 | |
| Company type | Private |
|---|---|
| Industry | Dietary supplements |
| Founded | 2014 |
| Founders |
|
| Headquarters | New York City, New York, U.S. |
| Website | elysiumhealth |
Elysium Health is an American manufacturer of dietary supplements based in New York City.
 | |
| Company type | Private |
|---|---|
| Industry | Dietary supplements |
| Founded | 2014 |
| Founders |
|
| Headquarters | New York City, New York, U.S. |
| Website | elysiumhealth |
Elysium Health is an American manufacturer of dietary supplements based in New York City.
Elysium Health was founded in 2014 by Leonard Guarente, Dan Alminana, and Eric Marcotulli. [1] In 2015, Elysium introduced its first product, Basis, which contains nicotinamide riboside and pterostilbene. [2] [3]
In December 2016, Elysium received an investment of $20 million in Series B funding. [4] [5] In 2019, Elysium introduced a test called Index that uses epigenetic analysis on saliva samples to estimate biological age. [6] [7]
In June 2020, Elysium launched a supplement called Matter, which purports to maintain brain health and slow brain aging/atrophy. [8] In October 2021, Elysium launched a supplement called Format, which is associated with anti-aging and immune system support. [9] [10]
In 2023, Elysium launched a daily supplement called Mosaic, which claims to prevent skin aging and protect collagen. [11] In October 2024, Elysium introduced a daily supplement called Vision, to maintain macular health and promote eye longevity. [12]
Elysium originally bought the ingredients in Basis from ChromaDex, which as of December 2016, sold the two ingredients to other supplement companies that also marketed products containing them. [13] The two companies had an agreement under which Elysium Health did not have to acknowledge ChromaDex as the source of the ingredients, but then after Elysium recruited the VP of business development from ChromaDex and reportedly stopped paying ChromaDex, ChromaDex sued Elysium and the information became public. [14]
In September 2018, Dartmouth College and ChromaDex sued Elysium for infringing on patents for nicotinamide riboside. [15] In August 2020, W.R. Grace and Company also sued Elysium for infringing on their patents for crystalline nicotinamide riboside. [16] In September 2021, the claims by Dartmouth and ChromaDex were dismissed by a U.S. district judge, essentially invalidating their patents. [17]
In February 2023, the United States Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit affirmed the district court’s judgment that these patent infringement claims are invalid under 35 U.S.C. § 101. [18]
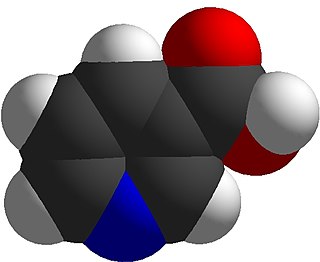
Niacin, also known as nicotinic acid, is an organic compound and a vitamer of vitamin B3, an essential human nutrient. It is produced by plants and animals from the amino acid tryptophan. Niacin is obtained in the diet from a variety of whole and processed foods, with highest contents in fortified packaged foods, meat, poultry, red fish such as tuna and salmon, lesser amounts in nuts, legumes and seeds. Niacin as a dietary supplement is used to treat pellagra, a disease caused by niacin deficiency. Signs and symptoms of pellagra include skin and mouth lesions, anemia, headaches, and tiredness. Many countries mandate its addition to wheat flour or other food grains, thereby reducing the risk of pellagra.

A dietary supplement is a manufactured product intended to supplement a person's diet by taking a pill, capsule, tablet, powder, or liquid. A supplement can provide nutrients either extracted from food sources, or that are synthetic. The classes of nutrient compounds in supplements include vitamins, minerals, fiber, fatty acids, and amino acids. Dietary supplements can also contain substances that have not been confirmed as being essential to life, and so are not nutrients per se, but are marketed as having a beneficial biological effect, such as plant pigments or polyphenols. Animals can also be a source of supplement ingredients, such as collagen from chickens or fish for example. These are also sold individually and in combination, and may be combined with nutrient ingredients. The European Commission has also established harmonized rules to help insure that food supplements are safe and appropriately labeled.

Life extension is the concept of extending the human lifespan, either modestly through improvements in medicine or dramatically by increasing the maximum lifespan beyond its generally-settled biological limit of around 125 years. Several researchers in the area, along with "life extensionists", "immortalists", or "longevists", postulate that future breakthroughs in tissue rejuvenation, stem cells, regenerative medicine, molecular repair, gene therapy, pharmaceuticals, and organ replacement will eventually enable humans to have indefinite lifespans through complete rejuvenation to a healthy youthful condition (agerasia). The ethical ramifications, if life extension becomes a possibility, are debated by bioethicists.

Ephedra is a medicinal preparation from the plant Ephedra sinica. Several additional species belonging to the genus Ephedra have traditionally been used for a variety of medicinal purposes, and are a possible candidate for the soma plant of Indo-Iranian religion. It has been used in traditional Chinese medicine, in which it is referred to as Ma Huang, for more than 2,000 years. Native Americans and Mormon pioneers drank a tea brewed from other Ephedra species, called "Mormon tea" and "Indian tea".
Roy Lee Walford, M. D. was a professor of pathology at University of California, Los Angeles School of Medicine, a leading advocate of calorie restriction for life extension and health improvement, and a crew member of Biosphere 2.

GNC Holdings, LLC is an American multinational retail and nutritional manufacturing company based in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. It specializes in health and nutrition related products, including vitamins, supplements, minerals, herbs, sports nutrition, diet, and energy products. It is a wholly owned subsidiary of Harbin Pharmaceutical Group, a Chinese state-owned pharmaceutical manufacturer.
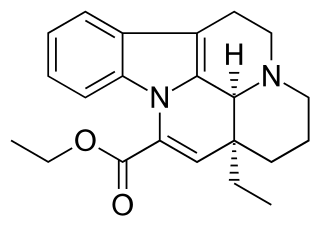
Vinpocetine is a synthetic derivative of the vinca alkaloid vincamine, differing by the removal of a hydroxyl group and by being the ethyl rather than the methyl ester of the underlying carboxylic acid. Vincamine is extracted from either the seeds of Voacanga africana or the leaves of Vinca minor.
Durk Pearson was a research scientist best known for coauthoring a series of books on longevity, beginning with Life Extension: A Practical Scientific Approach.
Hydroxycut is a brand of dietary supplements that is marketed as a weight loss aid. Hydroxycut was originally developed and manufactured by MuscleTech Research and Development; MuscleTech was sold to Iovate Health Sciences in 2003–2004 and declared bankruptcy in 2005; Iovate continues to use MuscleTech as a brand to market Hydroxycut.

David Andrew Sinclair is an Australian-American biologist and academic known for his research on aging and epigenetics. Sinclair is a professor of genetics at Harvard Medical School and the founding director of the Paul F. Glenn Laboratories for the Biological Mechanisms of Aging at Harvard. He is the co-author of Lifespan: Why We Age – and Why We Don't Have To.

Hoodia gordonii, also known as Bushman’s hat, is a leafless spiny succulent plant supposed to have therapeutic properties in folk medicine. It grows naturally in Botswana, South Africa and Namibia. The species became internationally known and threatened by collectors, after a marketing campaign falsely claimed that it was an appetite suppressant for weight loss. The flowers smell like rotten meat and are pollinated mainly by flies. The indigenous San people of the Namib desert call this plant ǁhoba.

Omega-3-acid ethyl esters are a mixture of ethyl eicosapentaenoic acid and ethyl docosahexaenoic acid, which are ethyl esters of the omega−3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) found in fish oil. Together with dietary changes, they are used to treat high blood triglycerides which may reduce the risk of pancreatitis. They are generally less preferred than statins, and use is not recommended by NHS Scotland as the evidence does not support a decreased risk of heart disease. Omega-3-acid ethyl esters are taken by mouth.
Charles Brenner is the inaugural Alfred E Mann Family Foundation Chair of the Department of Diabetes & Cancer Metabolism at the Beckman Research Institute of the City of Hope National Medical Center. Brenner previously held the Roy J. Carver Chair in Biochemistry and was head of biochemistry at the University of Iowa.

Methylhexanamine is an indirect sympathomimetic drug invented and developed by Eli Lilly and Company and marketed as an inhaled nasal decongestant from 1948 until it was voluntarily withdrawn from the market in the 1980s.

Sulfoaildenafil (thioaildenafil) is a synthetic drug that is a structural analog of sildenafil (Viagra). It was first reported in 2005, and it is not approved by any health regulation agency. Like sildenafil, sulfoaildenafil is a phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor.
ChromaDex is a dietary supplement and food ingredient company based in Los Angeles, California founded in 1999 that is publicly traded on the NASDAQ.

Nicotinamide riboside (NR, SR647) is a pyridine-nucleoside and a form of vitamin B3. It functions as a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, or NAD+, through a two-step and a three-step pathway.

Nicotinamide mononucleotide is a nucleotide derived from ribose, nicotinamide, nicotinamide riboside and niacin. In humans, several enzymes use NMN to generate nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH). In mice, it has been proposed that NMN is absorbed via the small intestine within 10 minutes of oral uptake and converted to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) through the Slc12a8 transporter. However, this observation has been challenged, and the matter remains unsettled.

Vitamin B3, colloquially referred to as niacin, is a vitamin family that includes three forms, or vitamers: niacin (nicotinic acid), nicotinamide (niacinamide), and nicotinamide riboside. All three forms of vitamin B3 are converted within the body to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD). NAD is required for human life and people are unable to make it within their bodies without either vitamin B3 or tryptophan. Nicotinamide riboside was identified as a form of vitamin B3 in 2004.

Mitoquinone mesylate (MitoQ) is a synthetic analogue of coenzyme Q10 which has antioxidant effects. It was first developed in New Zealand in the late 1990s. It has significantly improved bioavailability and improved mitochondrial penetration compared to coenzyme Q10, and has shown potential in a number of medical indications, being widely sold as a dietary supplement.