This article needs additional citations for verification .(June 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
The Equatoria Defense Force (EDF) was a Sudanese militia. [1]
This article needs additional citations for verification .(June 2021) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
The Equatoria Defense Force (EDF) was a Sudanese militia. [1]
It operated in the area around Juba and Torit (in modern-day South Sudan) and was perhaps the most politically effective group in the South Sudan Defence Forces. [1]
Most of its fighters were Latuku and Lokoya. [1] It was generally believed that the central government of Sudan supported the EDF. [1] The EDF signed a merger agreement with the SPLM/A in March 2004, although it was not clear how many EDF fighters accepted it. [1] The Bor Group consisted primarily of SPLA defectors from South Bor. [1] The governor of East Equatoria charged in 2006 that remnants of the EDF continued to carry out attacks and be a threat to security because they received arms from the central government of Sudan. [1]

Equatoria is a region of southern South Sudan, along the upper reaches of the White Nile. Originally a province of Anglo-Egyptian Condominium, it also contained most of northern parts of present-day Uganda, including Lake Albert and West Nile. It was an idealistic effort to create a model state in the interior of Africa that never consisted of more than a handful of adventurers and soldiers in isolated outposts.

Central Equatoria is a state in South Sudan. With an area of 43,033 square kilometres (16,615 sq mi), it was the smallest of the original South Sudanese states. Its previous name was Bahr al-Jabal, named after a tributary of the White Nile that flows through the state. It was renamed to its present name of Central Equatoria in the first Interim Legislative Assembly on 1 April 2005 under the government of Southern Sudan. Central Equatoria seceded from Sudan as part of the Republic of South Sudan on 9 July 2011. The state's capital of Juba is also the national capital of South Sudan. The state split into Jubek, Terekeka, and Yei River states on 2 October 2015, but was re-established by a peace agreement signed on 22 February 2020.

Jonglei is a state of South Sudan. On 2 October 2015 the President Salva Kiir Mayardit decreed the creation of a new Jonglei State along with 27 other states replacing 10 previous states. The earlier Jonglei state comprised nine counties of Akobo, Ayod, Bor, Duk, Fangak, Nyirol, Pigi, Twic East, and Uror and was the largest state by area before reorganisation, with approximately 122,581 km2, as well as the most populous according to the controversial 2008 census conducted during present-day South Sudan's second period of autonomy. The boundaries of the state were again changed as a result of a peace agreement signed on 22 February 2020. Bor is the capital of the state.
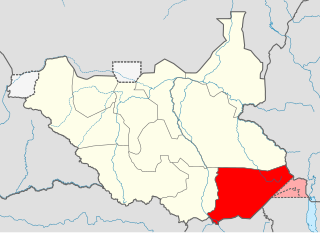
Eastern Equatoria is a state in South Sudan. It has an area of 73,472 km². The capital is Torit. On October 1, 1972, the state was divided into Imatong and Namorunyang states and was re-established by a peace agreement signed on 22 February 2020.

The Mundari are a small ethnic group of South Sudan and part of the Karo people one of the Nilotic peoples.

Bor is the capital of Jonglei State in South Sudan. Since 2016, it has also served as the headquarters of Bor Municipality. The city is situated on the east side of the White Nile at the southern extent of the sudd, South Sudan's vast central wetlands.
Moru is an ethnic group of South Sudan. Most of them live in Equatoria. They speak Moru, a Central Sudanic language. Many members of this ethnicity are Christians, most being members of the Episcopal Church of the Sudan (ECS). The Pioneer missionary in the area was Dr Kenneth Grant Fraser of the Church Missionary Society (CMS). The population of this ethnicity possibly does not exceed 200,000.
The Province of the Episcopal Church of South Sudan, formerly known as Episcopal Church of Sudan, is a province of the Anglican Communion located in South Sudan. The province consists of eight Internal Provinces and 61 dioceses. The current archbishop and primate is Justin Badi Arama. It received the current naming after the inception of the Province of the Episcopal Church of Sudan, on 30 July 2017.

The SPLA-Nasir was a splinter faction of the Sudan People's Liberation Army (SPLA), a rebel group that fought in the Second Sudanese Civil War. Originally created as an attempt by the Nuer tribe to replace SPLA leader John Garang in August 1991, it gradually became coopted by the government. The break away of Riek Machar from SPLM/A resulted in Nuer ethnic group massacring Garang's ethnic Dinka from Bor in the Bor massacre in 1991. This split resulted in the 1994 National Convention of New Sudan in Chukudum.

University of Juba is a public university located in Juba, South Sudan, founded in 1975 in response to the need for higher education in southern areas of Sudan. Due to the Second Sudanese Civil War, the university relocated to Khartoum, for safety of staff, students and infrastructure. In 2006, the government at that time agreed to change the name of the university to Juba National University. Following the attainment of independence by South Sudan in July 2011, the university has relocated back to Juba, where it was founded. The university gives instruction in the English language.

Dominic Dim Deng was a senior member of the Sudan People's Liberation Army, a distinguished military veteran General and the first Defence Minister in the Government of Southern Sudan who lost his life alongside his wife Madam Josephine Apieu Jenaro Aken, senior politician Dr. Justin Yac Arop and 18 other Sudan People's Liberation Army and Government of Southern Sudan officials on a leased CEM Air Beechcraft 1900 that crashed 375 km west of Juba, Sudan on May 2, 2008.

The South Sudan People's Defence Forces (SSPDF), formerly the Sudan People's Liberation Army (SPLA), is the army of the Republic of South Sudan. The SPLA was founded as a guerrilla movement against the government of Sudan in 1983 and was a key participant of the Second Sudanese Civil War, led by John Garang. After Garang's death in 2005, Salva Kiir was named the SPLA's new Commander-in-Chief. As of 2010, the SPLA was divided into divisions of 10,000–14,000 soldiers.
Bor County is a County located in Jonglei State, South Sudan. The county headquarters is Bor. Until 1906, the Bor-Duk District was part of the Upper Nile Province under the colonial Anglo-Egyptian Condominium Government and encompassed all Dinka-speaking communities living on the east side of the Bahr al Jabal River. In 1906 the Bor-Duk District was shifted to Mongalla Province, which had been created from the southern districts of the Upper Nile Province. In 1909–1910, colonial officials began forcibly resettling people along the northern border of the Bor-Duk district, with the aim of separating Nuer and Dinka communities, who had formerly lived together. The Bor-Duk district was later redesignated "Bor County," divided into two in August 2001, and then divided into three counties in 2003: Duk County, Twic East County, and Bor County. The phrase "Greater Bor" refers to the entirety of the former Bor-Duk District, from Cuei-keer in Kolnyang, to the south, to Cuei-thon in the former Duk County, to the north.

South Sudan, officially known as the Republic of South Sudan, is a landlocked country in east/central Africa. It is bordered to the east by Ethiopia, to the north by Sudan, to the west by the Central African Republic, to the southwest by Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south by Uganda and to the southeast by Kenya.
The history of South Sudan comprises the history of the territory of present-day South Sudan and the peoples inhabiting the region.
George Echom Ekeno is a politician who was deputy governor of Eastern Equatoria state in South Sudan, and was later appointed state minister for Environment, Wildlife Conservation & Tourism.

Mongalla or Mangalla is a community in Central Equatoria State in South Sudan, on the east side of the Bahr al Jebel or White Nile river. It lies about 75 km by road northeast of Juba. The towns of Terekeka and Bor lie downstream, north of Mongalla.
Ethnic violence in South Sudan has a long history among South Sudan's varied ethnic groups. South Sudan has 64 tribes with the largest being the Dinkas, who constitute about 35% of the population and predominate in government. The second largest are the Nuers. Conflict is often aggravated among nomadic groups over the issue of cattle and grazing land and is part of the wider Sudanese nomadic conflicts.

The South Sudanese Civil War was a multi-sided civil war in South Sudan between forces of the government and opposition forces. In December 2013, President Kiir accused his former deputy Riek Machar and ten others of attempting a coup d'état. Machar denied trying to start a coup and fled to lead the SPLM – in opposition (SPLM-IO). Fighting broke out between the Sudan People's Liberation Movement (SPLM) and SPLM-IO, igniting the civil war. Ugandan troops were deployed to fight alongside the South Sudanese government. The United Nations has peacekeepers in the country as part of the United Nations Mission in South Sudan (UNMISS).
Operation Thunderbolt was the codename for a military offensive by the South Sudanese SPLA rebel group and its allies during the Second Sudanese Civil War. The operation aimed at conquering several towns in Western and Central Equatoria, most importantly Yei, which served as strongholds for the Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF) and helped the Sudanese government to supply its allies, the Ugandan insurgents of the WNBF and UNRF (II) based in Zaire. These pro-Sudanese forces were defeated and driven from Zaire by the SPLA and its allies, namely Uganda and the AFDL, in course of the First Congo War, thus allowing the SPLA launch Operation Thunderbolt from the Zairian side of the border. Covertly supported by expeditionary forces from Uganda, Ethiopia, and Eritrea, the SPLA's offensive was a major success, with several SAF garrison towns falling to the South Sudanese rebels in a matter of days. Yei was encircled and put under siege on 11 March 1997. At the same time, a large group of WNBF fighters as well as SAF, FAZ, and ex-Rwandan Armed Forces soldiers was trying to escape from Zaire to Yei. The column was ambushed and destroyed by the SPLA, allowing it to capture Yei shortly afterward. Following this victory, the South Sudanese rebels continued their offensive until late April, capturing several other towns in Equatoria and preparing further anti-government campaigns.