
Fractional calculus is a branch of mathematical analysis that studies the several different possibilities of defining real number powers or complex number powers of the differentiation operator

In fractional calculus, an area of mathematical analysis, the differintegral is a combined differentiation/integration operator. Applied to a function ƒ, the q-differintegral of f, here denoted by

Joseph Liouville was a French mathematician and engineer.

Evolution-Data Optimized is a telecommunications standard for the wireless transmission of data through radio signals, typically for broadband Internet access. EV-DO is an evolution of the CDMA2000 (IS-2000) standard which supports high data rates and can be deployed alongside a wireless carrier's voice services. It uses advanced multiplexing techniques including code-division multiple access (CDMA) as well as time-division multiplexing (TDM) to maximize throughput. It is a part of the CDMA2000 family of standards and has been adopted by many mobile phone service providers around the world particularly those previously employing CDMA networks. It is also used on the Globalstar satellite phone network.
Scientometrics is the field of study which concerns itself with measuring and analysing scholarly literature. Scientometrics is a sub-field of informetrics. Major research issues include the measurement of the impact of research papers and academic journals, the understanding of scientific citations, and the use of such measurements in policy and management contexts. In practice there is a significant overlap between scientometrics and other scientific fields such as information systems, information science, science of science policy, sociology of science, and metascience. Critics have argued that over-reliance on scientometrics has created a system of perverse incentives, producing a publish or perish environment that leads to low-quality research.
Trajectory optimization is the process of designing a trajectory that minimizes some measure of performance while satisfying a set of constraints. Generally speaking, trajectory optimization is a technique for computing an open-loop solution to an optimal control problem. It is often used for systems where computing the full closed-loop solution is not required, impractical or impossible. If a trajectory optimization problem can be solved at a rate given by the inverse of the Lipschitz constant, then it can be used iteratively to generate a closed-loop solution in the sense of Caratheodory. If only the first step of the trajectory is executed for an infinite-horizon problem, then this is known as Model Predictive Control (MPC).

Eduardo Daniel Sontag is an American mathematician, and distinguished university professor at Northeastern University, who works in the fields control theory, dynamical systems, systems molecular biology, cancer and immunology, theoretical computer science, neural networks, and computational biology.
Quantum dot cellular automata are a proposed improvement on conventional computer design (CMOS), which have been devised in analogy to conventional models of cellular automata introduced by John von Neumann.

Yu-Chi "Larry" Ho is a Chinese-American mathematician, control theorist, and a professor at the School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, Harvard University.

Aerospace engineering is the primary field of engineering concerned with the development of aircraft and spacecraft. It has two major and overlapping branches: aeronautical engineering and astronautical engineering. Avionics engineering is similar, but deals with the electronics side of aerospace engineering.
Iso-damping is a desirable system property referring to a state where the open-loop phase Bode plot is flat—i.e., the phase derivative with respect to the frequency is zero, at a given frequency called the "tangent frequency", . At the "tangent frequency" the Nyquist curve of the open-loop system tangentially touches the sensitivity circle and the phase Bode is locally flat which implies that the system will be more robust to gain variations. For systems that exhibit iso-damping property, the overshoots of the closed-loop step responses will remain almost constant for different values of the controller gain. This will ensure that the closed-loop system is robust to gain variations.
Guanrong Chen (陈关荣) or Ron Chen is a Chinese mathematician who made contributions to Chaos theory. He has been the chair professor and the founding director of the Centre for Chaos and Complex Networks at the City University of Hong Kong since 2000. Prior to that, he was a tenured full professor at the University of Houston, Texas. Chen was elected Member of the Academy of Europe in 2014, elected Fellow of The World Academy of Sciences in 2015, and elected IEEE Fellow in 1997. He is currently the editor-in-chief for the International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos.
In the fields of dynamical systems and control theory, a fractional-order system is a dynamical system that can be modeled by a fractional differential equation containing derivatives of non-integer order. Such systems are said to have fractional dynamics. Derivatives and integrals of fractional orders are used to describe objects that can be characterized by power-law nonlocality, power-law long-range dependence or fractal properties. Fractional-order systems are useful in studying the anomalous behavior of dynamical systems in physics, electrochemistry, biology, viscoelasticity and chaotic systems.
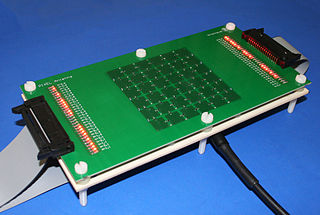
A reconfigurable antenna is an antenna capable of modifying its frequency and radiation properties dynamically, in a controlled and reversible manner. In order to provide a dynamic response, reconfigurable antennas integrate an inner mechanism that enable the intentional redistribution of the RF currents over the antenna surface and produce reversible modifications of its properties. Reconfigurable antennas differ from smart antennas because the reconfiguration mechanism lies inside the antenna, rather than in an external beamforming network. The reconfiguration capability of reconfigurable antennas is used to maximize the antenna performance in a changing scenario or to satisfy changing operating requirements.

Synchronverters or virtual synchronous generators are inverters which mimic synchronous generators (SG) to provide "synthetic inertia" for ancillary services in electric power systems. Inertia is a property of standard synchronous generators associated with the rotating physical mass of the system spinning at a frequency proportional to the electricity being generated. Inertia has implications towards grid stability as work is required to alter the kinetic energy of the spinning physical mass and therefore opposes changes in grid frequency. Inverter-based generation inherently lacks this property as the waveform is being created artificially via power electronics.

Soumitro Banerjee is an Indian electrical engineer and a professor at the Department of Physical Sciences of the Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Kolkata. He is known for his studies on bifurcation phenomena in power electronic circuits and is an elected fellow of all three major Indian science academies: the National Academy of Sciences, India, Indian Academy of Sciences, and Indian National Science Academy. He is also a fellow of The World Academy of Sciences, Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, West Bengal Academy of Sciences and the Indian National Academy of Engineering. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards for his contributions to Engineering Sciences in 2003.
In communication theory, time-varying phasors are used for analyzing narrow-band signals, whose signal bandwidths in the frequency domain are considerably smaller than the carrier frequency. Time-varying phasors are mostly used for analysis of frequency domain of band-pass systems. The method uses classical impulse response.
Frank L. Lewis is an American electrical engineer, academic and researcher. He is a professor of electrical engineering, Moncrief-O’Donnell Endowed Chair, and head of Advanced Controls and Sensors Group at The University of Texas at Arlington (UTA). He is a member of UTA Academy of Distinguished Teachers and a charter member of UTA Academy of Distinguished Scholars.

Maamar Bettayeb is a control theorist, educator and inventor. He is the author of publications on understanding the singular value decomposition and model order reduction. Bettayeb is also a promoter of scientific research.








