Life
Enno I was not particularly interested in succeeding his father as count, so his mother Theda stayed in power. Enno took part in a pilgrimage to the Holy Land, and in Jerusalem he was dubbed Knight of the Holy Sepulchre. During his absence in the county, his sister Almut fell in love with the noble Engelmann von Horstell, drost of Friedeburg. They made plans to marry, but they were prevented from marrying by Almut's mother Theda. Undeterred, Almut moved with her betrothed to Friedeburg and took the family jewels with her. When Enno returned to East Frisia, he thought his sister had been kidnapped, and he pursued the drost to his castle. As it was winter, the moat around the castle was frozen over and Enno believed he could cross it. Unfortunately, his armour was too heavy. Enno sank through the ice and drowned.
Enno I was only 30 years old when he died. His mother Theda had a memorial shield made in his honor, which is still on display in the Great Church, today the Johannes-a-Lasco Library in Emden, on a wall close to the crypt of the Lords of East Frisia.

Enno III of Ostfriesland or Enno III of East Frisia was a Count of Ostfriesland from 1599 to 1625 from the Cirksena family. He was the elder son of Count Edzard II of Ostfriesland and his wife Princess Katarina of Sweden, eldest daughter of King Gustav I of Sweden.

Catherine Vasa of Sweden was a Swedish princess, and the Countess consort of East Frisia as the spouse of Edzard II, Count of East Frisia. She was the oldest daughter of Gustav Vasa and Margareta Leijonhufvud. She was the autonomous Regent of Berum and Norden in Ostfriesland from 1599 to 1610.

Edzard II was Count of East Frisia from 1561 to 1599. He was the son of Enno II of East Frisia and Anna of Oldenburg.

Frisian freedom was the absence of feudalism and serfdom in Frisia, the area that was originally inhabited by the Frisians. Historical Frisia included the modern provinces of Friesland and Groningen, and the area of West Friesland, in the Netherlands, and East Friesland in Germany. During the period of Frisian freedom the area did not have a sovereign lord who owned and administered the land. The freedom of the Frisians developed in the context of ongoing disputes over the rights of local nobility.
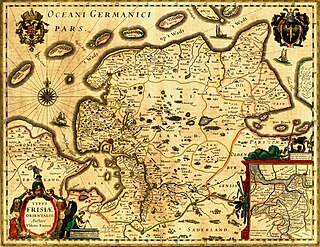
The County of East-Frisia was a county in the region of East Frisia in the northwest of the present-day German state of Lower Saxony.

Ulrich I of East Frisia, first count of East Frisia was a son of the chieftain Enno Edzardisna of Norden and Greetsiel, and Gela of Manslagt.

Edzard I, also Edzard the Great was count of East Frisia from 1491 until his death in 1528.

Enno II of East Frisia was the son of Edzard I of East Frisia. In 1528 he became count of East Frisia. For most of his life he ruled together with Johan I of East Frisia, who remained Catholic, while Enno was Lutheran.

Anna of Oldenburg was a Countess consort of East Frisia as the spouse of Count Enno II of East Frisia. She was the Regent of East Frisia in 1542–1561 as the guardian for her minor sons, Johan II and Edzard II. Her reign lasted until 1561 and was generally supported by the Estates.

Enno Louis of East Frisia, was count of East Frisia and after 1654 Fürst (Prince) of East Frisia, and the son of Ulrich II and Juliana of Hesse-Darmstadt.

The House of Cirksena was a East Frisian noble family descended from a line of East Frisian chieftains from Greetsiel.

Theda Ukena was from 1466 to about 1480 regent of the County of East Frisia.

Juliana of Hesse-Darmstadt was the wife of Count Ulrich II of East Frisia and was regent for her minor son Enno Louis from 1648 to 1651. Her parents were Landgrave Louis V of Hesse-Darmstadt and Magdalene of Brandenburg, daughter of Elector John George von Brandenburg.
The Treaty of Berum was a treaty concluded on 28 January 1600 at Berum Castle between the Count Enno III of East Frisia and the County of Rietberg, which regulated the sale of the Harlingerland to East Frisia.
Enno Edzardisna was a chieftain of Norden, Greetsiel, Berum and Pilsum in East Frisia. He was the son of the chieftain Edzard II of Appingen-Greetsiel and his wife Doda tom Brok. Enno was a pioneer of the claim of the house Cirksena to the rule over all of East Frisia, which his son finally Ulrich I formally achieved when he was made an Imperial Count in 1464.
Johan I of East Frisia (1506–1572) was a member of the house of Cirksena and a non-reigning Count of East Frisia and later imperial governor of Limburg. His father, Edzard the Great, had introduced primogeniture in the county of East Frisia, so that his older brother Enno II of East Frisia inherited the county alone and he had to hold back. Despite his ambitions, he always acknowledged his brother's rights and did not dispute the inheritance.
John III of Rietberg was a member of the Cirksena family. He founded the Catholic side line of the Cirksena in the Westphalian County of Rietberg, the so-called house of East Frisia.
The Saxon feud was a military conflict in the years 1514–1517 between the East Frisian Count Edzard I, 'West Frisian' rebels, the city of Groningen, and Charles II, Duke of Guelders on the one hand and the Imperial Frisian hereditary governor George, Duke of Saxony – replaced by Charles V of Habsburg in 1515 – and 24 German princes. The war took place predominantly on East Frisian soil and destroyed large parts of the region.

Maria of Jever, known in Jeverland as Fräulein Maria, was the last ruler of the Lordship of Jever from the Wiemken family. She ruled from 1517 to her death.
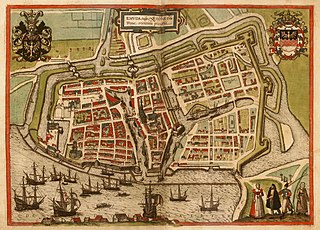
The Emden Revolution of 18 March 1595 marked the beginning of the status of Emden as a quasi-autonomous city-state.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.















