Related Research Articles
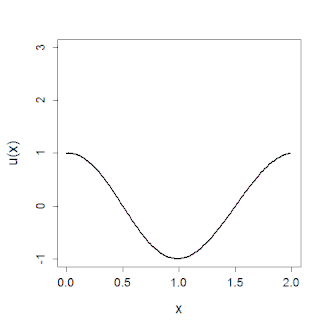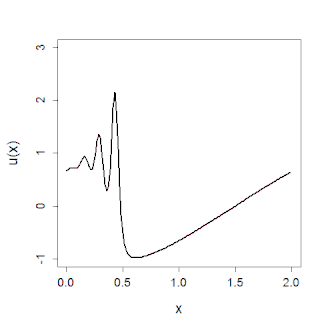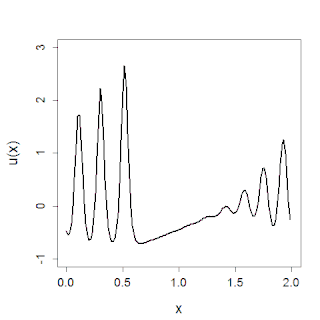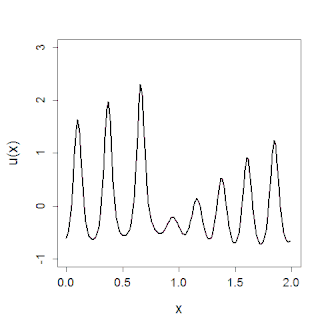
In mathematics, the Korteweg–De Vries (KdV) equation is a partial differential equation (PDE) which serves as a mathematical model of waves on shallow water surfaces. It is particularly notable as the prototypical example of an integrable PDE and exhibits many of the expected behaviors for an integrable PDE, such as a large number of explicit solutions, in particular soliton solutions, and an infinite number of conserved quantities, despite the nonlinearity which typically renders PDEs intractable. The KdV can be solved by the inverse scattering method (ISM). In fact, Gardner, Greene, Kruskal and Miura developed the classical inverse scattering method to solve the KdV equation.
In the general theory of relativity, the Einstein field equations relate the geometry of spacetime to the distribution of matter within it.
In mathematics, integral equations are equations in which an unknown function appears under an integral sign. In mathematical notation, integral equations may thus be expressed as being of the form: where is an integral operator acting on u. Hence, integral equations may be viewed as the analog to differential equations where instead of the equation involving derivatives, the equation contains integrals. A direct comparison can be seen with the mathematical form of the general integral equation above with the general form of a differential equation which may be expressed as follows:where may be viewed as a differential operator of order i. Due to this close connection between differential and integral equations, one can often convert between the two. For example, one method of solving a boundary value problem is by converting the differential equation with its boundary conditions into an integral equation and solving the integral equation. In addition, because one can convert between the two, differential equations in physics such as Maxwell's equations often have an analog integral and differential form. See also, for example, Green's function and Fredholm theory.

In the theory of partial differential equations, elliptic operators are differential operators that generalize the Laplace operator. They are defined by the condition that the coefficients of the highest-order derivatives be positive, which implies the key property that the principal symbol is invertible, or equivalently that there are no real characteristic directions.

In theoretical physics, the (one-dimensional) nonlinear Schrödinger equation (NLSE) is a nonlinear variation of the Schrödinger equation. It is a classical field equation whose principal applications are to the propagation of light in nonlinear optical fibers and planar waveguides and to Bose–Einstein condensates confined to highly anisotropic, cigar-shaped traps, in the mean-field regime. Additionally, the equation appears in the studies of small-amplitude gravity waves on the surface of deep inviscid (zero-viscosity) water; the Langmuir waves in hot plasmas; the propagation of plane-diffracted wave beams in the focusing regions of the ionosphere; the propagation of Davydov's alpha-helix solitons, which are responsible for energy transport along molecular chains; and many others. More generally, the NLSE appears as one of universal equations that describe the evolution of slowly varying packets of quasi-monochromatic waves in weakly nonlinear media that have dispersion. Unlike the linear Schrödinger equation, the NLSE never describes the time evolution of a quantum state. The 1D NLSE is an example of an integrable model.
In numerical analysis, the Crank–Nicolson method is a finite difference method used for numerically solving the heat equation and similar partial differential equations. It is a second-order method in time. It is implicit in time, can be written as an implicit Runge–Kutta method, and it is numerically stable. The method was developed by John Crank and Phyllis Nicolson in the 1940s.

Alpha Delta Gamma (ΑΔΓ), commonly known as ADG, is an American Greek-letter Catholic social fraternity and one of 75 members of the North American Interfraternity Conference (NIC). Based on Christian principles and the traditions of the Jesuit Order of the Catholic Church, Alpha Delta Gamma was founded at Loyola University Chicago on October 10, 1924, as a response to the unwillingness of most national fraternities to colonize at Catholic colleges and universities.

Sigma Alpha Iota (ΣΑΙ) is an international music fraternity. Formed to "uphold the highest standards of music" and "to further the development of music in America and throughout the world", it continues to provide musical and educational resources to its members and the general public. Sigma Alpha Iota operates its own national philanthropy, Sigma Alpha Iota Philanthropies, Inc. Sigma Alpha Iota is a member of the National Interfraternity Music Council and the Professional Fraternity Association.
In mathematics, delay differential equations (DDEs) are a type of differential equation in which the derivative of the unknown function at a certain time is given in terms of the values of the function at previous times. DDEs are also called time-delay systems, systems with aftereffect or dead-time, hereditary systems, equations with deviating argument, or differential-difference equations. They belong to the class of systems with the functional state, i.e. partial differential equations (PDEs) which are infinite dimensional, as opposed to ordinary differential equations (ODEs) having a finite dimensional state vector. Four points may give a possible explanation of the popularity of DDEs:
- Aftereffect is an applied problem: it is well known that, together with the increasing expectations of dynamic performances, engineers need their models to behave more like the real process. Many processes include aftereffect phenomena in their inner dynamics. In addition, actuators, sensors, and communication networks that are now involved in feedback control loops introduce such delays. Finally, besides actual delays, time lags are frequently used to simplify very high order models. Then, the interest for DDEs keeps on growing in all scientific areas and, especially, in control engineering.
- Delay systems are still resistant to many classical controllers: one could think that the simplest approach would consist in replacing them by some finite-dimensional approximations. Unfortunately, ignoring effects which are adequately represented by DDEs is not a general alternative: in the best situation, it leads to the same degree of complexity in the control design. In worst cases, it is potentially disastrous in terms of stability and oscillations.
- Voluntary introduction of delays can benefit the control system.
- In spite of their complexity, DDEs often appear as simple infinite-dimensional models in the very complex area of partial differential equations (PDEs).
While most of the traditional women's fraternities or sororities were founded decades before the start of the 20th century, the first ever specifically Christian-themed Greek Letter Organization formed was the Kappa Phi Club, founded in Kansas in 1916. Kappa Phi was a women's sisterhood that developed out of a bible study and remains one of the largest nationally present Christian women's collegiate clubs today. Later organizations added more defined social programming along with a Christian emphasis, bridging the gap between non-secular traditional sororities and church-sponsored bible study groups, campus ministries and sect-based clubs and study groups.
In mathematics, the logarithmic norm is a real-valued functional on operators, and is derived from either an inner product, a vector norm, or its induced operator norm. The logarithmic norm was independently introduced by Germund Dahlquist and Sergei Lozinskiĭ in 1958, for square matrices. It has since been extended to nonlinear operators and unbounded operators as well. The logarithmic norm has a wide range of applications, in particular in matrix theory, differential equations and numerical analysis. In the finite-dimensional setting, it is also referred to as the matrix measure or the Lozinskiĭ measure.
Steven Alan Orszag was an American mathematician.
Phi Beta Mu, International Bandmasters' Fraternity (ΦΒΜ), is an international honorary fraternity for band directors. It was founded in 1939 in Texas.

Phi Epsilon Kappa (ΦΕΚ) is a national professional fraternity for persons engaged in or pursuing careers in the fields of physical education, health, recreation, dance, human performance, exercise science, sports medicine and sports management.
References
- 1 2 Johnson., Elgy S. (February 22, 1999). Properties of solutions of nonlinear differential equations (Book, 1979). OCLC 10472636 . Retrieved February 1, 2019– via WorldCat.org.
- ↑ "UDC Consolidation" (PDF). Maryland – D.C. – Virginia Section of the MAA Newsletter. Fall 1978. Retrieved 1 February 2019.
- ↑ "Roberson v. District of Columbia Bd. of Higher Ed". Justia Law. January 12, 2019. Retrieved January 1, 2019.
- 1 2 3 "ELGY SIBLEY JOHNSON, 74, RETIRED UDC PROFESSOR, DIES". Washington Post. March 12, 1987. Retrieved February 1, 2019.
- ↑ Shakil, M (2010). "African-Americans in mathematical sciences – a chronological introduction" (PDF). Polygon. 4 (Spring): 27–42. Retrieved 8 April 2017.
- ↑ "Notable Members of Mu Lambda". Alpha Phi Alpha Fraternity, Mu Lambda chapter. Archived from the original on 21 January 2012. Retrieved 26 February 2012.