Related Research Articles

Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, opposite Estonia. Finland covers an area of 338,145 square kilometres (130,559 sq mi) and has a population of 5.6 million. Helsinki is the capital and largest city. The vast majority of the population are ethnic Finns. The official languages are Finnish and Swedish, of which 84.9 percent of the population speak the first as their mother tongue and 5.1 percent the latter. Finland's climate varies from humid continental in the south to boreal in the north. The land cover is predominantly boreal forest biome, with more than 180,000 recorded lakes.

The demographics of Finland is monitored by the Statistics Finland. Finland has a population of over 5.6 million people, ranking it 19th out of 27 within the European Union. The average population density in Finland is 19 inhabitants per square kilometre (49/sq mi), making it the third most sparsely populated country in Europe, after Iceland and Norway. Population distribution is extremely uneven, with the majority of the population concentrated in the southern and western regions of the country. The majority of the Finnish population - approximately 73% - lives in urban areas. Approximately 1.58 million, or almost 30%, reside solely in the Helsinki Metropolitan Area. Conversely, the Arctic Lapland region contains only two inhabitants per square kilometre (5.2/sq mi).

The Sámi are the traditionally Sámi-speaking Indigenous peoples inhabiting the region of Sápmi, which today encompasses large northern parts of Norway, Sweden, Finland, and of the Kola Peninsula in Russia. The region of Sápmi was formerly known as Lapland, and the Sámi have historically been known in English as Lapps or Laplanders, but these terms are regarded as offensive by the Sámi, who prefer their own endonym, e.g. Northern Sámi Sápmi. Their traditional languages are the Sámi languages, which are classified as a branch of the Uralic language family.
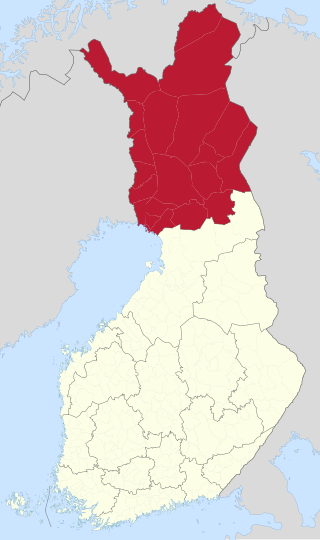
Lapland is the largest and northernmost region of Finland. The 21 municipalities in the region cooperate in a Regional Council. Lapland borders the region of North Ostrobothnia in the south. It also borders the Gulf of Bothnia, Norrbotten County in Sweden, Finnmark County and Troms County in Norway, and Murmansk Oblast and the Republic of Karelia in Russia. Topography varies from vast mires and forests of the South to fells in the North. The Arctic Circle crosses Lapland, so polar phenomena such as the midnight sun and polar night can be viewed in Lapland.

Enontekiö is a municipality in the Finnish part of Lapland with approx. 1,800 inhabitants. It is situated in the outermost northwest of the country and occupies a large and very sparsely populated area of about 8,400 square kilometres (3,200 sq mi) between the Swedish and Norwegian border. Finland's highest point, the Halti fell, with a height of 1,324 metres (4,344 ft) above the mean sea level, is situated in the north of Enontekiö. The municipality shares borders with regions of Sweden and Norway that encompass the Scandinavian Mountains. The administrative centre of Enontekiö is the village of Hetta. About one fifth of the community's population are Sami people. Enontekiö's main industries are tourism and reindeer husbandry.

Karelians are a Baltic Finnic ethnic group who are indigenous to the historical region of Karelia, which is today split between Finland and Russia. Karelians living in Russian Karelia are considered a distinct ethnic group closely related to Finnish Karelians, who are considered a subset of Finns. This distinction historically arose from Karelia having been fought over and eventually split between Sweden and Novgorod, resulting in Karelians being under different cultural spheres.

Southwest Finland, calqued as Finland Proper, is a region in the southwest of Finland. It borders the regions of Satakunta, Pirkanmaa, Tavastia Proper (Kanta-Häme), Uusimaa, and Åland. The region's capital and most populous city is Turku, which was the capital city of Finland before Helsinki.

Karelia is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for Russia, Finland, and Sweden. It is currently divided between northwestern Russia and Finland.

The culture of Finland combines indigenous heritage, as represented for example by the country's national languages Finnish and Swedish, and the sauna, with common Nordic and European cultural aspects. Because of its history and geographic location, Finland has been influenced by the adjacent areas, various Finnic and Baltic peoples as well as the former dominant powers of Sweden and Russia. Finnish culture is built upon the relatively ascetic environmental realities, traditional livelihoods, and heritage of egalitarianism and the traditionally widespread ideal of self-sufficiency.

South Ostrobothnia is one of the 19 regions of Finland. It borders the regions of Ostrobothnia, Central Ostrobothnia, Central Finland, Pirkanmaa, and Satakunta. Among the Finnish regions, South Ostrobothnia is the ninth largest in terms of population. Seinäjoki is the regional centre and by far the largest city in the area.
Finns or Finnish people are a Baltic Finnic ethnic group native to Finland.

The Ingrians, sometimes called Ingrian Finns, are the Finnish population of Ingria, descending from Lutheran Finnish immigrants introduced into the area in the 17th century, when Finland and Ingria were both parts of the Swedish Empire. In the forced deportations before and after World War II, and during the genocide of Ingrian Finns, most of them were relocated to other parts of the Soviet Union, or killed. Today the Ingrian Finns constitute the largest part of the Finnish population of the Russian Federation. According to some records, some 25,000 Ingrian Finns have returned or still reside in the region of Saint Petersburg.

The two main official languages of Finland are Finnish and Swedish. There are also several official minority languages: three variants of Sami, as well as Romani, Finnish Sign Language, Finland-Swedish Sign Language and Karelian.

Swedish is the official language of Sweden and is spoken by the vast majority of the 10.23 million inhabitants of the country. It is a North Germanic language and quite similar to its sister Scandinavian languages, Danish and Norwegian, with which it maintains partial mutual intelligibility and forms a dialect continuum. A number of regional Swedish dialects are spoken across the country. In total, more than 200 languages are estimated to be spoken across the country, including regional languages, indigenous Sámi languages, and immigrant languages.
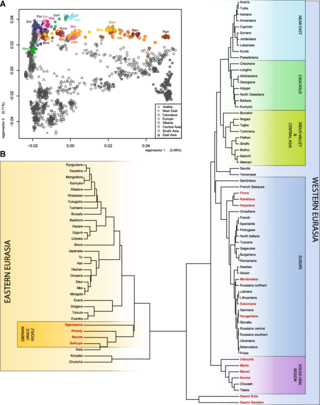
Genetic studies on Sami is the genetic research that have been carried out on the Sami people. The Sami languages belong to the Uralic languages family of Eurasia.

The Sámi homeland of Finland is the northernmost part of the Lappi (Lapland) administrative region in Finland, home of approximately half of Finland's Sámi population. The area is defined in and protected by the Finnish constitution to be autonomous on issues relating to the Sámi culture and language.
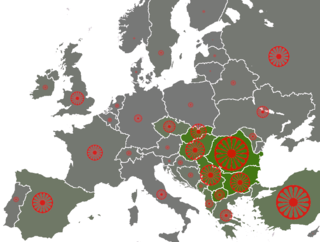
The Romani people have several distinct populations, the largest being the Roma and the Calé, who reached Anatolia and the Balkans in the early 12th century, from a migration out of the Indian subcontinent beginning about 1st century – 2nd century AD. They settled in the areas of present-day Turkey, Greece, Serbia, Romania, Croatia, Moldova, Bulgaria, North Macedonia, Hungary, Albania, Kosovo, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Czech Republic, Slovenia and Slovakia, by order of volume, and Spain. From the Balkans, they migrated throughout Europe and, in the nineteenth and later centuries, to the Americas. The Roma population in the United States is estimated at more than one million.

The Baltic Finnic peoples, often simply referred to as the Finnic peoples, are the peoples inhabiting the Baltic Sea region in Northern and Eastern Europe who speak Finnic languages. They include the Finns, Estonians, Karelians, Veps, Izhorians, Votes, and Livonians. In some cases the Kvens, Ingrians, Tornedalians and speakers of Meänkieli are considered separate from the Finns.

Immigration to Finland is the process by which people migrate to Finland to reside in the country. Some, but not all, become Finnish citizens. Immigration has been a major source of population growth and cultural change throughout much of the history of Finland. The economic, social, and political aspects of immigration have caused controversy regarding ethnicity, economic benefits, jobs for non-immigrants, settlement patterns, impact on upward social mobility, crime, and voting behaviour.
The various regional and minority languages in Europe encompass four categories:
References
- ↑ Tilastokeskus. "Population". www.stat.fi. Retrieved 2020-06-15.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Text from PD source: US Library of Congress: A Country Study: Finland , Library of Congress Call Number DL1012 .A74 1990.
- ↑ Tilastokeskus. "Population". www.stat.fi. Retrieved 2024-07-23.
- ↑ Tilastokeskus. "Population". www.stat.fi. Retrieved 2024-07-23.
- ↑ "BETWEEN TWO COUNTRIES : Estonian Immigrants" Identity Construction in Finland" (PDF). Helda.helsinki.fi. Retrieved 2024-07-23.
- ↑ Population 31.12. by Origin, Background country, Language, Year, Age, Sex and Information , retrieved 23 July 2024
- ↑ Niemi, Heli (2007). "Russian Immigrants in Finnish Society" (PDF). University of Vechta. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 February 2017. Retrieved 22 January 2017.
- ↑ "Ulkomaiden kansalaiset". Tilastokeskus (in Finnish). Retrieved 22 January 2017.
- ↑ "Population structure 2012 - annual review". Statistics Finland. 2013. Retrieved 21 January 2017.
- ↑ Population of mainland Finland (excluding Åland) according to language, 1990-2015 Archived 2013-01-06 at archive.today Statistics Finland
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 January 2021. Retrieved 19 February 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ "Karjalan kieli sai virallisen aseman". 26 November 2009.
- ↑ "Saame". Kotus (in Finnish). Retrieved 22 January 2017.
- ↑ "Tietoa meistä". Saamelaiskäräjät (in Finnish). Retrieved 2024-02-14.
- ↑ "Romanit ovat etninen vähemmistö | Näin se näkyy meillä". Romanit.fi (in Finnish). Retrieved 2024-02-14.
- ↑ "Tavismuslimit". Ylioppilaslehti (in Finnish). 2004. Retrieved 21 January 2017.