Energy conservation is the effort to reduce wasteful energy consumption by using fewer energy services. This can be done by using energy more effectively or changing one's behavior to use less service. Energy conservation can be achieved through efficient energy use, which has a number of advantages, including a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and a smaller carbon footprint, as well as cost, water, and energy savings.

The Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive 2002/95/EC, short for Directive on the restriction of the use of certain hazardous substances in electrical and electronic equipment, was adopted in February 2003 by the European Union.

EU Directive 92/75/EC (1992) established an energy consumption labelling scheme. The directive was implemented by several other directives thus most white goods, light bulb packaging and cars must have an EU Energy Label clearly displayed when offered for sale or rent. The energy efficiency of the appliance is rated in terms of a set of energy efficiency classes from A to G on the label, A being the most energy efficient, G the least efficient. The labels also give other useful information to the customer as they choose between various models. The information should also be given in catalogues and included by internet retailers on their websites.
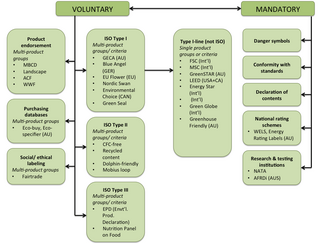
Ecolabels and Green Stickers are labeling systems for food and consumer products. The use of ecolabels is voluntary, whereas green stickers are mandated by law; for example, in North America major appliances and automobiles use Energy Star. They are a form of sustainability measurement directed at consumers, intended to make it easy to take environmental concerns into account when shopping. Some labels quantify pollution or energy consumption by way of index scores or units of measurement, while others assert compliance with a set of practices or minimum requirements for sustainability or reduction of harm to the environment. Many ecolabels are focused on minimising the negative ecological impacts of primary production or resource extraction in a given sector or commodity through a set of good practices that are captured in a sustainability standard. Through a verification process, usually referred to as "certification", a farm, forest, fishery, or mine can show that it complies with a standard and earn the right to sell its products as certified through the supply chain, often resulting in a consumer-facing ecolabel.
The best available technology or best available techniques (BAT) is the technology approved by legislators or regulators for meeting output standards for a particular process, such as pollution abatement. Similar terms are best practicable means or best practicable environmental option. BAT is a moving target on practices, since developing societal values and advancing techniques may change what is currently regarded as "reasonably achievable", "best practicable" and "best available".

The European Union Emissions Trading System is a "cap and trade" scheme intended to lower greenhouse gas emissions. Cap and trade schemes limit emissions of specified pollutants over an area and allow companies to trade emissions rights within that area. It covers around 45% of the EUs greenhouse gas emissions.

Renewable energy plays an important and growing role in the energy system of the European Union. The Europe 2020 strategy included a target of reaching 20% of gross final energy consumption from renewable sources by 2020, and at least 32% by 2030. The EU27 reached 22.1% in 2020, up from 9.6% in 2004, but declined to 21.8% in 2021. These figures are based on energy use in all its forms across all three main sectors, the heating and cooling sector, the electricity sector, and the transport sector.

The energy policy of the European Union focuses on energy security, sustainability, and integrating the energy markets of member states. A key energy policy adopted in 2009 are the 20/20/20 objectives, binding for all EU Member States. The target involved increasing the share of renewable energy in its final energy use to 20%, reduce greenhouse gases by 20% and increase energy efficiency by 20%. After this target was met, new targets for 2030 were set at a 55% reduction of greenhouse gas emissions by 2030 as part of the European Green Deal. After the Russian invasion of Ukraine, the EU's energy policy turned more towards energy security in their REPowerEU policy package, which boosts both renewable deployment and fossil fuel infrastructure for alternative suppliers.
The Commissioner for Environment, Oceans and Fisheries is a member of the European Commission. The current Commissioner is Virginijus Sinkevičius, who also serves as EU Commissioner for the Environment.
Vehicle regulations are requirements that automobiles must satisfy in order to be approved for sale or use in a particular country or region. They are usually mandated by legislation, and administered by a government body. The regulations concern aspects such as lighting, controls, crashworthiness, environment protection and theft protection, and might include safety belts or automated features.
Government regulation in the automotive industry directly affects the way cars look, how their components are designed, the safety features that are included, and the overall performance of any given vehicle. As a result, these regulations also have a significant effect on the automotive business by generally increasing production costs while also placing limitations on how cars are sold and marketed. Automotive regulations are designed to benefit the consumer and protect the environment, and automakers can face stiff fines and other penalties if they are not followed.

Efficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the process of reducing the amount of energy required to provide products and services. For example, insulating a building allows it to use less heating and cooling energy to achieve and maintain a thermal comfort. Installing light-emitting diode bulbs, fluorescent lighting, or natural skylight windows reduces the amount of energy required to attain the same level of illumination compared to using traditional incandescent light bulbs. Improvements in energy efficiency are generally achieved by adopting a more efficient technology or production process or by application of commonly accepted methods to reduce energy losses.
The Energy Performance of Buildings Directive is the European Union's main legislative instrument aiming to promote the improvement of the energy performance of buildings within the European Union. It was inspired by the Kyoto Protocol which commits the EU and all its parties by setting binding emission reduction targets.
The European Union's Ecodesign Directive establishes a framework to set mandatory ecological requirements for energy-using and energy-related products sold in all 27 member states. Its scope currently covers more than 40 product groups, which are responsible for around 40% of all EU greenhouse gas emissions.
Sustainable products are those products that provide environmental, social and economic benefits while protecting public health and environment over their whole life cycle, from the extraction of raw materials until the final disposal.

The European Union (EU) Environmental Policy was initiated in 1973 with the "Environmental Action Programme" at which point the Environmental Unit was formed. The policy has thereafter evolved "to cover a vast landscape of different topics enacted over many decades" (Reuters) and in 2015 the Institute for European Environmental Policy estimated that "the body of EU environmental law" amounted to 500+ directives, regulations and decisions.
"Over the past decades the European Union has put in place a broad range of environmental legislation. As a result, air, water and soil pollution has significantly been reduced. Chemicals legislation has been modernised and the use of many toxic or hazardous substances has been restricted. Today, EU citizens enjoy some of the best water quality in the world"
Energy brokers assist clients in procuring electric or natural gas from energy wholesalers/suppliers. Since electricity and natural gas are commodities, prices change daily with the market. It is challenging for most businesses without energy managers to obtain price comparisons from a variety of suppliers since prices must be compared on exactly the same day. In addition, the terms of the particular contract offered by the supplier influences the price that is quoted. An energy broker can provide a valuable service if they work with a large number of suppliers and can actually compile the sundry prices from suppliers. An important aspect of this consulting role is to assure that the client understands the differences between the contract offers. Under some State Laws they use the term "Suppliers" to refer to energy suppliers, brokers, and aggregators, however there are very important differences between them all.
Since the late 1970s, the European Union's (EU) policy has been to develop and drive appropriate measures to improve air quality throughout the EU. The control of emissions from mobile sources, improving fuel quality and promoting and integrating environmental protection requirements into the transport and energy sector are part of these aims.

The European Green Deal, approved in 2020, is a set of policy initiatives by the European Commission with the overarching aim of making the European Union (EU) climate neutral in 2050. The plan is to review each existing law on its climate merits, and also introduce new legislation on the circular economy, building renovation, biodiversity, farming and innovation.

The EU taxonomy for sustainable activities is a classification system established to clarify which investments are environmentally sustainable, in the context of the European Green Deal. The aim of the taxonomy is to prevent greenwashing and to help investors make greener choices. Investments are judged by six objectives: climate change mitigation, climate change adaptation, the circular economy, pollution, effect on water, and biodiversity. The taxonomy came into force in July 2020. The UK is working on its own separate taxonomy.






