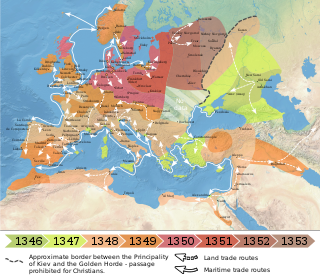
The Black Death was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Afro-Eurasia from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causing the death of 75–200 million people in Eurasia and North Africa, peaking in Europe from 1347 to 1351. Bubonic plague is caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis, but it may also cause septicaemic or pneumonic plagues.

Yersinia pestis is a gram-negative, non-motile, coccobacillus bacterium, without spores that is related to both Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia enterocolitica. It is a facultative anaerobic organism that can infect humans via the Oriental rat flea. It causes the disease plague, which caused the First plague pandemic and the Black Death, the deadliest pandemic in recorded history. Plague takes three main forms: pneumonic, septicemic, and bubonic.
Plague or The Plague may refer to:
Pest or The Pest may refer to:
An empire is a group of states or peoples under centralized rule.

The Plague of Justinian or Justinianic Plague was the first major outbreak of the first plague pandemic, the first Old World pandemic of plague, the contagious disease caused by the bacterium Yersinia pestis. The disease afflicted the entire Mediterranean Basin, Europe, and the Near East, severely affecting the Sasanian Empire and the Byzantine Empire and especially its capital, Constantinople. The plague is named for the Byzantine emperor in Constantinople, Justinian I who, according to his court historian Procopius, contracted the disease and recovered in 542, at the height of the epidemic which killed about a fifth of the population in the imperial capital. The contagion arrived in Roman Egypt in 541, spread around the Mediterranean Sea until 544, and persisted in Northern Europe and the Arabian Peninsula, until 549.
A nightmare is a frightening dream.
Wizard, the wizard, or wizards may refer to:
Halloween is an annual celebration on October 31.
The Labyrinth is an elaborate maze in Greek mythology.
Poison is a substance that causes injury, illness, or death.
Equinox commonly refers to:

Bubonic plague is one of three types of plague caused by the plague bacterium. One to seven days after exposure to the bacteria, flu-like symptoms develop. These symptoms include fever, headaches, and vomiting, as well as swollen and painful lymph nodes occurring in the area closest to where the bacteria entered the skin. Occasionally, the swollen lymph nodes, known as "buboes" may break open.
A midnight sun occurs when the sun is visible at midnight, local time.
Theories of the Black Death are a variety of explanations that have been advanced to explain the nature and transmission of the Black Death (1347–51). A number of epidemiologists since the 1980s have challenged the traditional view that the Black Death was caused by plague based on the type and spread of the disease. The confirmation in 2010 and 2011 that Yersinia pestis DNA was associated with a large number of plague sites has renewed focus on plague as the leading hypothesis, but has not yet led to a final resolution of all these questions.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.



