Karelians are a Baltic Finnic ethnic group who are indigenous to the historical region of Karelia, which is today split between Finland and Russia. Karelians living in Russian Karelia are considered a distinct ethnic group closely related to Finnish Karelians, who are considered a subset of Finns. This distinction historically arose from Karelia having been fought over and eventually split between Sweden and Novgorod, resulting in Karelians being under different cultural spheres.

Karelia is an area in Northern Europe of historical significance for Russia, Finland, and Sweden. It is currently divided between northwestern Russia and Finland.

Olonets Karelia is a historical and cultural region and the southern portion of East Karelia, which is part of Russia. Olonets Karelia is located between the other historical regions of Ladoga Karelia, to its west, White Karelia, to its north, the River Svir, to its south and Lake Onega on its eastern side. Olonets Karelia is home to its own dialect of the Karelian language, which is known as Livvi Karelian or sometimes as 'Olonets Karelian'.
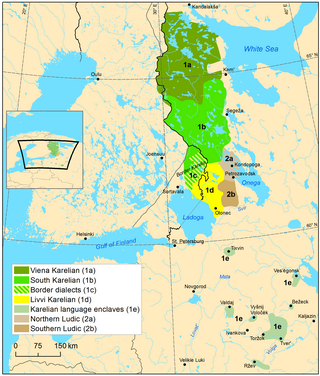
Livvi-Karelian is a supradialect of Karelian, which is a Finnic language of the Uralic family, spoken by Olonets Karelians, traditionally inhabiting the area between Ladoga and Onega lakes, northward of Svir River.

Ludic, Ludian, or Ludic Karelian, is a Finnic language in the Uralic language family or a Karelian dialect. It is transitional between the Olonets Karelian language and the Veps language. It is spoken by 300 Karelians in the Republic of Karelia in Russia, near the southwestern shore of Lake Onega, including a few children.

Greater Finland is an irredentist and nationalist idea which aims for the territorial expansion of Finland. It is associated with Pan-Finnicism. The most common concept saw the country as defined by natural borders encompassing the territories inhabited by Finns and Karelians, ranging from the White Sea to Lake Onega and along the Svir River and Neva River—or, more modestly, the Sestra River—to the Gulf of Finland. Some extremist proponents also included the Kola Peninsula, Finnmark, Swedish Meänmaa, Ingria, and Estonia.

Ladoga Karelia is a historical region of Karelia, currently largely in Russia. Today, the term refers to the part of the Republic of Karelia in the Russian Federation comprising the south-west part of the Republic, specifically Lakhdenpokhsky District, Pitkyarantsky District and Sortavala District. This region is on the northern littoral of Lake Ladoga, which borders Olonets Karelia to the East, Leningrad Oblast to the south-west and the North Karelia region of Finland to the west.

The East Karelian Uprising and the Soviet–Finnish conflict 1921–1922 were an attempt by a group of East Karelian separatists supported by Finland to gain independence from the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic. They were aided by a number of Finnish volunteers, starting from 6 November 1921. The conflict ended on 21 March 1922 with the Agreements between the governments of Soviet Russia and Finland about the measures of maintenance of the inviolability of the Soviet–Finnish border. The conflict is regarded in Finland as one of the heimosodat – "Kinship Wars".
Karjalan Sanomat is a weekly Finnish language newspaper from the Republic of Karelia, published in Petrozavodsk. The newspaper was founded in 1920 as 'Karjalan kommuuni'.
The Karelian language is spoken in Russia, mostly in the Karelian Republic and in a small region just north of Tver, though most residents there were expelled in 1939. Karelian has seen numerous proposed and adopted alphabets over the centuries, both Latin and Cyrillic. In 2007, the current standardized Karelian alphabet was introduced and is used to write all varieties of Karelian, including Tver Karelian which adopted it in 2017.

Tver Karelians are a people who inhabit regions of Tver, Saint Petersburg, and Moscow. Their dialect is remarkable in that it does not borrow from other Balto-Finnic languages due to centuries of geographical isolation. Although the number of Tver Karelian people was about 14,633 in 2002, very few named the dialect as their primary language. The number of Tver Karelians was 7,394 in 2010 and 2,764 in 2020.
Lyudmila Fyodorovna Markianova is a Karelian linguist and a professor emerita. She has been called "karjalan kielen muamo", i.e. 'mother of the Karelian language'.
Karelians, also known as Finnish Karelians or Karelian Finns, are a subgroup of the Finnish people, traditionally living in Finnish Karelia. Karelians speak eastern dialects of the Finnish language: the South Karelian dialects are spoken in South Karelia, while the eastern Savonian dialects are spoken in North Karelia. The South Karelian dialects were spoken in the Karelian Isthmus prior to the Winter War. Karelians are traditionally Lutheran Christians, with an Orthodox Christian minority, belonging to either the Evangelical Lutheran Church of Finland or the Orthodox Church of Finland respectively.

Karelian Proper is a supradialect of the Karelian language, which is a Finnic language. Karelian Proper is one of two/three Karelian dialects, along with Livvi-Karelian and Ludic. Karelian Proper is a direct descendent of the Old Karelian language, compared to Livvi-Karelian and Ludian supradialects which were formed through interactions between the Old Karelian and the Old Veps languages. Karelian Proper is situated in all of White Karelia and Central Karelia.

South Karelian is the most spoken of the two dialects of Karelian Proper, and it is spoken in the Republic of Karelia and in the Tver Oblast. South Karelian was also previously spoken in Border Karelia when it was apart of Finland. Many speakers of the South Karelian dialect were evacuated from Finnish Karelia into other areas of Finland during the 20th century, where a number of speakers are still retained. South Karelian displays a higher degree of regional variation than any other Karelian dialect.

Northern Karelian is one of the two dialects of Karelian Proper. Northern Karelian is spoken in White Karelia, and is spoken by some in Hietajärvi, Kuivajärvi and Kuhmo in Finland. Northern Karelian is the most mutually intelligible Karelian dialect to Finnish Language speakers.
The Karelian language is a Baltic Finnic language spoken mostly in the Republic of Karelia (Russia) and Finland. The earliest book of the Bible to be translated in Karelian dates to the 19th century, however the Lord's Prayer is known to have been translated already in the 16th century into Karelian. There have been recently new efforts to create translations into the Karelian language, and there exists two full New Testament translations in Karelian: "Uuzi Sana" in Livvi-Karelian and "Uuši Šana" in Northern Karelian.

The Tver Karelian dialect is a dialect of the Karelian language spoken in the Tver Oblast. It is descended from 17th century South Karelian speakers who migrated to the Tver region.

Proto-Karelian, also known as Old Karelian was a language once spoken on the western shore of Lake Ladoga in Karelia, from which the dialects of the Karelian language, Ludic, the Ingrian language, as well as the South Karelian and Savonian dialects of the Finnish language have developed. It was spoken around the 12th and 13th centuries, and the language was likely quite uniform with little regional variance. The Eastern Finnish dialects developed from Proto-Karelian when the language of the inhabitants who had moved to the area around present-day Mikkeli mixed with western, likely Tavastian, speakers of Finnish. The Livvi-Karelian dialect and Ludic developed from the mixture of the old Vepsian language spoken by the Vepsians of the Olonets Isthmus and Proto-Karelian.