
First aid is the first and immediate assistance given to any person with either a minor or serious illness or injury, with care provided to preserve life, prevent the condition from worsening, or to promote recovery. It includes initial intervention in a serious condition prior to professional medical help being available, such as performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) while waiting for an ambulance, as well as the complete treatment of minor conditions, such as applying a plaster to a cut. First aid is generally performed by someone with basic medical training. Mental health first aid is an extension of the concept of first aid to cover mental health, while psychological first aid is used as early treatment of people who are at risk for developing PTSD. Conflict First Aid, focused on preservation and recovery of an individual's social or relationship well-being, is being piloted in Canada.

A first aid kit or medical kit is a collection of supplies and equipment used to give immediate medical treatment, primarily to treat injuries and other mild or moderate medical conditions. There is a wide variation in the contents of first aid kits based on the knowledge and experience of those putting it together, the differing first aid requirements of the area where it may be used, and variations in legislation or regulation in a given area.
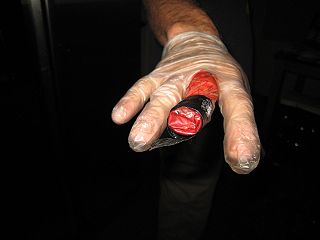
Emergency tourniquets are cuff-like devices designed to stop severe traumatic bleeding before or during transport to a care facility. They are wrapped around the limb, proximal to the site of trauma, and tightened until all blood vessels underneath are occluded. The design and construction of emergency tourniquets allows quick application by first aid responders or the injured persons themselves. Correct use of tourniquet devices has been shown to save lives under austere conditions with comparatively low risk of injury. In field trials, prompt application of emergency tourniquets before the patient goes into shock are associated with higher survival rates than any other scenario where tourniquets were used later or not at all.

Battlefield medicine, also called field surgery and later combat casualty care, is the treatment of wounded combatants and non-combatants in or near an area of combat. Civilian medicine has been greatly advanced by procedures that were first developed to treat the wounds inflicted during combat. With the advent of advanced procedures and medical technology, even polytrauma can be survivable in modern wars. Battlefield medicine is a category of military medicine.

Internal bleeding is a loss of blood from a blood vessel that collects inside the body. Internal bleeding is usually not visible from the outside. It is a serious medical emergency but the extent of severity depends on bleeding rate and location of the bleeding. Severe internal bleeding into the chest, abdomen, retroperitoneal space, pelvis, and thighs can cause hemorrhagic shock or death if proper medical treatment is not received quickly. Internal bleeding is a medical emergency and should be treated immediately by medical professionals.

The Expert Field Medical Badge (EFMB) is a United States Army special skills badge first created on June 18, 1965. This badge is the non-combat equivalent of the Combat Medical Badge (CMB) and is awarded to U.S. military personnel and North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) military personnel who successfully complete a set of qualification tests, including both written and performance portions. The EFMB is known for its adherence to its testing standards and, as such, requires strict attention to detail from candidates in order to receive a "GO" on its combat testing lanes. The pass rate for FY 2017 was 7%, making the EFMB one of the most difficult and prestigious Army special skill badges to earn.

Casualty evacuation, also known as CASEVAC or by the callsign Dustoff or colloquially Dust Off, is a military term for the emergency patient evacuation of casualties from a combat zone. Casevac can be done by both ground and air. "DUSTOFF" is the callsign specific to U.S. Army Air Ambulance units. CASEVACs by air today are almost exclusively done by helicopter, a practice begun on a small scale toward the end of World War II; before that, STOL aircraft, such as the Fieseler Fi 156 or Piper J-3 were used.

A combat medic, or healthcare specialist, is responsible for providing emergency medical treatment at a point of wounding in a combat or training environment, as well as primary care and health protection and evacuation from a point of injury or illness. Additionally, medics may also be responsible for the creation, oversight, and execution of long-term patient care plans in consultation with or in the absence of a readily-available physician or advanced practice provider. Combat medics may be used in hospitals and clinics, where they have the opportunity to work in additional roles such as operating medical and laboratory equipment and performing and assisting with procedures.
Outdoor emergency care (OEC) was first developed by the National Ski Patrol in the 1980s for certification in first aid, and other pre-hospital care and treatment for possible injuries in non-urban settings. Outdoor emergency care technicians provide care at ski resorts, wilderness settings, white-water excursions, mountain bike events, and in many other outdoor environments.

A field dressing or battle dressing is a kind of bandage intended to be carried by soldiers for immediate use in case of wounds. It consists of a large pad of absorbent cloth, attached to the middle of a strip of thin fabric used to bind the pad in place. Field dressings are issued in sealed waterproof pouches to keep them clean and dry; the pouch can be torn open when required.
Buddy Aid is is a term used in the US military to describe first aid delivered by fellow troopers on the battlefield. It is basic first aid only, such as dressing wounds, stemming blood loss, splinting fractures, etc, and possibly responding to nerve agents. The Iranian Military also utilizes the system. Urgent medical care can be vital for personnel in conflicts and wars, and many countries have similar practices.
68W is the Military Occupational Specialty (MOS) for the United States Army's Combat Medic. 68Ws are primarily responsible for providing emergency medical treatment at point of wounding on the battlefield, limited primary care, and health protection and evacuation from a point of injury or illness. 68W's hold the license of EMT-B through the NREMT, and often serve the role similar to an EMT-B or Medical Assistant. However, 68Ws often have a scope of practice much wider than EMT-B's and Medical Assistants. This specialty is open to males and females with minimum line scores of 107 GT and 101 ST on the Armed Services Vocational Aptitude Battery (ASVAB).

The Emergency Bandage or Israeli bandage is a specially designed, first-aid device that is used to stop bleeding from hemorrhagic wounds caused by traumatic injuries in pre-hospital emergency situations. First used for saving lives during a NATO peacekeeping operation in Bosnia and Herzegovina, the bandage was successfully used during operations Enduring Freedom and Iraqi Freedom. The bandage was nicknamed "Israeli bandage" by American soldiers and has been "the bandage of choice for the US Army and special forces." The Israeli Bandage was included in the first aid kits of emergency personnel and first responders at the 2011 Tucson shooting, and was used to treat some victims of the shooting.

The 274th Forward Surgical Team (Airborne)—part of the 274th Forward Resuscitative and Surgical Detachment (Airborne)—is an airborne forward surgical team of the United States Army providing Level II care far forward on the battlefield. It was first constituted in 1944 and served in Europe during World War II. More recently it has been involved in relief operations following natural disasters and has undertaken several recent deployments to Iraq and Afghanistan. The 274th Forward Surgical Team was part of both the initial entry forces of Operation Enduring Freedom in 2001 and Operation Iraqi Freedom in 2003. Currently the unit falls under the command of the 28th Combat Support Hospital and is based at Fort Bragg, North Carolina.

Charles Norman Shay is a Penobscot tribal elder, writer, and decorated veteran of both World War II and the Korean War. Along with a Bronze Star and Silver Star, Shay was also awarded the Legion d'Honneur, making him the first Native American in Maine with the distinction of French chevalier. He was instrumental in the re-publishing of a book by his own grandfather, Joseph Nicolar: The Life and Traditions of the Red Man, originally published in 1893. He has recently written an autobiography, Project Omaha Beach: The Life and Military Service of a Penobscot Indian Elder that details his time abroad in the military. Shay is also a direct descendant of Jean-Vincent d'Abbadie de Saint-Castin.

Tactical Emergency medical services (TEMS) is out-of-hospital care given in hostile situations by specially trained practitioners. Tactical support provided through TEMS can be applied in either the civilian world, generally with special law enforcement teams such as SWAT and SERT, as well as with military special operations teams. Tactical EMS providers are paramedics, nurses, and physicians who are trained to provide life-saving care and, sometimes, transport in situations such as tactical police operations, active shooters, bombings, and natural disasters. Tactical medical providers (TMPs) provide care in high risk situations where there is an increased likelihood for law enforcement, civilian, or suspect casualties. TEMS units are also deployed in situations where traditional EMS or firefighters cannot respond. TMPs are specially trained and authorized to perform live-saving medical procedures in austere and often times unconventional environments. TMPs are also expected to be competent in weapons safety and marksmanship, small unit tactics, waterborne operations, urban search and rescue, and HAZMAT. TMPs also serve to train their respective teams in complex medical procedures that may be performed in their absence. TEMS providers are sometimes sworn police officers cross trained as paramedics, paramedics that are operators trained and integrated into the SWAT Team, or medical providers trained in tactical EMS who are then integrated into law enforcement or military units.

QuikClot is a brand of hemostatic wound dressing, that contains an agent that promotes blood clotting. It is primarily used by militaries and law enforcement to treat hemorrhaging from trauma.

The US Army Combat Lifesaver Course is an official medical training course conducted by the US Army. The course is intended to provide an intermediate step between the buddy aid-style basic life support taught to every soldier and the advanced life support skills that are taught to US Army Combat Medics and to US Army Special Forces Medical Sergeants.

Tactical Combat Casualty Care are the United States military guidelines for trauma life support in prehospital combat medicine, designed to reduce preventable deaths while maintaining operation success. The TCCC guidelines are routinely updated and published by the Committee on Tactical Combat Casualty Care (CoTCCC), which is part of the Defense Committees on Trauma (DCoT) division of the Defense Health Agency (DHA). TCCC was designed in the 1990s for the Special Operations Command medical community. Originally a joint Naval Special Warfare Command and Special Operations Medical Research & Development initiative, CoTCCC developed combat-appropriate and evidence-based trauma care based on injury patterns of previous conflicts. The original TCCC corpus was published in a Military Medicine supplement in 1996. TCCC has since become a Department of Defense (DoD) course, conducted by National Association of Emergency Medical Technicians.















