Related Research Articles

Qo inhibitors (QoI), or quinone outside inhibitors, are a group of fungicides used in agriculture. Some of these fungicides are among the most popular in the world. QoI are chemical compounds which act at the quinol outer binding site of the cytochrome bc1 complex.
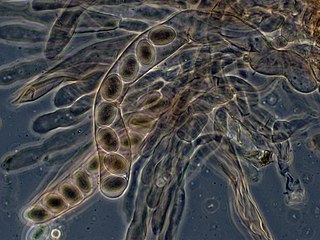
An ascospore is a spore contained in an ascus or that was produced inside an ascus. This kind of spore is specific to fungi classified as ascomycetes (Ascomycota).
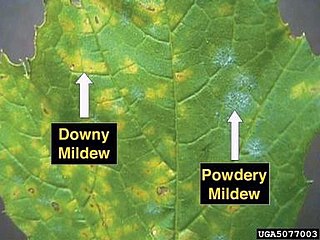
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease that affects a wide range of plants. Powdery mildew diseases are caused by many different species of fungi in the order Erysiphales. Powdery mildew is one of the easier plant diseases to identify, as its symptoms are quite distinctive. Infected plants display white powdery spots on the leaves and stems. The lower leaves are the most affected, but the mildew can appear on any above-ground part of the plant. As the disease progresses, the spots get larger and denser as large numbers of asexual spores are formed, and the mildew may spread up and down the length of the plant.

Uncinula necator is a fungus that causes powdery mildew of grape. It is a common pathogen of Vitis species, including the wine grape, Vitis vinifera. The fungus is believed to have originated in North America. European varieties of Vitis vinifera are more or less susceptible to this fungus. Uncinula necator infects all green tissue on the grapevine, including leaves and young berries. It can cause crop loss and poor wine quality if untreated. The sexual stage of this pathogen requires free moisture to release ascospores from its cleistothecia in the spring. However, free moisture is not needed for secondary spread via conidia; high atmospheric humidity is sufficient. Its anamorph is called Oidium tuckeri.

Oidium is a genus of Deuteromycetes, where traditionally most anamorphs of the order Erysiphales are included. Most of them are plant pathogens causing different forms of powdery mildew, for example:

Erysiphales are an order of ascomycete fungi. The order contains one family, Erysiphaceae. Many of them cause plant diseases called powdery mildew.

Blumeria graminis is a fungus that causes powdery mildew on grasses, including cereals. It is the only species in the genus Blumeria. It has also been called Erysiphe graminis and Oidium monilioides or Oidium tritici.
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease of barley caused by Blumeria graminis f. sp. hordei. The disease has a worldwide distribution and is most damaging in cool, wet climates. The host range of the form species hordei is restricted to barley and other Hordeum species.
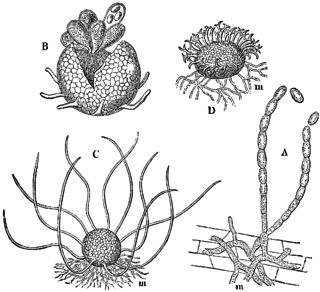
Erysiphe cruciferarum is a plant pathogen of the family Erysiphaceae, which causes the main powdery mildew of crucifers, including on Brassica crops, such as cauliflower, cabbage, broccoli, and Brussels sprouts. E. cruciferarum is distributed worldwide, and is of particular concentration in continental Europe and the Indian subcontinent. E. cruciferarum is an ascomycete fungus that has both sexual and asexual stages. It is also an obligate parasite that appears to have host specificity; for example, isolates from turnip will not infect Brussels sprout, and vice versa. While being a part of the family Erysiphaceae, it belongs to those members in which the conidia are formed singly and whose haustoria are multilobed.

Erysiphe betae is a plant pathogen. It is a form of powdery mildew that can affect crops of sugar beet, when it can cause up to a 30% yield loss. The fungus occurs worldwide in all regions where sugar beet is grown and it also infects other edible crops, e.g. beetroot.
Erysiphe heraclei is a plant pathogen that causes powdery mildew on several species including dill, carrot and parsley.

Erysiphe cichoracearum is a fungal plant pathogen that causes powdery mildew disease of cucurbits, including melon, cucumber, pumpkin, and squash. The primary symptoms are white, powder-like spots on the leaves and stems. Sphaerotheca fuliginea causes a similar looking powdery mildew of cucurbits.

Oidium mangiferae is a plant pathogen that infects mango trees causing powdery mildew. Powdery mildew of mango is an Ascomycete pathogen of the Erysiphales family that was initially described by Berthet in 1914, using samples collected from Brazil. O. mangiferae is found in all areas where mangoes have been raised long term, but is particularly widespread in India where both the host and the pathogen are native. Currently no teleomorph stage has been identified, but due to certain morphological characteristics it has been suggested that O. mangiferae belongs in the Erysiphe polygony group. Mango is the only known host for this pathogen, though O. mangiferae appears to be identical to fungi responsible for powdery mildew diseases on various other plant species, particularly oak, though some differences may be observed. In particular, the number of cells in conidiophores varies from 2 on mango to 3-5 on oak. O. mangiferae has been known to infect oak leaves in the laboratory, however due to the lack of a known teleomorph stage O. mangiferae is still considered to only be a pathogen of mango. Recent analysis of its ribosomal DNA suggests it is conspecific with Erysiphe alphitoides, the causative agent of powdery mildew in European oaks.

Podosphaera fuliginea is a plant pathogen that causes powdery mildew on cucurbits. Podosphaera fuliginea and Erysiphe cichoracearum are the two most commonly recorded fungi causing cucurbit powdery mildew. In the past, Erysiphe cichoracearum was considered to be the primary causal organism throughout most of the world. Today, Podosphaera fuliginea is more commonly reported.

Erysiphe is a genus of fungi in the family Erysiphaceae. Many of the species in this genus are plant pathogens which cause powdery mildew.

Uncinula is a genus of fungi. Its species are plant pathogens that cause powdery mildew diseases on various plant hosts. The genus is characterized by its dark chasmothecia which bear filamentous, hyaline appendages with hooked tips. Over one hundred species have been described from mostly dicotyledenous hosts. Braun and Takamatsu (2000) suggested that Uncinula should be considered a later synonym of Erysiphe; not all subsequent researchers have accepted their conclusions.

Erysiphe alphitoides is a species of fungus which causes powdery mildew on oak trees.

Ampelomyces quisqualis is an anamorphic fungus that is a hyperparasite of powdery mildews. This parasitism reduces growth and may eventually kill the mildew. These mycoparasites can live up to 21 days on mildew-free host plant surfaces, attacking powdery mildew structures as soon as they appear. A. quisqualis is used as the active ingredient in a commercial fungicide.
Cecil Edmund Yarwood (1908–1981) was an American-Canadian plant pathologist whose work focused on obligate parasites of plants, viruses, and conditions that predisposed plants to infections. He is considered an authority on rust (fungus) and powdery mildew.

Powdery mildew of lilac, or Erysiphe syringae is a fungal pathogen of lilacs.
References
- ↑ Agrios (2005). Plant Pathology.
- ↑ "Blumeria graminis Grass Mildew". Encyclopedia of Life. Retrieved 25 February 2017.