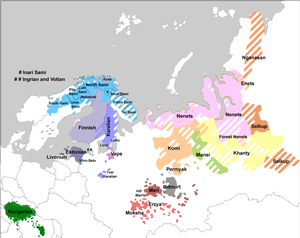
The Uralic languages, sometimes called the Uralian languages, are spoken predominantly in Europe and North Asia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian, Finnish, and Estonian. Other languages with speakers above 100,000 are Erzya, Moksha, Mari, Udmurt and Komi spoken in the European parts of the Russian Federation. Still smaller minority languages are Sámi languages of the northern Fennoscandia; other members of the Finnic languages, ranging from Livonian in northern Latvia to Karelian in northwesternmost Russia; and the Samoyedic languages, Mansi and Khanty spoken in Western Siberia.

Votic or Votian, is a Finnic language spoken by the Votes of Ingria, belonging to the Finnic branch of the Uralic languages. Votic is spoken only in Krakolye and Luzhitsy, two villages in Kingiseppsky District in Leningrad Oblast, Russia. In the 2020–2021 Russian census, 21 people claimed to speak Votic natively, which is an increase from 4 in 2010. Arvo Survo also estimated that around 100 people have knowledge of the language to some degree.
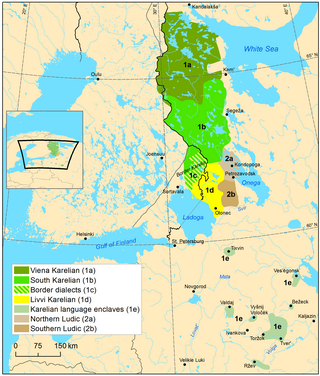
Livvi-Karelian is a supradialect of Karelian, which is a Finnic language of the Uralic family, spoken by Olonets Karelians, traditionally inhabiting the area between Ladoga and Onega lakes, northward of Svir River.

Komi, also known as Zyran, Zyrian or Komi-Zyryan, is the native language of the Komi (Zyrians). It is one of the Permian languages; the other regional variety is Komi-Permyak.

Udmurt is a Permic language spoken by the Udmurt people who are native to Udmurtia. As a Uralic language, it is distantly related to languages such as Finnish, Estonian, Mansi, Khanty, and Hungarian. The Udmurt language is co-official with Russian within Udmurtia.

Enets is a Samoyedic language of Northern Siberia spoken on the Lower Yenisei within the boundaries of the Taimyr Municipality District, a subdivision of Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russian Federation. Enets belongs to the Northern branch of the Samoyedic languages, in turn a branch of the Uralic language family.

The Mordvinic languages, also known as the Mordvin, Mordovian or Mordvinian languages , are a subgroup of the Uralic languages, comprising the closely related Erzya language and Moksha language, both spoken in Mordovia.

Khanty, previously known as Ostyak, is a Uralic language family composed of multiple dialect continuua, varyingly considered a language or a collection of distinct languages, spoken in the Khanty-Mansi and Yamalo-Nenets Okrugs. There were thought to be around 7,500 speakers of Northern Khanty and 2,000 speakers of Eastern Khanty in 2010, with Southern Khanty being extinct since the early 20th century. The number of speakers reported in the 2020 census was 13,900.

The Mansi languages are spoken by the Mansi people in Russia along the Ob River and its tributaries, in the Khanty–Mansi Autonomous Okrug, and Sverdlovsk Oblast. Traditionally considered a single language, they constitute a branch of the Uralic languages, often considered most closely related to neighbouring Khanty and then to Hungarian.

Selkup is the language of the Selkups, belonging to the Samoyedic group of the Uralic language family. It is spoken by some 1,570 people in the region between the Ob and Yenisei Rivers. The language name Selkup comes from the Russian селькуп, based on the native name used in the Taz dialect, шӧльӄумыт әты. Different dialects use different names.
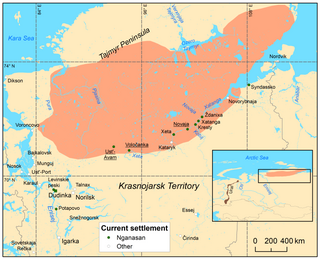
The Nganasan language is a moribund Samoyedic language spoken by about 30 of the Nganasan people.

Kamas is an extinct Samoyedic language, formerly spoken by the Kamasins. It is included by convention in the Southern group together with Mator and Selkup. The last native speaker of Kamas, Klavdiya Plotnikova, died in 1989. It has been noted that at present a few activists still have knowledge of the Kamasin language, however. Kamas was spoken in Russia, north of the Sayan Mountains, by Kamasins. The last speakers lived mainly in the village of Abalakovo, where they moved from the mountains in the 18th-19th centuries. Prior to its extinction, the language was strongly influenced by Turkic and Yeniseian languages.

Mator or Motor is an extinct Uralic language belonging to the group of Samoyedic languages, extinct since around 1839. It was spoken in the northern region of the Sayan Mountains in Siberia, close to the Mongolian north border. The speakers of Mator, Matorians or Mators, lived in a wide area from the eastern parts of the Minusinsk District (okrug) along the Yenisei River to the region of Lake Baikal. Three dialects of Mator were recorded: Mator proper as well as Taygi and Karagas. Mator was influenced by Mongolic, Tungusic and Turkic languages before it went extinct, and may have even been possibly influenced by the Iranic languages. It went extinct as a result of the Mator people shifting linguistically to the related Kamas language or nearby Altaic-sprachbund languages, like Buryat, Soyot, Khakas, Evenki and Tatar.
Proto-Samoyedic, or Proto-Samoyed, is the reconstructed ancestral language of the Samoyedic languages: Nenets, Enets, Nganasan, Selkup, as well as extinct Kamas and Mator. Samoyedic is one of the principal branches of the Uralic language family, and its ancestor is Proto-Uralic. It has been suggested that Proto-Samoyedic greatly influenced the development of Tocharian, an Indo-European language.

The Ob-Ugric languages are a commonly proposed branch of the Uralic languages, grouping together the Khanty (Ostyak) and Mansi (Vogul) languages. Both languages are split into numerous and highly divergent dialects, more accurately referred to as languages. The Ob-Ugric languages and Hungarian comprise the proposed Ugric branch of the Uralic language family.

Forest Nenets (Neshan) is a Samoyedic language spoken in northern Russia, around the Agan, Pur, Lyamin and Nadym rivers, by the Nenets people. It is closely related to the Tundra Nenets language, and the two are still sometimes seen as simply being dialects of a single Nenets language, despite there being low mutual intelligibility between the two. The next closest relatives are Nganasan and Enets, after them Selkup, and even more distantly the other Uralic languages.

Tundra Nenets is a Uralic language spoken in European Russia and North-Western Siberia. It is the largest and best-preserved language in the Samoyedic group.

Eastern or Konda Mansi is an extinct member of the Mansi languages, and was spoken in Russia in the Khanty–Mansi Autonomous Okrug around the river Konda. It became extinct in 2018, when its last speaker Maksim Shivtorov died. It has Khanty and Siberian Tatar influence. There is vowel harmony, and for it has, frequently diphthongized.

Southern or Tavda Mansi is an extinct Uralic language spoken in Russia in the Sverdlovsk. It was recorded from an area isolated from the other Mansi varieties along the river Tavda. Around 1900 a couple hundred speakers existed; in the 1960s it was spoken only by a few elderly speakers, and it has since then become extinct. It had strong Tatar lexical influence and displayed several archaisms such as vowel harmony, retention of, , and.

Western Mansi was described as "probably extinct" in 1988. Although the last speaker is not known, none were left by the end of the 20th century. It had strong Russian and Komi influences; dialect differences were also considerable. Long vowels were diphthongized.