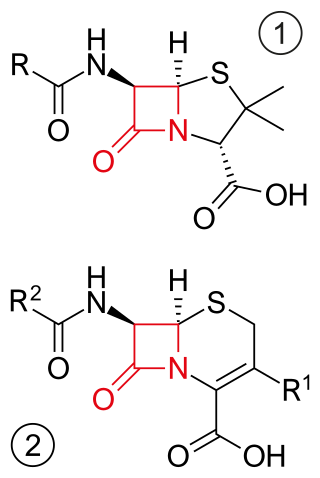
β-lactam antibiotics are antibiotics that contain a beta-lactam ring in their chemical structure. This includes penicillin derivatives (penams), cephalosporins and cephamycins (cephems), monobactams, carbapenems and carbacephems. Most β-lactam antibiotics work by inhibiting cell wall biosynthesis in the bacterial organism and are the most widely used group of antibiotics. Until 2003, when measured by sales, more than half of all commercially available antibiotics in use were β-lactam compounds. The first β-lactam antibiotic discovered, penicillin, was isolated from a strain of Penicillium rubens.

The rove beetles are a family (Staphylinidae) of beetles, primarily distinguished by their short elytra that typically leave more than half of their abdominal segments exposed. With roughly 63,000 species in thousands of genera, the group is the second largest family in the beetle order, after the true weevils (Curculionidae), which also makes in one of the largest families of organisms. It is an ancient group, with fossilized rove beetles known from the Triassic, 200 million years ago, and possibly even earlier if the genus Leehermania proves to be a member of this family. They are an ecologically and morphologically diverse group of beetles, and commonly encountered in terrestrial ecosystems.
Polyketides are a class of natural products derived from a precursor molecule consisting of a chain of alternating ketone (or reduced forms of a ketone) and methylene groups: (-CO-CH2-). First studied in the early 20th century, discovery, biosynthesis, and application of polyketides has evolved. It is a large and diverse group of secondary metabolites caused by its complex biosynthesis which resembles that of fatty acid synthesis. Because of this diversity, polyketides can have various medicinal, agricultural, and industrial applications. Many polyketides are medicinal or exhibit acute toxicity. Biotechnology has enabled discovery of more naturally-occurring polyketides and evolution of new polyketides with novel or improved bioactivity.
Okadaic acid, C44H68O13, is a toxin produced by several species of dinoflagellates, and is known to accumulate in both marine sponges and shellfish. One of the primary causes of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning, okadaic acid is a potent inhibitor of specific protein phosphatases and is known to have a variety of negative effects on cells. A polyketide, polyether derivative of a C38 fatty acid, okadaic acid and other members of its family have shined light upon many biological processes both with respect to dinoflagellete polyketide synthesis as well as the role of protein phosphatases in cell growth.

Malonyl-CoA is a coenzyme A derivative of malonic acid.

Phorbol is a natural, plant-derived organic compound. It is a member of the tigliane family of diterpenes. Phorbol was first isolated in 1934 as the hydrolysis product of croton oil, which is derived from the seeds of the purging croton, Croton tiglium. The structure of phorbol was determined in 1967. Various esters of phorbol have important biological properties, the most notable of which is the capacity to act as tumor promoters through activation of protein kinase C. They mimic diacylglycerols, glycerol derivatives in which two hydroxyl groups have reacted with fatty acids to form esters. The most common and potent phorbol ester is 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA), also called phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA), which is used as a biomedical research tool in contexts such as models of carcinogenesis.
Topoisomerase inhibitors are chemical compounds that block the action of topoisomerases, which are broken into two broad subtypes: type I topoisomerases (TopI) and type II topoisomerases (TopII). Topoisomerase plays important roles in cellular reproduction and DNA organization, as they mediate the cleavage of single and double stranded DNA to relax supercoils, untangle catenanes, and condense chromosomes in eukaryotic cells. Topoisomerase inhibitors influence these essential cellular processes. Some topoisomerase inhibitors prevent topoisomerases from performing DNA strand breaks while others, deemed topoisomerase poisons, associate with topoisomerase-DNA complexes and prevent the re-ligation step of the topoisomerase mechanism. These topoisomerase-DNA-inhibitor complexes are cytotoxic agents, as the un-repaired single- and double stranded DNA breaks they cause can lead to apoptosis and cell death. Because of this ability to induce apoptosis, topoisomerase inhibitors have gained interest as therapeutics against infectious and cancerous cells.

Nairobi fly is the common name for two species of rove beetle in the genus Paederus, native to East Africa. The beetles contain a corrosive substance known as pederin, which can cause chemical burns if it comes into contact with skin. Because of these burns, the Nairobi fly is sometimes referred to as a "dragon bug."
Polyketide synthases (PKSs) are a family of multi-domain enzymes or enzyme complexes that produce polyketides, a large class of secondary metabolites, in bacteria, fungi, plants, and a few animal lineages. The biosyntheses of polyketides share striking similarities with fatty acid biosynthesis.

Fatty acid synthase (FAS) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FASN gene.
In enzymology, an erythronolide synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Nodularins are potent toxins produced by the cyanobacterium Nodularia spumigena, among others. This aquatic, photosynthetic cyanobacterium forms visible colonies that present as algal blooms in brackish water bodies throughout the world. The late summer blooms of Nodularia spumigena are among the largest cyanobacterial mass occurrences in the world. Cyanobacteria are composed of many toxic substances, most notably of microcystins and nodularins: the two are not easily differentiated. A significant homology of structure and function exists between the two, and microcystins have been studied in greater detail. Because of this, facts from microcystins are often extended to nodularins.

Indolocarbazoles (ICZs) are a class of compounds that are under current study due to their potential as anti-cancer drugs and the prospective number of derivatives and uses found from the basic backbone alone. First isolated in 1977, a wide range of structures and derivatives have been found or developed throughout the world. Due to the extensive number of structures available, this review will focus on the more important groups here while covering their occurrence, biological activity, biosynthesis, and laboratory synthesis.

Psymberin, also known as irciniastatin A, is a cytotoxin derived from sea sponges. It was discovered by two independent research groups, one led by Dr. Phil Crews and one led by Dr. Jean Schmidt, in 2004. Psymberin was found to be highly bioactive as it showed LC50s at nanomolar concentrations against various types of tumors.

Paederus dermatitis, medically known as dermatitis linearis, is a skin irritation resulting from contact with the hemolymph of certain rove beetles, a group that belongs to the insect order Coleoptera and the genus Paederus. Other local names given to Paederus dermatitis include spider-lick, whiplash dermatitis, and Nairobi fly dermatitis.

Callystatin A is a polyketide natural product from the leptomycin family of secondary metabolites. It was first isolated in 1997 from the marine sponge Callyspongia truncata which was collected from the Goto Islands in the Nagasaki Prefecture of Japan by the Kobayashi group. Since then its absolute configuration has been elucidated and callystatin A was discovered to have anti-fungal and anti-tumor activities with extreme potency against the human epidermoid carcinoma KB cells (IG50 = 10 pg/ml) and the mouse lymphocytic leukemia Ll210 cells (IG50 = 20 pg/ml).

Paederus is a genus of small beetles of the family Staphylinidae. With 622 valid species assigned by 1987 to the subtribe Paederina, and with all but 148 within Paederus itself, the genus is large. Due to toxins in the hemolymph of some species within this genus, it has given its name to paederus dermatitis, a characteristic skin irritation that occurs if one of the insects is crushed against skin. That name, Paederus dermatitis, is a poor choice because, decades earlier, the affliction had been called dermatitis linearis, a name that works in all languages, not just English, because of its Latin origin; the name Paederus dermatitis is also inappropriate because it has shown to be caused by (a) only a few species of the genus Paederus, but (b) also a few species that belong to closely related genera within the subtribe Paederina. A scholarly paper in 2002 suggested that a Paederus species could have been responsible for some of the ten Plagues of Egypt described in the Bible's Book of Exodus.
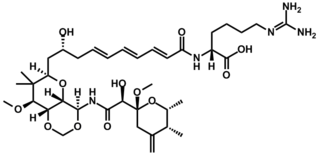
Onnamide A is a bioactive natural product found in Theonella swinhoei, a species of marine sponge whose genus is well known for yielding a diverse set of biologically active natural products, including the swinholides and polytheonamides. It bears structural similarities to the pederins, a family of compounds known to inhibit protein synthesis in eukaryotic cells. Onnamide A and its analogues have attracted academic interest due to their cytotoxicity and potential for combating the growth and proliferation of cancer cells.
Christmas Eye refers to a seasonal epidemic of corneal ulceration which predominantly occurs in a particular region of Australia, caused by chemicals released upon death by small native beetles in the area.
Fostriecin is a type I polyketide synthase (PKS) derived natural product, originally isolated from the soil bacterium Streptomyces pulveraceus. It belongs to a class of natural products which characteristically contain a phosphate ester, an α,β-unsaturated lactam and a conjugated linear diene or triene chain produced by Streptomyces. This class includes structurally related compounds cytostatin and phoslactomycin. Fostriecin is a known potent and selective inhibitor of protein serine/threonine phosphatases, as well as DNA topoisomerase II. Due to its activity against protein phosphatases PP2A and PP4 which play a vital role in cell growth, cell division, and signal transduction, fostriecin was looked into for its antitumor activity in vivo and showed in vitro activity against leukemia, lung cancer, breast cancer, and ovarian cancer. This activity is thought to be due to PP2A's assumed role in regulating apoptosis of cells by activating cytotoxic T-lymphocytes and natural killer cells involved in tumor surveillance, along with human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) transcription and replication.















