Related Research Articles

Erica Jong is an American novelist, satirist, and poet, known particularly for her 1973 novel Fear of Flying. The book became famously controversial for its attitudes towards female sexuality and figured prominently in the development of second-wave feminism. According to The Washington Post, it has sold more than 20 million copies worldwide.

The Columbia University School of Social Work is the graduate school of social work of Columbia University in New York City. It is one of the oldest social work programs in the US, with roots extending back to 1898. It began awarding a Master of Science degree in 1940. As of 2018, it was one of the largest social work schools in the United States, with an enrollment of over 1,000 students.

Lillian D. Wald was an American nurse, humanitarian and author. She strove for human rights and started American community nursing. She founded the Henry Street Settlement in New York City and was an early advocate for nurses in public schools.

Grace Paley, née Goodside was an American short story author, poet, teacher, and political activist.

Maria de Lourdes Hinojosa Ojeda is a Mexican-American journalist. She is the anchor and executive producer of Latino USA on National Public Radio, a public radio show devoted to Latino issues. She is also the founder, president and CEO of Futuro Media Group, which produces the show. In 2022, Hinojosa won a Pulitzer Prize.

Faye Glenn Abdellah was an American pioneer in nursing research. Abdellah was the first nurse and woman to serve as the Deputy Surgeon General of the United States. Preceding her appointment, she served in active duty during the Korean War, where she earned a distinguished ranking equivalent to a Navy Rear Admiral, making her the highest-ranked woman and nurse in the Federal Nursing Services at the time. In addition to these achievements, Abdellah led the formation of the National Institute of Nursing Research at the NIH, and was the founder and first dean of the Graduate School of Nursing at the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences (USUHS). A few of Abdellah's more passionate interests in public health included the importance of long-term care planning for elderly patients; the need to strengthen nursing school infrastructure; and the necessity of patient-centered approaches in nursing. In 2000, Abdellah was inducted into the National Women's Hall of Fame. During her acceptance speech, Abdellah made the following quote: "We cannot wait for the world to change. .. Those of us with intelligence, purpose, and vision must take the lead and change the world. .. I promise never to rest until my work has been completed!”
Virginia Avenel Henderson was an American nurse, researcher, theorist, and writer.
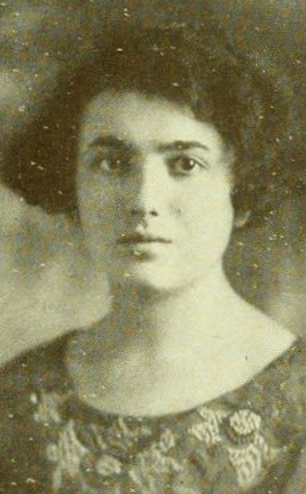
Mirra Komarovsky, was an American pioneer in the sociology of gender.

Mary Adelaide Nutting was a Canadian nurse, educator, and pioneer in the field of hospital care. After graduating from Johns Hopkins University's first nurse training program in 1891, Nutting helped to found a modern nursing program at the school. In 1907, she became involved in an experimental program at the new Teachers College at Columbia University. Ascending to the role of chair of the nursing and health department, Nutting authored a vanguard curriculum based on preparatory nursing education, public health studies, and social service emphasis. She served as president of a variety of councils and committees that served to standardize nursing education and ease the process of meshing nurse-profession interest with state legislation. Nutting was also the author of a multitude of scholarly works relating to the nursing field, and her work, A History of Nursing, remains an essential historic writing today. She is remembered for her legacy as a pioneer in the field of nursing, but also her activist role in a time where women still had limited rights.

Jane Edna Hunter, an African-American social worker, Hunter was born on the Woodburn Farm plantation near Pendleton, South Carolina. She was involved in the NAACP and NAACW. Jane Edna Hunter is widely Known for her work in 1911 when she established the Working Girls Association in Cleveland, Ohio, which later became the Phillis Wheatley Association of Cleveland.
Sally Elizabeth Thorne CM, PhD, FAAN, FCAHS, RN is a Canadian academic nursing teacher, researcher and author. She researched the human experience of chronic illness and cancer, and qualitative research methodologies including metasynthesis and interpretive description.
Teresa Thomas "Terry" Fulmer, is the current president of The John A. Hartford Foundation. Earlier positions include distinguished professor and dean of the Bouvé College of Health Sciences at Northeastern University and dean of the College of Nursing at New York University. She is known for her extensive research in geriatrics and elder abuse. She has received funding from the National Institute on Aging, the National Institute of Nursing Research and other foundations for her research regarding elder abuse.

(Rachel) Louise McManus was the first nurse to earn a Ph.D. She established schools of nursing in college and helped to develop nationally standardized methods for nursing licensure in the United States.
Muriel Petioni was a medical doctor and community activist in Harlem. She was known as the "matron of Harlem health" because she sought to fulfill the healthcare needs of the underprivileged people in Harlem.
Clotilda Adessa Douglas-Yakimchuk was a Canadian nurse. She was the first African-Canadian to graduate from the Nova Scotia Hospital School of Nursing and the first black president of the Registered Nurses’ Association of Nova Scotia.
Abosede George is the Tow Associate Professor of History at Barnard College and Columbia University in New York. She teaches courses on African migrations, historical mapping, urban history, African history, childhood and youth studies, girl studies, women's studies, and migration studies gender, and sexuality in African History. She is the incumbent President of the Nigerian Studies Association, an affiliate organization of the African Studies Association.

Ethel Elizabeth McGhee Davis was an American educator, social worker, and college administrator. She served as the student adviser (1928–1931) and as the Dean of Women (1931–1932) for Spelman College in Atlanta.

Winifred Latimer Norman was an American social worker, active in efforts to preserve her grandfather Lewis Howard Latimer's legacy in Flushing, Queens.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Roberts, Sam (November 26, 2019). "Ethel Paley, Champion of Nursing Home Patients, Dies at 99". The New York Times. Retrieved 9 January 2023.
- ↑ Minichello, Michael D (2011-01-01). "Ethel Paley". West Village Originals. Retrieved 9 January 2023.