Related Research Articles
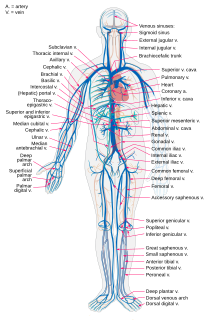
Veins are blood vessels that carry blood towards the heart. Most veins carry deoxygenated blood from the tissues back to the heart; exceptions are the pulmonary and umbilical veins, both of which carry oxygenated blood to the heart. In contrast to veins, arteries carry blood away from the heart.
Thrombosis is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel is injured, the body uses platelets (thrombocytes) and fibrin to form a blood clot to prevent blood loss. Even when a blood vessel is not injured, blood clots may form in the body under certain conditions. A clot, or a piece of the clot, that breaks free and begins to travel around the body is known as an embolus.

Dura mater is a thick membrane made of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It is the outermost of the three layers of membrane called the meninges that protect the central nervous system. The other two meningeal layers are the arachnoid mater and the pia mater. The dura surrounds the brain and the spinal cord. It envelops the arachnoid mater, which is responsible for keeping in the cerebrospinal fluid. It is derived primarily from the neural crest cell population, with postnatal contributions of the paraxial mesoderm.
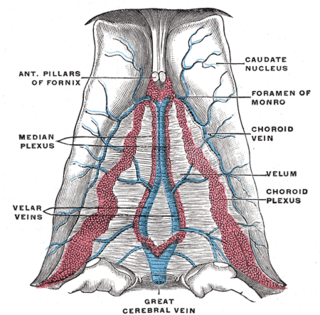
The great cerebral vein is one of the large blood vessels in the skull draining the cerebrum of the brain. It is also known as the "vein of Galen", named for its discoverer, the Greek physician Galen. However, it is not the only vein with this eponym.

A subdural hematoma (SDH) is a type of bleeding in which a collection of blood—usually associated with a traumatic brain injury—gathers between the inner layer of the dura mater and the arachnoid mater of the meninges surrounding the brain. It usually results from tears in bridging veins that cross the subdural space.

Coronary thrombosis is defined as the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel of the heart. This blood clot may then restrict blood flow within the heart, leading to heart tissue damage, or a myocardial infarction, also known as a heart attack.

Intracranial hemorrhage (ICH), also known as intracranial bleed, is bleeding within the skull. Subtypes are intracerebral bleeds, subarachnoid bleeds, epidural bleeds, and subdural bleeds. More often than not it ends in a lethal outcome.

Epidural hematoma is when bleeding occurs between the tough outer membrane covering the brain and the skull. Often there is loss of consciousness following a head injury, a brief regaining of consciousness, and then loss of consciousness again. Other symptoms may include headache, confusion, vomiting, and an inability to move parts of the body. Complications may include seizures.
The emissary veins connect the extracranial venous system with the intracranial venous sinuses. They connect the veins outside the cranium to the venous sinuses inside the cranium. They drain from the scalp, through the skull, into the larger meningeal veins and dural venous sinuses.

The cavernous sinus within the human head is one of the dural venous sinuses creating a cavity called the lateral sellar compartment bordered by the temporal bone of the skull and the sphenoid bone, lateral to the sella turcica.

The dural venous sinuses are venous channels found between the endosteal and meningeal layers of dura mater in the brain. They receive blood from the cerebral veins, receive cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the subarachnoid space via arachnoid granulations, and mainly empty into the internal jugular vein.

A dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF) or Malformation, is an abnormal direct connection (fistula) between a meningeal artery and a meningeal vein or dural venous sinus.

Cavernous sinus thrombosis (CST) is the formation of a blood clot within the cavernous sinus, a cavity at the base of the brain which drains deoxygenated blood from the brain back to the heart. This is a rare disorder and can be of two types–septic cavernous thrombosis and aseptic cavernous thrombosis. Most commonly the form is of septic cavernous sinus thrombosis. The cause is usually from a spreading infection in the nose, sinuses, ears, or teeth. Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus are often the associated bacteria.

Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST), cerebral venous and sinus thrombosis or cerebral venous thrombosis (CVT), is the presence of a blood clot in the dural venous sinuses, the cerebral veins, or both. Symptoms may include severe headache, visual symptoms, any of the symptoms of stroke such as weakness of the face and limbs on one side of the body, and seizures.

Pott's puffy tumor, first described by Sir Percivall Pott in 1760, is a rare clinical entity characterized by subperiosteal abscess associated with osteomyelitis. It is characterized by an osteomyelitis of the frontal bone, either direct or through haematogenic spread. This results in a swelling on the forehead, hence the name. The infection can also spread inwards, leading to an intracranial abscess. Pott's puffy tumor can be associated with cortical vein thrombosis, epidural abscess, subdural empyema, and brain abscess.
Blood clots are a relatively common occurrence in the general population and are seen in approximately 1-2% of the population by age 60. Typically blood clots develop in the deep veins of the lower extremities, deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or as a blood clot in the lung, pulmonary embolism (PE). A very small number of people who develop blood clots have a more serious and often life-threatening condition, known as Thrombotic Storm (TS). TS is characterized by the development of more than one blood clot in a short period of time. These clots often occur in multiple and sometimes unusual locations in the body and are often difficult to treat. TS may be associated with an existing condition or situation that predisposes a person to blood clots such as injury, infection, or pregnancy. In many cases a risk assessment will identify interventions that will prevent the formation of blood clots.

Pediatric stroke is a stroke that happens in children or adolescents. Stroke affects about 6 in 100,000 children.

A developmental venous anomaly is a congenital variant of the cerebral venous drainage. On imaging it is seen as a number of small deep parenchymal veins converging toward a larger collecting vein.

An MRI sequence in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a particular setting of pulse sequences and pulsed field gradients, resulting in a particular image appearance.
A pseudosubarachnoid hemorrhage is an apparent increased attenuation on CT scans within the basal cisterns that mimics a true subarachnoid hemorrhage. This occurs in cases of severe cerebral edema, such as by cerebral hypoxia. It may also occur due to intrathecally administered contrast material, leakage of high-dose intravenous contrast material into the subarachnoid spaces, or in patients with cerebral venous sinus thrombosis, severe meningitis, leptomeningeal carcinomatosis, intracranial hypotension, cerebellar infarctions, or bilateral subdural hematomas.
References
- ↑ Ropper, Allan H.; Klein, Joshua P. (1 July 2021). "Cerebral Venous Thrombosis". New England Journal of Medicine. 385 (1): 59–64. doi:10.1056/NEJMra2106545.
- ↑ Virapongse, C; Cazenave, C; Quisling, R; Sarwar, M; Hunter, S (March 1987). "The empty delta sign: frequency and significance in 76 cases of dural sinus thrombosis". Radiology. 162 (3): 779–785. doi:10.1148/radiology.162.3.3809494.
- ↑ Gaillard, Frank. "Empty delta sign (dural venous sinus thrombosis) | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org". Radiopaedia.