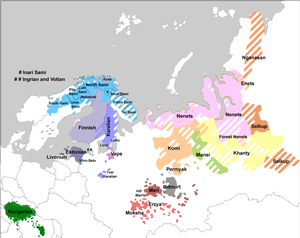
Estonian is a Finnic language of the Uralic family. Estonian is the official language of Estonia. It is written in the Latin script and is the first language of the majority of the country's population; it is also an official language of the European Union. Estonian is spoken natively by about 1.1 million people: 922,000 people in Estonia and 160,000 elsewhere.

The Ket language, or more specifically Imbak and formerly known as Yenisei Ostyak, is a Siberian language long thought to be an isolate, the sole surviving language of a Yeniseian language family. It is spoken along the middle Yenisei basin by the Ket people.
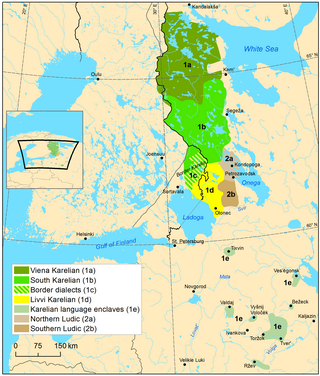
Karelian is a Finnic language spoken mainly in the Russian Republic of Karelia. Linguistically, Karelian is closely related to the Finnish dialects spoken in eastern Finland, and some Finnish linguists have even classified Karelian as a dialect of Finnish, but nowadays it is widely considered a separate language. Karelian is not to be confused with the Southeastern dialects of Finnish, sometimes referred to as karjalaismurteet in Finland. In the Russian 2020–2021 census, around 9,000 people spoke Karelian natively, but around 14,000 said they were able to speak the language. There are around 11,000 speakers of Karelian in Finland. And around 30,000 people in Finland have at least some knowledge of Karelian.
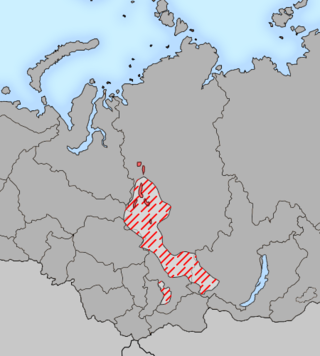
The Yeniseian languages are a family of languages that are spoken by the Yeniseian people in the Yenisei River region of central Siberia. As part of the proposed Dené–Yeniseian language family, the Yeniseian languages have been argued to be part of "the first demonstration of a genealogical link between Old World and New World language families that meets the standards of traditional comparative-historical linguistics". The only surviving language of the group today is Ket.
Madras Bashai was the variety of the Tamil language spoken by native people in the city of Chennai in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It was then sometimes considered a pidgin (as its vocabulary was heavily influenced by each of Hindustani, Indian English, Telugu, Malayalam, and Burmese. However, among these, it is mutually intelligible with none of them.

The Hunnic language, or Hunnish, was the language spoken by Huns in the Hunnic Empire, a heterogeneous, multi-ethnic tribal confederation which invaded Eastern and Central Europe, and ruled most of Pannonian Central Europe, during the 4th and 5th centuries CE. A variety of languages were spoken within the Hun Empire. A contemporary report by Priscus has that Hunnish was spoken alongside Gothic and the languages of other tribes subjugated by the Huns.

The Miyakoan language is a diverse dialect cluster spoken in the Miyako Islands, located southwest of Okinawa. The combined population of the islands is about 52,000. Miyakoan is a Southern Ryukyuan language, most closely related to Yaeyama. The number of competent native speakers is not known; as a consequence of Japanese language policy which refers to the language as the Miyako dialect, reflected in the education system, people below the age of 60 tend to not use the language except in songs and rituals, and the younger generation mostly uses Japanese as their first language. Miyakoan is notable among the Japonic languages in that it allows non-nasal syllable-final consonants, something not found in most Japonic languages.

Chanyu or Shanyu, short for Chengli Gutu Chanyu, was the title used by the supreme rulers of Inner Asian nomads for eight centuries until superseded by the title "Khagan" in 402 CE. The title was most famously used by the ruling Luandi clan of the Xiongnu during the Qin dynasty and Han dynasty. It was later also used infrequently by the Chinese as a reference to Tujue leaders.

The Kamasins are a collection of tribes of Samoyedic peoples in the Sayan Mountains who lived along the Kan River and Mana River in the 17th century in the southern part of today's Krasnoyarsk Krai.

Kamas is an extinct Samoyedic language, formerly spoken by the Kamasins. It is included by convention in the Southern group together with Mator and Selkup. The last native speaker of Kamas, Klavdiya Plotnikova, died in 1989. It has been noted that at present a few activists still have knowledge of the Kamasin language, however. Kamas was spoken in Russia, north of the Sayan Mountains, by Kamasins. The last speakers lived mainly in the village of Abalakovo, where they moved from the mountains in the 18th-19th centuries. Prior to its extinction, the language was strongly influenced by Turkic and Yeniseian languages.

Mator or Motor is an extinct Uralic language belonging to the group of Samoyedic languages, extinct since around 1839. It was spoken in the northern region of the Sayan Mountains in Siberia, close to the Mongolian north border. The speakers of Mator, Matorians or Mators, lived in a wide area from the eastern parts of the Minusinsk District (okrug) along the Yenisei River to the region of Lake Baikal. Three dialects of Mator were recorded: Mator proper as well as Taygi and Karagas. Mator was influenced by Mongolic, Tungusic and Turkic languages before it went extinct, and may have even been possibly influenced by the Iranic languages. It went extinct as a result of the Mator people shifting linguistically to the related Kamas language or nearby Altaic-sprachbund languages, like Buryat, Soyot, Khakas, Evenki and Tatar.

The Kott (Kot) language is an extinct Yeniseian language that was formerly spoken in central Siberia by the banks of the Mana River, a tributary of the Yenisei river. It became extinct in the 1850s. Kott was closely related to Ket, still spoken farther north along the Yenisei river. Assan, a close relative, is sometimes considered a dialect of Kott. The term kott may be derived from Buryat qota 'town', applied to neighbouring non-pastoral peoples, including the last few Kotts.

Pumpokol is one of the Yeniseian languages, formerly spoken by the Pumpokol people. It has been extinct since the 18th century. It shares many features with the ancient Xiongnu and Jie languages, and according to Alexander Vovin, Edward Vajda, and Étienne de la Vaissière, is closely related to them. It is poorly attested, the only available lexicon amounting to about 65 words, and some of them have been identified as being Yugh, not Pumpokol.
Dene–Yeniseian is a proposed language family consisting of the Yeniseian languages of central Siberia and the Na-Dene languages of northwestern North America.
The Koibal are one of the subdivisions of the Khakass people of Southern Siberia. Although they speak the Turkic Khakas language, the Koibal have mixed ancestry and used to speak a Yeniseian language and the Koibal dialect of the Kamas language, both of which are now extinct. They formed in the late 19th century from the merger of the Abugach, Baikot, Kandyk, Tarazhak, Kol and Arsh peoples. Most of these people are believed to have been of ancestry more closely related to Samoyedic peoples than to Turks. Koibals live in the Beysky District of Khakassia.
Koibal language may refer to:

Finnish is a Finnic language of the Uralic language family, spoken by the majority of the population in Finland and by ethnic Finns outside of Finland. Finnish is one of the two official languages of Finland, alongside Swedish. In Sweden, both Finnish and Meänkieli are official minority languages. Kven, which like Meänkieli is mutually intelligible with Finnish, is spoken in the Norwegian counties of Troms and Finnmark by a minority of Finnish descent.

The Karay-a language is an Austronesian regional language in the Philippines spoken by the Karay-a people, mainly in Antique.