Related Research Articles

Boötes is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from Latin Boōtēs, which comes from Greek Βοώτης Boṓtēs 'herdsman' or 'plowman'.

Carina is a constellation in the southern sky. Its name is Latin for the keel of a ship, and it was the southern foundation of the larger constellation of Argo Navis until it was divided into three pieces, the other two being Puppis, and Vela.

Corona Australis is a constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere. Its Latin name means "southern crown", and it is the southern counterpart of Corona Borealis, the northern crown. It is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations. The Ancient Greeks saw Corona Australis as a wreath rather than a crown and associated it with Sagittarius or Centaurus. Other cultures have likened the pattern to a turtle, ostrich nest, a tent, or even a hut belonging to a rock hyrax.

The Leonids are a prolific meteor shower associated with the comet Tempel–Tuttle, which are also known for their spectacular meteor storms that occur about every 33 years. The Leonids get their name from the location of their radiant in the constellation Leo: the meteors appear to radiate from that point in the sky. Their proper Greek name should be Leontids, but the word was initially constructed as a Greek/Latin hybrid and it has been used since. They peak in the month of November.

A meteoroid is a small rocky or metallic body in outer space.

The Geminids are a prolific meteor shower caused by the object 3200 Phaethon, which is thought to be a Palladian asteroid with a "rock comet" orbit. This would make the Geminids, together with the Quadrantids, the only major meteor showers not originating from a comet. The meteors from this shower are slow moving, can be seen in December and usually peak around December 4–16, with the date of highest intensity being the morning of December 14. The shower is thought to be intensifying every year and recent showers have seen 120–160 meteors per hour under optimal conditions, generally around 02:00 to 03:00 local time. Geminids were first observed in 1862, much more recently than other showers such as the Perseids and Leonids.

A meteor shower is a celestial event in which a number of meteors are observed to radiate, or originate, from one point in the night sky. These meteors are caused by streams of cosmic debris called meteoroids entering Earth's atmosphere at extremely high speeds on parallel trajectories. Most meteors are smaller than a grain of sand, so almost all of them disintegrate and never hit the Earth's surface. Very intense or unusual meteor showers are known as meteor outbursts and meteor storms, which produce at least 1,000 meteors an hour, most notably from the Leonids. The Meteor Data Centre lists over 900 suspected meteor showers of which about 100 are well established. Several organizations point to viewing opportunities on the Internet. NASA maintains a daily map of active meteor showers.

The Perseids are a prolific meteor shower associated with the comet Swift–Tuttle. The meteors are called the Perseids because the point from which they appear to hail lies in the constellation Perseus.
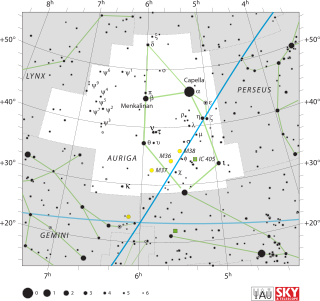
Auriga is one of the 88 modern constellations; it was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy. It is north of the celestial equator. Its name is Latin for '(the) charioteer', associating it with various mythological beings, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the northern Hemisphere, as are five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far south as -34°; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest, Hydra.
The Quadrantids (QUA) are a meteor shower that peaks in early January and whose radiant lies in the constellation Boötes. The zenithal hourly rate (ZHR) of this shower can be as high as that of two other reliably rich meteor showers, the Perseids in August and the Geminids in December, yet Quadrantid meteors are not seen as often as those of the two other showers because the time frame of the peak is exceedingly narrow, sometimes lasting only hours. Moreover, the meteors are quite faint, with mean apparent magnitudes between 3.0 and 6.0).
Jean Chacornac was a French astronomer and discoverer of a comet and several asteroids.
The American Meteor Society, Ltd. (AMS) is a non-profit scientific organization established to encourage and support the research activities of both amateur and professional astronomers who are interested in the field of meteor astronomy. Its affiliates observe, monitor, collect data on, study, and report on meteors, meteor showers, meteoric fireballs, and related meteoric phenomena.

The Eta Aquariids are a meteor shower associated with Halley's Comet.

Comet IRAS–Araki–Alcock is a long-period comet that, in 1983, made the closest known approach to Earth of any comet in 200 years, at a distance of about 0.0312 AU. The comet was named after its discoverers – the Infrared Astronomical Satellite and two amateur astronomers, George Alcock of the United Kingdom and Genichi Araki of Japan. Both men were schoolteachers by profession, although Alcock was retired. Alcock had made his discovery simply by observing through the window of his home, using binoculars. During the closest approach, the comet appeared as a circular cloud about the size of the full moon, having no discernible tail, and shining at a naked eye magnitude of 3–4. It swept across the sky at an angular speed of about 30 degrees per day. On May 11th the comet was detected on radar by Arecibo Observatory and Goldstone Solar System Radar making it the first comet detected by two different radar systems. A second detection was made by Goldstone on 14 May.
The Orionids meteor shower, often shortened to the Orionids, is the most prolific meteor shower associated with Halley's Comet. The Orionids are so-called because the point they appear to come from, called the radiant, lies in the constellation Orion, but they can be seen over a large area of the sky. The Orionids are an annual meteor shower which last approximately one week in late October. In some years, meteors may occur at rates of 50–70 per hour.
The Delta Cancrids is a medium strength meteor shower lasting from December 14 to February 14, the main shower from January 1 to January 24. The radiant is located in the constellation of Cancer, near Delta Cancri. It peaks on January 17 each year, with only four meteors per hour. It was first discovered in 1872, but the first solid evidence of this phenomenon came in 1971. The source of this meteor shower is unknown, it has been suggested that it is similar to the orbit of asteroid 2001 YB5.
The Virginids are a meteor shower. There are many major and minor meteor shower streams that occur during the Virginid Complex, including the Alpha Virginids, Gamma Virginids, Eta Virginids, Theta Virginids, Iota Virginids, Lambda Virginids, Mu Virginids, Pi Virginids, and Psi Virginids, and March Virginids, emanating mostly from the constellation Virgo between February and May. Collectively, the shower normally lasts from late January to mid-April and into early May, peaking in March and April, with one to two meteors per hour on average. The main radiant shifts southeastwards from central Leo in late January to central Virgo near Spica in mid-May.

209P/LINEAR is a periodic comet discovered on 3 February 2004 by Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research (LINEAR) using a 1.0-metre (39 in) reflector. Initially it was observed without a coma and named 2004 CB as a minor planet or asteroid, but in March 2004 Robert H. McNaught observed a comet tail which confirmed it as a comet. It was given the permanent number 209P on 12 December 2008 as it was the second observed appearance of the comet. Prediscovery images of the comet, dating back to December 2003, were found during 2009. Arecibo imaging in 2014 showed the comet nucleus is peanut shaped and about 2.4 km in diameter. The comet has extremely low activity for its size and is probably in the process of evolving into an extinct comet.

Comet 252P/LINEAR is a periodic comet and near-Earth object discovered by the LINEAR survey on April 7, 2000. The comet is an Earth-Jupiter family comet, meaning that it passes quite close to both Earth and Jupiter. This causes its orbit to be perturbed frequently on an astronomical timescale.

CAMS is a NASA-sponsored international project that tracks and triangulates meteors during night-time video surveillance in order to map and monitor meteor showers. Data processing is housed at the Carl Sagan Center of the SETI Institute in California, USA. Goal of CAMS is to validate the International Astronomical Union's Working List of Meteor Showers, discover new meteor showers, and predict future meteor showers.
References
- ↑ Kronk, Gary W. "Eta Carinids". Meteor Showers Online. p. 1. Archived from the original on 2017-01-26. Retrieved 2007-01-21.
- ↑ "Eta Carinids". maa.mhn.de. p. 1. Retrieved 2008-08-05.
