
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems which use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the latter half of the 19th century after the commercialization of the electric telegraph, the telephone, and electrical power generation, distribution, and use.

Thomas Alva Edison was an American inventor and businessman. He developed many devices in fields such as electric power generation, mass communication, sound recording, and motion pictures. These inventions, which include the phonograph, the motion picture camera, and early versions of the electric light bulb, have had a widespread impact on the modern industrialized world. He was one of the first inventors to apply the principles of organized science and teamwork to the process of invention, working with many researchers and employees. He established the first industrial research laboratory.
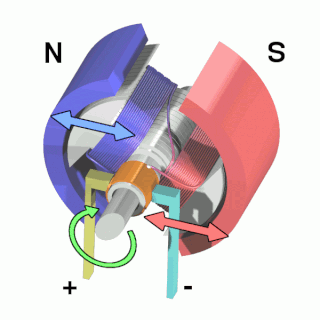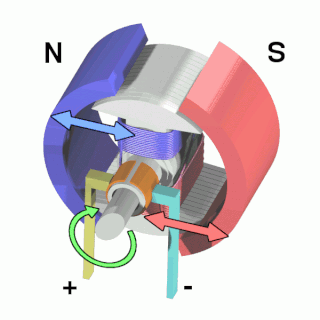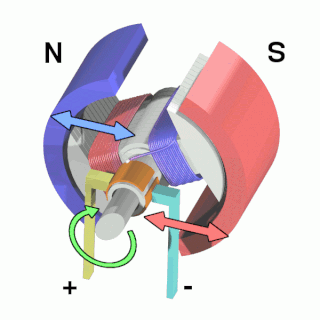
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate force in the form of torque applied on the motor's shaft. An electric generator is mechanically identical to an electric motor, but operates in reverse, converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.

A kilowatt-hour is a non-SI unit of energy equal to 3.6 megajoules (MJ) in SI units which is the energy delivered by one kilowatt of power for one hour. Kilowatt-hours are a common billing unit for electrical energy supplied by electric utilities. Metric prefixes are used for multiples and submultiples of the basic unit, the watt-hour.

Allgemeine Elektricitäts-Gesellschaft AG was a German producer of electrical equipment. It was founded in 1883 by Emil Rathenau as the Deutsche Edison-Gesellschaft für angewandte Elektricität in Berlin.

Mains electricity by country includes a list of countries and territories, with the plugs, voltages and frequencies they commonly use for providing electrical power to low voltage appliances, equipment, and lighting typically found in homes and offices. Some countries have more than one voltage available. For example, in North America, a unique split-phase system is used to supply to most premises that works by center tapping a 240 volts transformer. This system is able to concurrently provide 240 volts and 120 volts. Consequently, this allows homeowners to wire up both 240 V or 120 V circuits as they wish Most sockets are connected to 120 V for the use of small appliances and electronic devices. While larger appliances such as dryer, electric oven, range and EV charger use dedicated 240 V sockets. Different sockets are mandated for different voltage or maximum current levels.

Münchenstein is a municipality in the district of Arlesheim in the canton of Basel-Landschaft in Switzerland.

This history of the telephone chronicles the development of the electrical telephone, and includes a brief overview of its predecessors. The first telephone patent was granted to Alexander Graham Bell in 1869.
MIEV (Mitsubishi In-wheel motor Electric Vehicle) or MiEV (Mitsubishi innovative Electric Vehicle) is the name given by Japanese automaker Mitsubishi Motors (MMC) to its alternative propulsion technologies. From late 2006, “MiEV” encompasses all of Mitsubishi Motors’s electric drive systems work, including lithium-ion batteries, in-wheel motors and other technologies related to electric vehicle (EV), hybrid-electric vehicle and fuel-cell vehicles.

A battery electric bus is an electric bus that is driven by an electric motor and obtains energy from on-board batteries. Many trolleybuses use batteries as an auxiliary or emergency power source.

The Schaulager is a museum in Newmünchenstein, a sub-district of Münchenstein in the canton of Basel-Country, Switzerland.

An electric battery is a source of electric power consisting of one or more electrochemical cells with external connections for powering electrical devices. When a battery is supplying power, its positive terminal is the cathode and its negative terminal is the anode. The terminal marked negative is the source of electrons that will flow through an external electric circuit to the positive terminal. When a battery is connected to an external electric load, a redox reaction converts high-energy reactants to lower-energy products, and the free-energy difference is delivered to the external circuit as electrical energy. Historically the term "battery" specifically referred to a device composed of multiple cells; however, the usage has evolved to include devices composed of a single cell.
The Villa Ehinger is in the Neue Welt, a sub-district of Münchenstein, in the canton of Basel-Country in Switzerland.

An electric vehicle charging network is an infrastructure system of charging stations to recharge electric vehicles. The term electric vehicle infrastructure (EVI) may refer to charging stations in general or the network of charging stations across a nation or region. The proliferation of charging stations can be driven by charging station providers or government investment, and is a key influence on consumer behaviour in the transition from internal combustion engine vehicles to electric vehicles. While charging network vendors have in the past offered proprietary solutions limited to specific manufacturers, vendors now usually supply energy to electric vehicles regardless of manufacturer.
The Neue Welt is a sub-district of Münchenstein, in the canton of Basel-Country in Switzerland.

The Watermill Museum Brüglingen is housed within the former watermill and stands in the lower plain of Brüglingen, in the sub-district "Neue Welt", Münchenstein, in the canton of Basel-Country in Switzerland.

Berahle is a town in north-eastern Ethiopia. Located in Kilbet Rasu, Afar Region, this town has a latitude and longitude of 13°51′N40°01′E with an altitude of 639 meters above sea level. It is the largest town in Berhale woreda.

Primeo Energie or EBM(Cooperative Elektra Birseck, Münchenstein) is a Swiss energy supplier with head office in Münchenstein. It was founded as a cooperative under private law in 1897. EBM supplies around 230,000 people with electricity in North-West Switzerland and Alsace. The company operates 167 local heat supply systems in Switzerland, Alsace and South Germany.

The Augustiner Museum is a museum in Freiburg im Breisgau, Germany located in the former Augustinian Monastery building. It is undergoing an extensive renovation and expansion, the first phase of which ended in 2010.

The electricity sector in Switzerland relies mainly on hydroelectricity, since the Alps cover almost two-thirds of the country's land mass, providing many large mountain lakes and artificial reservoirs suited for hydro power. In addition, the water masses drained from the Swiss Alps are intensively used by run-of-the-river hydroelectricity (ROR). With 9,052 kWh per person in 2008, the country's electricity consumption is relatively high and was 22% above the European Union's average.


















