
The L17 downstream element RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure identified in bacteria by bioinformatics. All known L17 downstream elements were detected immediately downstream of genes encoding the L17 subunit of the ribosome, and therefore might be in the 3' untranslated regions of these genes. The element is found in a variety of lactic acid bacteria and in the genus Listeria.

The Actino-ugpB RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. Actino-ugpB motifs are found in strains of the species Gardnerella vaginalis, within the phylum Actinomycetota.
The algC RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. algC motifs are found in Enterobacteriaceae.

The COG2908 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. COG2908 motif RNAs are found in genomic sequences extracted from fresh water environments. They have not, as of 2018, been detected in any classified organism.
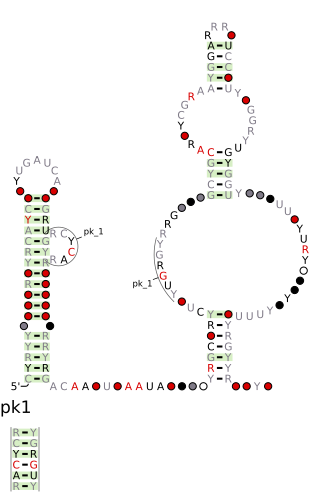
The DUF2800 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. DUF2800 motif RNAs are found in Bacillota. DUF2800 RNAs are also predicted in the phyla Actinomycetota and Synergistota, although these RNAs are likely the result of recent horizontal gene transfer or conceivably sequence contamination.

The DUF805 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. The motif is subdivided into the DUF805 motif and the DUF805b motif, which have similar, but distinct secondary structures. Together, these motifs are found in Bacteroidota, Chlorobiota, and Pseudomonadota.
The freshwater-2 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. Freshwater-2 motif RNAs are found in metagenomic sequences that are isolated from aquatic and especially freshwater environments. As of 2018, no freshwater-2 RNA has been identified in a classified organism.
The gltS RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. gltS motifs are found in the bacterial lineage Vibrionaceae.

The HTH-XRE RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. HTH-XRE motifs are found in Clostridiales.

The hya RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. hya motif RNAs are found in Actinomycetota.

The MDR-NUDIX RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. The MDR-NUDIX motif is found in the poorly studied phylum TM7.

The nhaA-I RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. nhaA-I motif RNAs are found in Acidobacteriota, alpha-, beta- and Gammaproteobacteria, Verrucomicrobiota and the tentative phylum NC10.

The NLPC-P60 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. NLPC-P60 motif RNAs are found in Streptomyces.
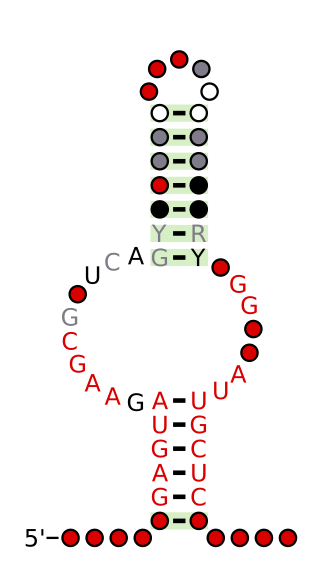
The NMT1 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. NMT1 motif RNAs are found in Pseudomonadota. There is also one NMT1 RNA in each of Bacteroidota and Actinomycetota, but these appear to be the result of recent horizontal gene transfer or sequence contamination before or during genome sequencing

The PGK RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. PGK motif RNAs are found in metagenomic sequences isolated from the gastrointestinal tract of mammals. PGK RNAs have not yet been detected in a classified organism.
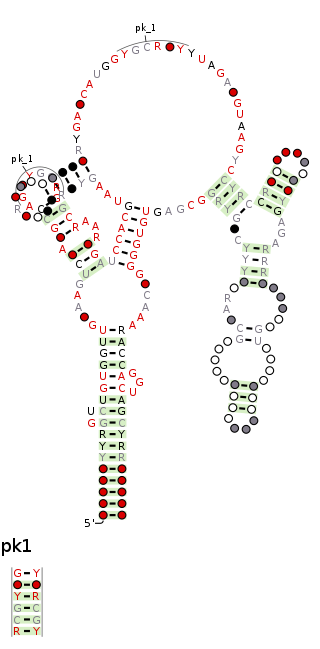
The raiA RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. raiA motif RNAs are found in Actinomycetota and Bacillota, and have many conserved features—including conserved nucleotide positions, conserved secondary structures and associated protein-coding genes—in both of these phyla. Some conserved features of the raiA RNA motif suggest that they function as cis-regulatory elements, but other aspects of the motif suggest otherwise.
A Streptomyces-metKH RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. Such motifs are found in the genus Streptomyces, and are present upstream of either metK genes, which encode the S-adenosylmethionine synthetase enzyme or metH genes, which encodes the adenosylcobalamin-dependent form of methionine synthase. The RNA structures upstream of metK and metH genes are distinct from each other, but exhibit overall similar sequence and secondary structure features, suggesting that they are related to one another. Their presence upstream of protein-coding genes, and the fact that the genes perform related steps in metabolism, suggests that the RNAs function as cis-regulatory elements.

The sul1 RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. Energetically stable tetraloops often occur in this motif. sul1 motif RNAs are found in Alphaproteobacteria.

The terC RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. terC motif RNAs are found in Pseudomonadota, within the sub-lineages Alphaproteobacteria and Pseudomonadales.

The uup RNA motif is a conserved RNA structure that was discovered by bioinformatics. uup motif RNAs are found in Bacillota and Gammaproteobacteria.
















