Related Research Articles
Agricultural science is a broad multidisciplinary field of biology that encompasses the parts of exact, natural, economic and social sciences that are used in the practice and understanding of agriculture. Professionals of the agricultural science are called agricultural scientists or agriculturists.

Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to solve technical problems, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve systems. Modern engineering comprises many subfields which include designing and improving infrastructure, machinery, vehicles, electronics, materials, and energy systems.

Gelatin or gelatine is a translucent, colorless, flavorless food ingredient, commonly derived from collagen taken from animal body parts. It is brittle when dry and rubbery when moist. It may also be referred to as hydrolyzed collagen, collagen hydrolysate, gelatine hydrolysate, hydrolyzed gelatine, and collagen peptides after it has undergone hydrolysis. It is commonly used as a gelling agent in food, beverages, medications, drug or vitamin capsules, photographic films, papers, and cosmetics.
Rheology is the study of the flow of matter, primarily in a fluid state but also as "soft solids" or solids under conditions in which they respond with plastic flow rather than deforming elastically in response to an applied force. Rheology is the branch of physics that deals with the deformation and flow of materials, both solids and liquids.
In engineering, a fail-safe is a design feature or practice that, in the event of a failure of the design feature, inherently responds in a way that will cause minimal or no harm to other equipment, to the environment or to people. Unlike inherent safety to a particular hazard, a system being "fail-safe" does not mean that failure is naturally inconsequential, but rather that the system's design prevents or mitigates unsafe consequences of the system's failure. If and when a "fail-safe" system fails, it remains at least as safe as it was before the failure. Since many types of failure are possible, failure mode and effects analysis is used to examine failure situations and recommend safety design and procedures.

Ketchup or catsup is a table condiment with a sweet and sour flavor. "Ketchup" now typically refers to tomato ketchup, although early recipes for various different varieties of ketchup contained mushrooms, oysters, mussels, egg whites, grapes, or walnuts, among other ingredients.

Agricultural productivity is measured as the ratio of agricultural outputs to inputs. While individual products are usually measured by weight, which is known as crop yield, varying products make measuring overall agricultural output difficult. Therefore, agricultural productivity is usually measured as the market value of the final output. This productivity can be compared to many different types of inputs such as labour or land. Such comparisons are called partial measures of productivity.
The field of strength of materials typically refers to various methods of calculating the stresses and strains in structural members, such as beams, columns, and shafts. The methods employed to predict the response of a structure under loading and its susceptibility to various failure modes takes into account the properties of the materials such as its yield strength, ultimate strength, Young's modulus, and Poisson's ratio. In addition, the mechanical element's macroscopic properties such as its length, width, thickness, boundary constraints and abrupt changes in geometry such as holes are considered.

In mechanics, compressive strength is the capacity of a material or structure to withstand loads tending to reduce size (compression). It is opposed to tensile strength which withstands loads tending to elongate, resisting tension. In the study of strength of materials, compressive strength, tensile strength, and shear strength can be analyzed independently.

In materials science, fatigue is the initiation and propagation of cracks in a material due to cyclic loading. Once a fatigue crack has initiated, it grows a small amount with each loading cycle, typically producing striations on some parts of the fracture surface. The crack will continue to grow until it reaches a critical size, which occurs when the stress intensity factor of the crack exceeds the fracture toughness of the material, producing rapid propagation and typically complete fracture of the structure.

Corticosterone, also known as 17-deoxycortisol and 11β,21-dihydroxyprogesterone, is a 21-carbon steroid hormone of the corticosteroid type produced in the cortex of the adrenal glands. In the very rare case of congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 17α-hydroxylase deficiency cortisol production is blocked.

Shelf life is the length of time that a commodity may be stored without becoming unfit for use, consumption, or sale. In other words, it might refer to whether a commodity should no longer be on a pantry shelf, or no longer on a supermarket shelf. It applies to cosmetics, foods and beverages, medical devices, medicines, explosives, pharmaceutical drugs, chemicals, tyres, batteries, and many other perishable items. In some regions, an advisory best before, mandatory use by or freshness date is required on packaged perishable foods. The concept of expiration date is related but legally distinct in some jurisdictions.
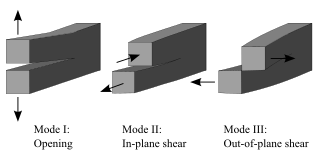
Fracture mechanics is the field of mechanics concerned with the study of the propagation of cracks in materials. It uses methods of analytical solid mechanics to calculate the driving force on a crack and those of experimental solid mechanics to characterize the material's resistance to fracture.
Failure causes are defects in design, process, quality, or part application, which are the underlying cause of a failure or which initiate a process which leads to failure. Where failure depends on the user of the product or process, then human error must be considered.
The five techniques, also known as deep interrogation, are a group of interrogation methods developed by the United Kingdom during the 20th century and are currently regarded as a form of torture. Originally developed by British forces in a variety of 20th-century conflicts, they are most notable for being applied to detainees in Northern Ireland during the Troubles. The five collective methods are prolonged wall-standing, hooding, subjection to noise, deprivation of sleep, and deprivation of food and drink.

Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) is the growth of crack formation in a corrosive environment. It can lead to unexpected and sudden failure of normally ductile metal alloys subjected to a tensile stress, especially at elevated temperature. SCC is highly chemically specific in that certain alloys are likely to undergo SCC only when exposed to a small number of chemical environments. The chemical environment that causes SCC for a given alloy is often one which is only mildly corrosive to the metal. Hence, metal parts with severe SCC can appear bright and shiny, while being filled with microscopic cracks. This factor makes it common for SCC to go undetected prior to failure. SCC often progresses rapidly, and is more common among alloys than pure metals. The specific environment is of crucial importance, and only very small concentrations of certain highly active chemicals are needed to produce catastrophic cracking, often leading to devastating and unexpected failure.
Autoxidation refers to oxidations brought about by reactions with oxygen at normal temperatures, without the intervention of flame or electric spark. The term is usually used to describe the gradual degradation of organic compounds in air at ambient temperatures. Many common phenomena can be attributed to autoxidation, such as food going rancid, the 'drying' of varnishes and paints, and the perishing of rubber. It is also an important concept in both industrial chemistry and biology. Autoxidation is therefore a fairly broad term and can encompass examples of photooxygenation and catalytic oxidation.

Forensic materials engineering, a branch of forensic engineering, focuses on the material evidence from crime or accident scenes, seeking defects in those materials which might explain why an accident occurred, or the source of a specific material to identify a criminal. Many analytical methods used for material identification may be used in investigations, the exact set being determined by the nature of the material in question, be it metal, glass, ceramic, polymer or composite. An important aspect is the analysis of trace evidence such as skid marks on exposed surfaces, where contact between dissimilar materials leaves material traces of one left on the other. Provided the traces can be analysed successfully, then an accident or crime can often be reconstructed. Another aim will be to determine the cause of a broken component using the technique of fractography.
Forensic polymer engineering is the study of failure in polymeric products. The topic includes the fracture of plastic products, or any other reason why such a product fails in service, or fails to meet its specification. The subject focuses on the material evidence from crime or accident scenes, seeking defects in those materials that might explain why an accident occurred, or the source of a specific material to identify a criminal. Many analytical methods used for polymer identification may be used in investigations, the exact set being determined by the nature of the polymer in question, be it thermoset, thermoplastic, elastomeric or composite in nature.

Cracks can be formed in many different elastomers by ozone attack, and the characteristic form of attack of vulnerable rubbers is known as ozone cracking. The problem was formerly very common, especially in tires, but is now rarely seen in those products owing to preventive measures.
References
- 1 2 Lauriola, Rosanna; Demetriou, Kyriakos (2015). Brill's Companion to the Reception of Euripides. Leiden: BRILL. p. 253. ISBN 9789004249370.
- ↑ "Elegant Degradation".
- ↑ Rutkowski, A. (1978). Advances in Smoking of Foods. Oxford: Pergamon Press. p. 1643. ISBN 0080220029.
- ↑ Lindberg, Thomas (1991). Strategies and Tactics in Organic Synthesis, Volume 3. San Diego, CA: Academic Press. p. 201. ISBN 0124502822.
- ↑ "Elegant Degradation: An Adaptation of Orestes 2.0". Kickstarter. Retrieved 2019-01-04.