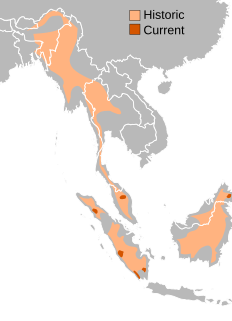
The Sumatran rhinoceros, also known as the hairy rhinoceros or Asian two-horned rhinoceros, is a rare member of the family Rhinocerotidae and one of five extant species of rhinoceros. It is the only extant species of the genus Dicerorhinus. It is the smallest rhinoceros, although it is still a large mammal; it stands 112–145 cm (3.67–4.76 ft) high at the shoulder, with a head-and-body length of 2.36–3.18 m (7.7–10.4 ft) and a tail of 35–70 cm (14–28 in). The weight is reported to range from 500 to 1,000 kg, averaging 700–800 kg (1,540–1,760 lb), although there is a single record of a 2,000 kg (4,410 lb) specimen. Like both African species, it has two horns; the larger is the nasal horn, typically 15–25 cm (5.9–9.8 in), while the other horn is typically a stub. A coat of reddish-brown hair covers most of the Sumatran rhino's body.

Dicerorhinus is a genus of the family Rhinocerotidae, consisting of a single extant species, the only two-horned Sumatran rhinoceros, and several extinct species.

Conyza sumatrensis is an annual herb probably native to South America, but widely naturalised in tropical and subtropical regions, and regarded as an invasive weed in many places. In the British Isles it is known as Guernsey fleabane. Other common names include fleabane, tall fleabane, broad-leaved fleabane, white horseweed, and Sumatran fleabane.
The Belize Premier Football League (BPFL) was the premier division of association football in Belize sanctioned by the Football Federation of Belize. The league disbanded in 2011 after the merger with the Super League of Belize to create a new top league in Belize, the Premier League of Belize.

Rhizomys is a genus of rodents in the family Spalacidae. They are all stocky burrowers with short, naked tails. Rhizomys contains these species:

The large bamboo rat, Sumatran rat, or Indomalayan rat is a species of rodent in the family Spalacidae found in Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Thailand, and Vietnam. It is one of four species of bamboo rat. Individuals can reach lengths of nearly 50 cm (20 in) with a 20 cm (7.9 in) tail, and weigh up to 4 kilograms (8.8 lb).

Scleria sumatrensis, commonly known as nutrush and Sumatran scleria, is a plant species in the sedge family. It is native to temperate and tropical Asia, where it is usually found growing in wetlands, and is considered a noxious weed on the island of Borneo. It has been used in traditional medicine against gonorrhea.
The Gwune language, also known as Agwagwune, is an Upper Cross River language of Nigeria spoken by the Akunakuna people. It is a dialect cluster named after its prestige variety; others are Abayongo, Abini, Dim, Orum, Erei, Etono.

Filopaludina sumatrensis is a species of large freshwater snail with a gill and an operculum, an aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Viviparidae.

Mesosini is a tribe of longhorn beetles of the Lamiinae subfamily.
Ereis is a genus of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae, containing the following species:

The Northern Sumatran rhinoceros, also known as Chittagong rhinoceros or northern hairy rhinoceros was the most widespread subspecies of Sumatran rhinoceros, also the only known subspecies native to mainland Asia whilst the latter live in Indonesian islands.
Ereis annulicornis is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Francis Polkinghorne Pascoe in 1862. It is known from Cambodia.
Ereis anthriboides is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Francis Polkinghorne Pascoe in 1857. It is known from Sumatra and Malaysia.
Ereis distincta is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Maurice Pic in 1935. It is known from Vietnam.
Ereis javanica is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1936. It is known from Java.
Ereis roseomaculata is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1968.
Ereis subfasciata is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Maurice Pic in 1925. It is known from Vietnam and China.
Obereopsis sumatrensis is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1951.
The Beriguruk were an indigenous Australian people, now thought to be extinct, of the Northern Territory.










