Electronic data interchange (EDI) is the concept of businesses electronically communicating information that was traditionally communicated on paper, such as purchase orders, advance ship notices, and invoices. Technical standards for EDI exist to facilitate parties transacting such instruments without having to make special arrangements.

Accounts payable (AP) is money owed by a business to its suppliers shown as a liability on a company's balance sheet. It is distinct from notes payable liabilities, which are debts created by formal legal instrument documents. An accounts payable department's main responsibility is to process and review transactions between the company and its suppliers and to make sure that all outstanding invoices from their suppliers are approved, processed, and paid. The accounts payable process starts with collecting supply requirements from within the organization and seeking quotes from vendors for the items required. Once the deal is negotiated, purchase orders are prepared and sent. The goods delivered are inspected upon arrival and the invoice received is routed for approvals. Processing an invoice includes recording important data from the invoice and inputting it into the company's financial, or bookkeeping, system. After this is accomplished, the invoices must go through the company's respective business process in order to be paid.

A laboratory information management system (LIMS), sometimes referred to as a laboratory information system (LIS) or laboratory management system (LMS), is a software-based solution with features that support a modern laboratory's operations. Key features include—but are not limited to—workflow and data tracking support, flexible architecture, and data exchange interfaces, which fully "support its use in regulated environments". The features and uses of a LIMS have evolved over the years from simple sample tracking to an enterprise resource planning tool that manages multiple aspects of laboratory informatics.
Enterprise application integration (EAI) is the use of software and computer systems' architectural principles to integrate a set of enterprise computer applications.
Business software is any software or set of computer programs used by business users to perform various business functions. These business applications are used to increase productivity, measure productivity, and perform other business functions accurately.
A translation management system (TMS), formerly globalization management system (GMS), is a type of software for automating many parts of the human language translation process and maximizing translator efficiency. The idea of a translation management system is to automate all repeatable and non-essential work that can be done by software/systems and leaving only the creative work of translation and review to be done by human beings. A translation management system generally includes at least two types of technology: process management technology to automate the flow of work, and linguistic technology to aid the translator.
Enterprise content management (ECM) extends the concept of content management by adding a timeline for each content item and, possibly, enforcing processes for its creation, approval, and distribution. Systems using ECM generally provide a secure repository for managed items, analog or digital. They also include one methods for importing content to bring manage new items, and several presentation methods to make items available for use. Although ECM content may be protected by digital rights management (DRM), it is not required. ECM is distinguished from general content management by its cognizance of the processes and procedures of the enterprise for which it is created.

Kofax Inc. is an Irvine, California-based intelligent automation software provider. Founded in 1985, the company's software allows businesses to automate and improve business workflows by simplifying the handling of data and documents.

Adobe LiveCycle Enterprise Suite (ES4) is a service-oriented architecture Java EE server software product from Adobe Systems used to build applications that automate a broad range of business processes for enterprises and government agencies. LiveCycle ES4 is an enterprise document and form platform that allows capturing and processing information, delivering personalized communications, and protecting and tracking sensitive information. It is used for purposes such as account opening, services, and benefits enrollment, correspondence management, requests for proposal processes, and other manual-based workflows. LiveCycle ES4 incorporates new features with a particular focus on mobile devices. LiveCycle applications also function in both online and offline environments. These capabilities are enabled through the use of Adobe Reader, HTML/PhoneGap, and Flash Player clients to reach desktop computers and mobile devices.
System integration is defined in engineering as the process of bringing together the component sub-systems into one system and ensuring that the subsystems function together as a system, and in information technology as the process of linking together different computing systems and software applications physically or functionally, to act as a coordinated whole.
Expense management refers to the systems deployed by a business to process, pay, and audit employee-initiated expenses. These costs include, but are not limited to, expenses incurred for travel and entertainment. Expense management includes the policies and procedures that govern such spending, as well as the technologies and services utilized to process and analyze the data associated with it.

On-premises software is installed and runs on computers on the premises of the person or organization using the software, rather than at a remote facility such as a server farm or cloud. On-premises software is sometimes referred to as "shrinkwrap" software, and off-premises software is commonly called "software as a service" ("SaaS") or "cloud computing".
A paperless office is a work environment in which the use of paper is eliminated or greatly reduced. This is done by converting documents and other papers into digital form, a process known as digitization. Proponents claim that "going paperless" can save money, boost productivity, save space, make documentation and information sharing easier, keep personal information more secure, and help the environment. The concept can be extended to communications outside the office as well.
An integration competency center (ICC), sometimes referred to as an integration center of excellence (COE), is a shared service function providing methodical data integration, system integration, or enterprise application integration within organizations, particularly large corporations and public sector institutions.
Business process management (BPM) is the discipline in which people use various methods to discover, model, analyze, measure, improve, optimize, and automate business processes. Any combination of methods used to manage a company's business processes is BPM. Processes can be structured and repeatable or unstructured and variable. Though not required, enabling technologies are often used with BPM.
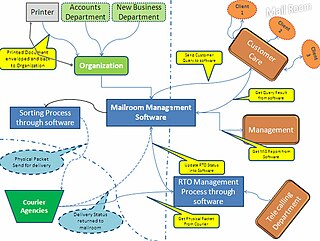
Digital mailroom is the automation of incoming mail processes. Using document scanning and document capture technologies, companies can digitise incoming mail and automate the classification and distribution of mail within the organization. Both paper and electronic mail (email) can be managed through the same process allowing companies to standardize their internal mail distribution procedures and adhere to company compliance policies.
HP Business Service Automation was a collection of software products for data center automation from the HP Software Division of Hewlett-Packard Company. The products could help Information Technology departments create a common, enterprise-wide view of each business service; enable the automation of change and compliance across all devices that make up a business service; connect IT processes and coordinate teams via common workflows; and integrate with monitoring and ticketing tools to form a complete, integrated business service management solution. HP now provides many of these capabilities as part of HP Business Service Management software and solutions.
Enterprise legal management (ELM) is a practice management strategy of corporate legal departments, insurance claims departments, and government legal and contract management departments.
Robotic process automation (RPA) is a form of business process automation that is based on software robots (bots) or artificial intelligence (AI) agents. It is sometimes referred to as software robotics.
A human resources management system (HRMS) or Human Resources Information System (HRIS) or Human Capital Management (HCM) is a form of Human Resources (HR) software that combines a number of systems and processes to ensure the easy management of human resources, business processes and data. Human resources software is used by businesses to combine a number of necessary HR functions, such as storing employee data, managing payroll, recruitment, benefits administration, time and attendance, employee performance management, and tracking competency and training records.




