Design
In 1794, a frigate squadron under the command of Captain Sir John Borlase Warren captured the French 40-gun frigate Pomone. Surprisingly to her captors, the ship was armed with 26 × 24-pounder long guns, a main armament that was relatively uncommon for frigates in the 18th century. Furthermore, Pomone impressed the British with outstanding sailing qualities in every variation of the wind, and being capable of sailing more than 13 knots (24 km/h; 15 mph).
On 30 April 1795, the Admiralty ordered three frigates – with 36 guns, 38 guns and 40 guns – the first and third built to the lines of the captured French frigate and the second to a new design by the Surveyors (the ship designers of the Royal Navy). The 40-gun French design was copied from Pomone, and in November 1795 the keel was laid down at the Rotherhithe shipyard of John Randall & Company for the new ship, which on 14 November 1795 was named as HMS Endymion. She was launched on 29 March 1797 and towed to Deptford Dockyard, where she was commissioned in April 1797 and completed on 12 June 1797.
Endymion was not an exact copy of Pomone, being built to British design standards with stronger construction. Surprisingly, Endymion sailed even better than Pomone, reaching 14.4 knots (26.7 km/h; 16.6 mph), the highest recorded speed during the Age of Sail. Reclassified as a 48-gun fourth-rate frigate in February 1817, then as 50-gun, and finally as 44-gun in February 1839, Endymion's fine qualities were such that she continued to be praised for nearly half a century. She was finally broken up at Plymouth Dockyard in June 1868.
1812 Programme
Early in 1812, war with the United States seemed inevitable. To cope with the heavy American 24-pounder frigates of the Constitution-type, the Admiralty decided to build a batch of new 24-pounder frigates. During the long war with France, the standard British frigate was of about 1,000 tons and armed with a main battery of only 18-pounders, no match for the big US ships. The only proven design for a suitable 24-pounder frigate was that of Endymion, and in May 1812 two ships were ordered from Wigram, Wells & Green of Blackwall Yard, who were to construct all five ships eventually built. They differed from the prototype by being constructed of "fir" (actually, pitch pine) rather than oak, and mounted an extra (fourteenth) pair of 24-pounder guns on the upper deck forward. All would be reclassified as 50-gun fourth-rate frigates in February 1817; however, the use of softwood in their construction was such that they were only intended for a short lifetime, and indeed all five were taken to pieces after a few years' service.
The first pair were originally ordered on 4 May 1812 as Tagus and Eridanus of the 18-pounder armed Leda class, but were renamed on 7 January 1813 as Severn and Liffey. The War of 1812 broke out in June, and on 26 December two further ships were ordered, becoming Glasgow and Liverpool. The final ship was Forth, ordered on 7 January 1813. These five new ships were of a slightly modified design, having ports for 28 instead of 26 × 24-pounders and were built of softwood, to speed up the construction. The ships were launched from June 1813 to February 1814.

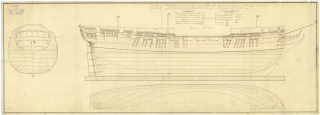
HMS Leander was a 50-gun spar-decked frigate of the Royal Navy which saw service in the Napoleonic Wars, the War of 1812, and the Second Barbary War.

HMS Endymion was a 40-gun fifth rate that served in the French Revolutionary Wars, the Napoleonic Wars, the War of 1812 and during the First Opium War. She was built to the lines of the French prize Pomone captured in 1794. Due to her exceptional handling and sailing properties, the Severn-class frigates were built to her lines, although the gunports were rearranged to mount an extra pair of guns per side, the ships were made of softwood and were not built until nearly the end of the Napoleonic Wars.
HMS Prince Regent was a 56-gun British warship that served on Lake Ontario during the War of 1812. Prince Regent was built at the Kingston Royal Naval Dockyard in Kingston, Upper Canada and launched on 14 April 1814. Rated as a fourth-rate frigate, Prince Regent took part in the Raid on Fort Oswego in 1814. Following the War of 1812 the frigate was renamed HMS Kingston on 9 December 1814. In 1817, the vessel was placed in reserve following the Rush-Bagot Treaty that demilitarized all the lakes along the United States-Canada border. Discarded in 1832, the vessel found no buyer and sank in Deadman Bay off Kingston after 1832.

The Black Prince-class ships of the line were a class of four 74-gun third rates built for the Royal Navy in the closing years of the Napoleonic War. The draught for this class of ship was essentially a reduced version of the captured Danish ship Christian VII.

The Téméraire-class ships of the line were a class of a hundred and twenty 74-gun ships of the line ordered between 1782 and 1813 for the French navy or its attached navies in dependent (French-occupied) territories. Although a few of these were cancelled, the type was and remains the most numerous class of capital ship ever built to a single design.

Pomone was a 40-gun frigate of the French Navy, launched in 1785. The British captured her off the Île de Batz in April 1794 and incorporated her into the Royal Navy. Pomone subsequently had a relatively brief but active career in the British Navy off the Atlantic and Mediterranean coasts of France before suffering sufficient damage from hitting a rock. Due to this, the ship was taken out of service and then broken up in 1803.

The Leda-class frigates, were a successful class of forty-seven British Royal Navy 38-gun sailing frigates constructed from 1805 to 1832. Based on a French design, the class came in five major groups, all with minor differences in their design. During their careers, they fought in the Napoleonic Wars and the War of 1812. Forty-five of the 47 were eventually scrapped; two still exist: HMS Trincomalee and HMS Unicorn.

The Scipion class was a class of three 74-gun ships of the line built to a design by François-Guillaume Clairin-Deslauriers, the ingénieur-constructeur en chef at Rochefort Dockyard. These were the shortest 74-gun ships built by France since the 1750s, and they were found to lack stability as a consequence. The third ship - originally the Pluton - was 'girdled' (sheathed) with 32 cm of pine at Rochefort in 1799 to overcome her instability, and the design of two further ships ordered at the same dockyard in 1779 were lengthened.

Sir Henry Hope KCB was an English officer of the Royal Navy whose distinguished service in the Napoleonic Wars and the War of 1812 earned him acclaim. As captain of HMS Endymion, he was involved in the action on 14 January 1815 which ended in the capture of the American warship USS President.
HMS Newcastle was a 50-gun fourth rate of the Royal Navy which saw service in the Napoleonic Wars and the War of 1812.

HMS Myrmidon was a 20-gun Hermes-class sixth-rate post ship built for the Royal Navy during the 1810s. She was commissioned in 1813 and was in the Mediterranean four years later. The ship was on the Africa Station in 1819 and was paid off three years later. Myrmidon was broken up in 1823.
HMS Valorous was a 20-gun Hermes-class post ship sixth-rate post ship built for the Royal Navy during the 1810s. She was placed in commission in 1821 for service abroad in the Caribbean and Newfoundland. Two of her captains were forced to resign their commands during this time and the ship was placed in reserve in 1826 until she was broken up in 1829.

HMS Thetis was a 46-gun Leda-class fifth-rate frigate built for the Royal Navy during the 1810s. She was first commissioned in 1823 and was assigned to the South America Station three years later. The ship was wrecked in 1830 off Cape Frio, Brazil, with the loss of 22 crewmen; most of her cargo of bullion was successfully salvaged.

HMS Arethusa was a 46-gun Leda-class fifth-rate frigate built for the Royal Navy during the 1810s. The ship was never commissioned and was converted into a lazarette in 1836. She was renamed HMS Bacchus in 1844 and was further converted into a coal hulk in 1851–52. The ship was sold for scrap in 1883.
The Maidstone-class frigate was a 32-gun fifth-rate frigate class of two ships designed by Sir John Henslow and ordered on 4 February 1795. The class was a close copy of Henslow's earlier Alcmene class, but was constructed of pitch pine instead of oak. With concerns over whether the lighter building material would safely hold an armament of 18-pounder long guns, the class was instead armed with smaller 12-pounders. Both ships of the class served through the French Revolutionary Wars, but neither had a long career. Shannon was sold at Sheerness Dockyard in May 1802 and Maidstone was placed in ordinary at Chatham Dockyard in 1804 before being broken up in 1810.
The Thames-class frigate was a 32-gun fifth-rate frigate class of eight ships of the Royal Navy based on the Richmond-class frigate designed by William Bately. The ships were ordered to the older design, which was of a smaller type of ship compared to more modern designs, so that they could be built quickly and cheaply in time to assist in defending against Napoleon's expected invasion of Britain. The class received several design changes to the Richmond class, being built of fir instead of oak, with these changes making the class generally slower and less weatherly than their predecessors, especially when in heavy weather conditions. The first two ships of the class, Pallas and Circe, were ordered on 16 March 1804 with two more ordered on 1 May and the final four on 12 July. The final ship of the class, Medea, was cancelled on 22 October before construction could begin but the other seven ships of the class were commissioned between 1804 and 1806.

The Perseverance-class frigate was a 36-gun, later 42-gun, 18-pounder fifth-rate frigate class of twelve ships of the Royal Navy, constructed in two batches. Designed by Surveyor of the Navy Sir Edward Hunt the first iteration, consisting of four ships, was constructed as a rival to the similar Flora-class frigate. Strongly built ships, the Perseverance class provided favourable gunnery characteristics and was highly manoeuvrable, but bought these traits with a loss of speed. The name ship of the class, Perseverance, was ordered in 1779 and participated in the American Revolutionary War, but her three sister ships were constructed too late to take part. The class continued in service after the war, but soon became outdated.

The Narcissus-class frigate was a 32-gun, 18-pounder fifth-rate frigate class of five ships of the Royal Navy. Designed by Surveyor of the Navy Sir John Henslow, the class was created to make use of shipyards that could not construct larger frigates. They were similar in design to the preceding 32-gun frigate class, the Amphion class, but were slightly shorter. Two ships were initially constructed, with a later batch of three being ordered in response to an Admiralty request for the resumption of production of proven frigate designs. The final two ships of the class were cancelled when the shipyard they were being constructed at went bankrupt. Unlike her sister ships, the name ship of the class Narcissus was armed with experimental short 24 pounders rather than 18 pounders.
The Serpente class was a class of four 20-gun corvettes for the French Navy, designed by Charles-Henri Tellier as a follow-on to the Etna-class corvettes of the previous year. Four separate commercial shipbuilders were involved in their construction by contract, with three being ordered at Honfleur in 1794 and a fourth at Le Havre in 1795. The vessels were flush-decked and designed to carry a battery of twenty 18-pounder guns.













