Ethnologue: Languages of the World is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensive catalogue of languages. It was first issued in 1951, and is now published by SIL International, an American evangelical Christian non-profit organization.

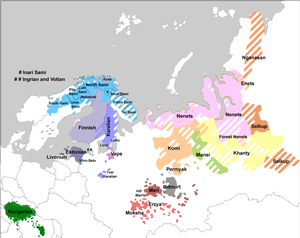
The Uralic languages, sometimes called the Uralian languages, form a language family of 42 languages spoken predominantly in Europe and North Asia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian, Finnish, and Estonian. Other languages with speakers above 100,000 are Erzya, Moksha, Mari, Udmurt and Komi spoken in the European parts of the Russian Federation. Still smaller minority languages are Sámi languages of the northern Fennoscandia; other members of the Finnic languages, ranging from Livonian in northern Latvia to Karelian in northwesternmost Russia; and the Samoyedic languages, Mansi and Khanty spoken in Western Siberia.
In grammar, the prolative case, also called the vialis case, prosecutive case, traversal case, mediative case, or translative case, is a grammatical case of a noun or pronoun that has the basic meaning of "by way of" or "via".

The Nenets, also known as 'Samoyeds' or 'Yuraks', are a Samoyedic ethnic group native to Arctic Russia, Russian Far North. According to the latest census in 2021, there were 49,646 Nenets in the Russian Federation, most of them living in the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Nenets Autonomous Okrug and Taymyrsky Dolgano-Nenetsky District stretching along the coastline of the Arctic Ocean near the Arctic Circle between Kola and Taymyr peninsulas. The Nenets people speak either the Tundra or Forest Nenets languages. In the Russian Federation they have a status of Indigenous small-numbered peoples. Today, the Nenets people face numerous challenges from the state and oil and gas companies that threaten the environment and their way of life. As a result, many cite a rise in locally based activism.

The Samoyedic or Samoyed languages are spoken around the Ural Mountains, in northernmost Eurasia, by approximately 25,000 people altogether, accordingly called the Samoyedic peoples. They derive from a common ancestral language called Proto-Samoyedic, and form a branch of the Uralic languages. Having separated perhaps in the last centuries BC, they are not a diverse group of languages, and are traditionally considered to be an outgroup, branching off first from the other Uralic languages.

The Enets are a Samoyedic ethnic group who live on the east bank, near the mouth, of the Yenisei River. Historically they were nomadic people. As of 2002, most enetses lived in the village of Potapovo in Krasnoyarsk Krai in western Siberia near the Arctic Circle. According to the 2010 Census, there are 227 Enets in Russia. In Ukraine, there were 26 Entsi in 2001, of whom 18 were capable of speaking the Enets language.

The Nganasans are a Uralic people of the Samoyedic branch native to the Taymyr Peninsula in north Siberia. In the Russian Federation, they are recognized as one of the indigenous peoples of the Russian North. They reside primarily in the settlements of Ust-Avam, Volochanka, and Novaya in the Taymyrsky Dolgano-Nenetsky District of Krasnoyarsk Krai, with smaller populations residing in the towns of Dudinka and Norilsk as well.

Nenets is a pair of closely related languages spoken in northern Russia by the Nenets people. They are often treated as being two dialects of the same language, but they are very different and mutual intelligibility is low. The languages are Tundra Nenets, which has a higher number of speakers, spoken by some 30,000 to 40,000 people in an area stretching from the Kanin Peninsula to the Yenisei River, and Forest Nenets, spoken by 1,000 to 1,500 people in the area around the Agan, Pur, Lyamin and Nadym rivers.

Enets is a Samoyedic language of Northern Siberia spoken on the Lower Yenisei within the boundaries of the Taimyr Municipality District, a subdivision of Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russian Federation. Enets belongs to the Northern branch of the Samoyedic languages, in turn a branch of the Uralic language family.
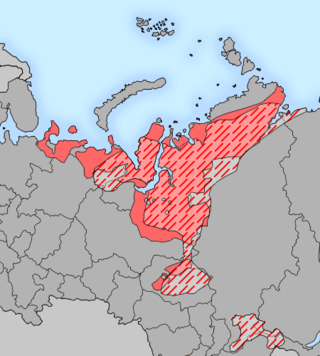
The Samoyedic peoples are a group of closely related peoples who speak Samoyedic languages, which are part of the Uralic family. They are a linguistic, ethnic, and cultural grouping. The name derives from the obsolete term Samoyed used in Russian Empire for some Indigenous people of Siberia, see Samoyedic languages#Etymology for comments of the etymology.
The Selkup are a Samoyedic speaking Uralic ethnic group native to Siberia. They live in the northern parts of Tomsk Oblast, Krasnoyarsk Krai and Tyumen Oblast. Selkups from 1850s until the 1930s exclusively in the scientific literature were called Ostyak-Samoyeds. This ethnonym has never been widely used.
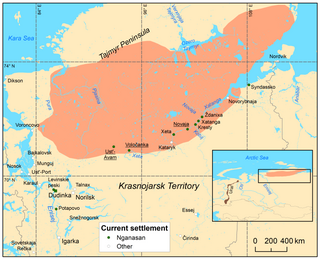
The Nganasan language is a moribund Samoyedic language spoken by the Nganasan people.
Proto-Samoyedic, or Proto-Samoyed, is the reconstructed ancestral language of the Samoyedic languages: Nenets, Enets, Nganasan, Selkup, as well as extinct Kamas and Mator. Samoyedic is one of the principal branches of the Uralic language family, and its ancestor is Proto-Uralic. It has been suggested that Proto-Samoyedic greatly influenced the development of Tocharian, an Indo-European language.

The Ob-Ugric languages are a commonly proposed branch of the Uralic languages, grouping together the Khanty (Ostyak) and Mansi (Vogul) languages. Both languages are split into numerous and highly divergent dialects, more accurately referred to as languages. The Ob-Ugric languages and Hungarian comprise the proposed Ugric branch of the Uralic language family.

A large minority of people in North Asia, particularly in Siberia, follow the religio-cultural practices of shamanism. Some researchers regard Siberia as the heartland of shamanism.

En with hook is a letter of the Cyrillic script. Its form is derived from the Cyrillic letter En (Н н) by adding a hook to the right leg.

Forest Nenets is a Samoyedic language spoken in northern Russia, around the Agan, Pur, Lyamin and Nadym rivers, by the Nenets people. It is closely related to the Tundra Nenets language, and the two are still sometimes seen as simply being dialects of a single Nenets language, despite there being low mutual intelligibility between the two. The next closest relatives are Nganasan and Enets, after them Selkup, and even more distantly the other Uralic languages.

Tundra Nenets is a Uralic language spoken in European Russia and North-Western Siberia. It is the largest and best-preserved language in the Samoyedic group.

Northern Khanty is a Uralic language, frequently considered a dialect of a unified Khanty language, spoken by about 9,000 people. It is the most widely spoken out of all the Khanty languages, the majority composed of 5,000 speakers in the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug. The reason for this discrepancy is that dialects of Northern Khanty have been better preserved in its northern reaches, and the Middle Ob and Kazym dialects are losing favor to Russian. All four dialects have been literary, beginning with the Middle Ob dialects, but shifting to Kazym, and back to Middle Ob, now the most used dialect in writing. The Shuryshkary dialects are also written, primarily due to an administrative division between the two, as the latter is spoken in the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug.