Politics in Estonia takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic republic, whereby the Prime Minister of Estonia is the head of government, and of a multi-party system. Legislative power is vested in the Estonian parliament. Executive power is exercised by the government, which is led by the prime minister. The judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature. Estonia is a member of the United Nations, the European Union, and NATO.
The dissolution of a legislative assembly is the simultaneous termination of service of all of its members, in anticipation that a successive legislative assembly will reconvene later with possibly different members. In a democracy, the new assembly is chosen by a general election. Dissolution is distinct on the one hand from abolition of the assembly, and on the other hand from its adjournment or prorogation, or the ending of a legislative session, any of which begins a period of inactivity after which it is anticipated that the same members will reassemble. For example, the "second session of the fifth parliament" could be followed by the "third session of the fifth parliament" after a prorogation, but would be followed by the "first session of the sixth parliament" after a dissolution.

The prime minister of Estonia is the head of government of the Republic of Estonia. The prime minister is nominated by the president after appropriate consultations with the parliamentary factions and confirmed by the parliament (Riigikogu). In case of disagreement, the parliament can reject the president's nomination and choose their own candidate. In practice, since the prime minister must maintain the confidence of parliament in order to remain in office, they are usually the leader of the senior partner in the governing coalition. The current prime minister is Kristen Michal of the Reform Party. He took the office on 23 July 2024 following the resignation of Kaja Kallas.
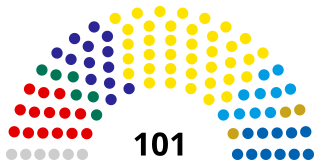
The Riigikogu is the unicameral parliament of Estonia. In addition to approving legislation, the Parliament appoints high officials, including the prime minister and chief justice of the Supreme Court, and elects the president. Among its other tasks, the Riigikogu also ratifies significant foreign treaties that impose military and proprietary obligations and bring about changes in law, as well as approves the budget presented by the government as law, and monitors the executive power.

Konstantin Päts was an Estonian statesman and the country's president from 1938 to 1940. Päts was one of the most influential politicians of the independent democratic Republic of Estonia, and during the two decades prior to World War II he also served five times as the country's State Elder. He carried out a self-coup on 12 March 1934. After the 16–17 June 1940 Soviet invasion and occupation of Estonia, Päts remained formally in office for over a month, until he was forced to resign, imprisoned by the new Stalinist regime, and deported to the USSR, where he died in 1956.

The president of the Republic of Estonia is the head of state of the Republic of Estonia. The current president is Alar Karis, elected by Parliament on 31 August 2021, replacing Kersti Kaljulaid.

Jaan Tõnisson was an Estonian statesman, serving as the Prime Minister of Estonia twice during 1919 to 1920, as State Elder from 1927 to 1928 and in 1933, and as Foreign Minister of Estonia from 1931 to 1932.
The State Elder, sometimes also translated as Head of State, was the official title of the Estonian head of state from 1920 to 1937. He combined some of the functions held by a president and prime minister in most other democracies.

August Rei was an Estonian politician. He served as State Elder of Estonia from 1928 to 1929, and as Prime Minister in duties of the President of the Estonian government-in-exile from 1945 to 1963.
The Constitution of Estonia is the fundamental law of the Republic of Estonia and establishes the state order as that of a democratic republic where the supreme power is vested in its citizens. The first Constitution was adopted by the freely elected Estonian Constituent Assembly on 15 June 1920 and came into force on 21 December 1920. Heavily amended on 24 January 1934, following a referendum in 1933, it was in force until the second Constitution was enacted on 1 January 1938. It remained in force, de facto, until 16 June 1940, when the Soviet Union occupied Estonia and, de jure, until 28 June 1992, when the third and current Constitution of the Republic of Estonia was adopted by referendum.
The Supreme Court of Estonia is the court of last resort in Estonia. It is both a court of cassation and a constitutional court. The courthouse is in Tartu.
The history of Estonia from 1918 to 1940 spanned the interwar period from the end of the Estonian War of Independence until the outbreak of World War II. It covers the years of parliamentary democracy, the Great Depression and the period of corporatist authoritarian rule.
This is a list of members of the sixth legislative session of the Estonian Parliament (Riigikogu) following the 1938 elections. It sat between 7 April 1938 and 5 July 1940, after which Estonia was occupied by the Soviet Union for the first time. Estonia's previous unicameral parliamentary system had been suspended in 1934 and formally dissolved in 1937; on 1 January 1938, the country's Third Constitution came into force, creating a bicameral National Assembly, consisting of the Chamber of Deputies (Riigivolikogu) and the National Council (Riiginõukogu). These were de facto dissolved when the Soviet Union occupied Estonia and established the Supreme Soviet of the Estonian Soviet Socialist Republic.
August Kohver was an Estonian agronomist and politician.
VI Riigikogu was the sixth legislature of the Estonian Parliament (Riigikogu). The legislature was elected after the 1938 elections. It sat between 7 April 1938 and 5 July 1940, after which the Soviet Union occupied Estonia for the first time. Estonia's previous unicameral parliamentary system had been suspended in 1934 and formally dissolved in 1937; on 1 January 1938, the country's Third Constitution came into force, creating a bicameral National Assembly, consisting of the Chamber of Deputies (Riigivolikogu) and the National Council (Riiginõukogu). These were de facto dissolved when the Soviet Union occupied Estonia and established the Supreme Soviet of the Estonian Soviet Socialist Republic.
Viktor Päts was an Estonian politician, lawyer, and son of Estonian president Konstantin Päts. He was a member of VI Riigikogu.
The 1938 Estonian presidential election took place on April 24, 1938. The electoral assembly, which consisted of the bicameral legislature and 120 representatives of municipalities, assembled to elect a President. The only candidate set forth was State Treasurer Konstantin Päts, who was elected President with 219 votes out of the total 240 delegates. Two delegates were absent. Konstantin Päts was elected as the first President of Estonia but failed to serve a full term due to the subsequent Soviet occupation.





