading companies during the time of the Massachusetts Miracle.

Federico Faggin is an Italian physicist, engineer, inventor and entrepreneur. He is best known for designing the first commercial microprocessor, the Intel 4004. He led the 4004 (MCS-4) project and the design group during the first five years of Intel's microprocessor effort. Faggin also created, while working at Fairchild Semiconductor in 1968, the self-aligned MOS (metal-oxide-semiconductor) silicon-gate technology (SGT), which made possible MOS semiconductor memory chips, CCD image sensors, and the microprocessor. After the 4004, he led development of the Intel 8008 and 8080, using his SGT methodology for random logic chip design, which was essential to the creation of early Intel microprocessors. He was co-founder and CEO of Zilog, the first company solely dedicated to microprocessors, and led the development of the Zilog Z80 and Z8 processors. He was later the co-founder and CEO of Cygnet Technologies, and then Synaptics.

Olivetti S.p.A. is an Italian manufacturer of computers, tablets, smartphones, printers and other such business products as calculators and fax machines. Headquartered in Ivrea, in the Metropolitan City of Turin, the company has been part of the TIM Group since 2003. One of the first commercial programmable desktop calculators, the Programma 101, was produced by Olivetti in 1964 and was a commercial success.
Prime Computer, Inc. was a Natick, Massachusetts-based producer of minicomputers from 1972 until 1992. With the advent of PCs and the decline of the minicomputer industry, Prime was forced out of the market in the early 1990s, and by the end of 2010 the trademarks for both PRIME and PRIMOS no longer existed
The Intelligent Platform Management Interface (IPMI) is a set of computer interface specifications for an autonomous computer subsystem that provides management and monitoring capabilities independently of the host system's CPU, firmware and operating system. IPMI defines a set of interfaces used by system administrators for out-of-band management of computer systems and monitoring of their operation. For example, IPMI provides a way to manage a computer that may be powered off or otherwise unresponsive by using a network connection to the hardware rather than to an operating system or login shell. Another use case may be installing a custom operating system remotely. Without IPMI, installing a custom operating system may require an administrator to be physically present near the computer, insert a DVD or a USB flash drive containing the OS installer and complete the installation process using a monitor and a keyboard. Using IPMI, an administrator can mount an ISO image, simulate an installer DVD, and perform the installation remotely.
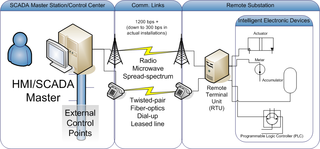
Distributed Network Protocol 3 (DNP3) is a set of communications protocols used between components in process automation systems. Its main use is in utilities such as electric and water companies. Usage in other industries is not common. It was developed for communications between various types of data acquisition and control equipment. It plays a crucial role in SCADA systems, where it is used by SCADA Master Stations, Remote Terminal Units (RTUs), and Intelligent Electronic Devices (IEDs). It is primarily used for communications between a master station and RTUs or IEDs. ICCP, the Inter-Control Center Communications Protocol, is used for inter-master station communications. Competing standards include the older Modbus protocol and the newer IEC 61850 protocol.
Wired for Management (WfM) was a primarily hardware-based system allowing a newly built computer without any software to be manipulated by a master computer that could access the hard disk of the new PC to paste the install program. It could also be used to update software and monitor system status remotely. Intel developed the system in the 1990s; it is now considered obsolete.
The seven institutions of the European Union (EU) are seated in four different cities, which are Brussels (Belgium), Frankfurt am Main (Germany), Luxembourg (Luxembourg) and Strasbourg (France), rather than being concentrated in a single capital city. All four were chosen, among various reasons, for their location halfway between France and Germany, the countries whose rivalry led to two World Wars and whose reconciliation paved the way for European integration. The EU agencies and other bodies are located all across the union, but usually not fixed in the treaties. The Hague is the only exception, as the fixed seat of the Agency for Law Enforcement Cooperation (Europol). Luxembourg City is the EU capital that can lay claim to having the most of the seven EU institutions based wholly or partly upon its territory, with only the European Council and European Central Bank not having a presence in the city. Over the years, Brussels has become the EU's political hub, with the College of the Commissioners – the European Commission's politically accountable executive – and the European Council both meeting at their Brussels-based headquarters, and the European Parliament and Council of the EU holding the majority of their meetings annually within the city. This has led media to describe it as the de facto "capital of the EU".

The city of Strasbourg in France is the official seat of the European Parliament. The institution is legally bound by the decision of Edinburgh European Council of 11 and 12 December 1992 and Article 341 of the TFEU to meet there twelve times a year for a session, each of which usually takes about four days. The majority of work, however, takes place in Brussels, and some other work is undertaken in Luxembourg City. Also all votes of the European Parliament must take place in Strasbourg. "Additional" sessions and committees take place in Brussels. Although de facto a majority of the Parliament's work is now geared to its Brussels site, it is legally bound to keep Strasbourg as its official home; a situation which garners much criticism from the European Parliament itself, as well as many interest groups, administrative staff, and environmentalist groups amongst others.
Deliberative assemblies – bodies that use parliamentary procedure to arrive at decisions – use several methods of voting on motions. The regular methods of voting in such bodies are a voice vote, a rising vote, and a show of hands. Additional forms of voting include a recorded vote and balloting.

Net3 was a Wi-Fi-like system developed, manufactured and commercialised by Olivetti in the early 1990s. It could wirelessly connect PCs to an Ethernet fixed LAN at a speed of up to 512kbit/s, over a very wide area. It was a micro-cellular system, in which each base station had an effective range of about 100m indoors, 300m outdoors, and the system supported seamless handover between base stations.

The Espace Léopold or Leopoldruimte is the complex of parliament buildings in Brussels, Belgium, housing the European Parliament, a legislative chamber of the European Union (EU). It consists of a number of buildings, primarily the oldest, the Paul-Henri Spaak building, which houses the debating chamber and the President's offices, and the Altiero Spinelli building, which is the largest. The buildings are located in the European Quarter of Brussels, with construction starting in 1989.
The European Parliament's presence in Kirchberg, Luxembourg currently consists of the Parliament's secretariat, although the Parliament had held plenary sessions in the city for a brief period.

The history of the personal computer as a mass-market consumer electronic device began with the microcomputer revolution of the 1970s. A personal computer is one intended for interactive individual use, as opposed to a mainframe computer where the end user's requests are filtered through operating staff, or a time-sharing system in which one large processor is shared by many individuals. After the development of the microprocessor, individual personal computers were low enough in cost that they eventually became affordable consumer goods. Early personal computers – generally called microcomputers – were sold often in electronic kit form and in limited numbers, and were of interest mostly to hobbyists and technicians.

Pier Giorgio Perotto was an Italian electrical engineer and inventor. Working for the manufacturer Olivetti, he led a design team that built the Programma 101, one of the world's first programmable calculators.
The Olivetti company, an Italian manufacturer of computers, tablets, smartphones, printers and other such business products as calculators and fax machines, was founded as a typewriter manufacturer by Camillo Olivetti in 1908 in the Turin commune of Ivrea, Italy. Olivetti was a pioneer in computer development, starting with the mainframe systems in the 1950s, and continuing into the 1990s with PC-compatible laptops and desktops.















