
Waxes are a diverse class of organic compounds that are lipophilic, malleable solids near ambient temperatures. They include higher alkanes and lipids, typically with melting points above about 40 °C (104 °F), melting to give low viscosity liquids. Waxes are insoluble in water but soluble in nonpolar organic solvents such as hexane, benzene and chloroform. Natural waxes of different types are produced by plants and animals and occur in petroleum.
Transesterification is the process of exchanging the organic functional group R″ of an ester with the organic group R' of an alcohol. These reactions are often catalyzed by the addition of an acid or base catalyst. Strong acids catalyze the reaction by donating a proton to the carbonyl group, thus making it a more potent electrophile. Bases catalyze the reaction by removing a proton from the alcohol, thus making it more nucleophilic. The reaction can also be accomplished with the help of enzymes, particularly lipases.

A drying oil is an oil that hardens to a tough, solid film after a period of exposure to air, at room temperature. The oil hardens through a chemical reaction in which the components crosslink by the action of oxygen. Drying oils are a key component of oil paint and some varnishes. Some commonly used drying oils include linseed oil, tung oil, poppy seed oil, perilla oil, castor oil and walnut oil. The use of natural drying oils has declined over the past several decades, as they have been replaced by alkyd resins and other binders.

Ethyl oleate is a fatty acid ester formed by the condensation of oleic acid and ethanol. It is a colorless oil although degraded samples can appear yellow.

Valeric acid or pentanoic acid is a straight-chain alkyl carboxylic acid with the chemical formula CH3(CH2)3COOH. Like other low-molecular-weight carboxylic acids, it has an unpleasant odor. It is found in the perennial flowering plant Valeriana officinalis, from which it gets its name. Its primary use is in the synthesis of its esters. Salts and esters of valeric acid are known as valerates or pentanoates. Volatile esters of valeric acid tend to have pleasant odors and are used in perfumes and cosmetics. Several, including ethyl valerate and pentyl valerate are used as food additives because of their fruity flavors.

Mink oil is an oil used in medical and cosmetic products. It is obtained by the rendering of mink fat which has been removed from pelts bound for the fur industry.

Soybean oil is a vegetable oil extracted from the seeds of the soybean. It is one of the most widely consumed cooking oils and the second most consumed vegetable oil. As a drying oil, processed soybean oil is also used as a base for printing inks and oil paints.
Omega−9 fatty acids are a family of unsaturated fatty acids which have in common a final carbon–carbon double bond in the omega−9 position; that is, the ninth bond from the methyl end of the fatty acid.
Jojoba esters are the hydrogenation or transesterification product of Jojoba oil. Jojoba Esters are commonly used in cosmetic formulations as an emollient, due to its remarkable similarity to the natural oils produced by the human skin, and its high oxidative stability. Fully hydrogenated jojoba esters are most often small beads used to exfoliate the skin.

Monoglycerides are a class of glycerides which are composed of a molecule of glycerol linked to a fatty acid via an ester bond. As glycerol contains both primary and secondary alcohol groups two different types of monoglycerides may be formed; 1-monoacylglycerols where the fatty acid is attached to a primary alcohol, or a 2-monoacylglycerols where the fatty acid is attached to the secondary alcohol.
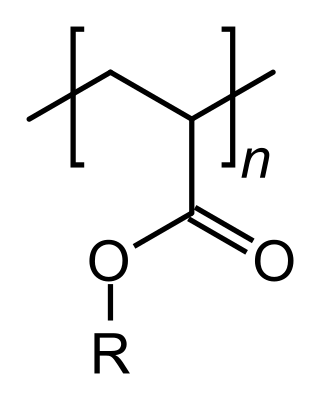
An acrylate polymer is any of a group of polymers prepared from acrylate monomers. These plastics are noted for their transparency, resistance to breakage, and elasticity.

Macadamia oil, also known as macadamia nut oil, is a non-volatile oil extracted from the nuts of the macadamia tree, indigenous to Australia. This oil is used in culinary applications as a frying or salad oil, and in cosmetics for its emollient properties and as a fragrance fixative.
A hydrolyzed jojoba ester (HJE) is the hydrolysate of jojoba ester derived by acid, enzyme or other method of hydrolysis. Hydrolyzed jojoba esters are commonly used in cosmetic formulations.
Ethylhexyl palmitate, also known as octyl palmitate, is the fatty acid ester derived from 2-ethylhexanol and palmitic acid. It is frequently utilized in cosmetic formulations.

Omega-3-acid ethyl esters are a mixture of ethyl eicosapentaenoic acid and ethyl docosahexaenoic acid, which are ethyl esters of the omega−3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) found in fish oil. Together with dietary changes, they are used to treat high blood triglycerides which may reduce the risk of pancreatitis. They are generally less preferred than statins, and use is not recommended by NHS Scotland as the evidence does not support a decreased risk of heart disease. Omega-3-acid ethyl esters are taken by mouth.
Chill filtering is a method in whisky making for removing residue. In chill filtering, whisky is cooled to between 5–10 °C (41–50 °F) and passed through a fine adsorption filter. This is done mostly for cosmetic reasons — to remove cloudiness — however by many whisky drinkers it is thought to impair the taste by removing the details which differentiate between the many distilleries. It is only necessary for whisky that's bottled below 46.3% percent alcohol, as the cloudiness does not occur at or above this concentration.
Omega−7 fatty acids are a class of unsaturated fatty acids in which the site of unsaturation is seven carbon atoms from the end of the carbon chain.
Omega−3-carboxylic acids (Epanova) is a formerly marketed yet still not a Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved prescription medication–since taken off market by the manufacturer–used alongside a low fat and low cholesterol diet that lowers high triglyceride (fat) levels in adults with very high levels. This was the third class of fish oil-based drug, after omega−3-acid ethyl esters and ethyl eicosapentaenoic acid (Vascepa), to be approved for use as a drug. The first approval in the United States by the FDA was granted 05 May 2014. These fish oil drugs are similar to fish oil dietary supplements, but the ingredients are better controlled and have been tested in clinical trials. Specifically, Epanova contained at least 850 mg omega−3-acid ethyl esters per 1 g capsule.

Sucrose esters or sucrose fatty acid esters are a group of non-naturally occurring surfactants chemically synthesized from the esterification of sucrose and fatty acids. This group of substances is remarkable for the wide range of hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB) that it covers. The polar sucrose moiety serves as a hydrophilic end of the molecule, while the long fatty acid chain serves as a lipophilic end of the molecule. Due to this amphipathic property, sucrose esters act as emulsifiers; i.e., they have the ability to bind both water and oil simultaneously. Depending on the HLB value, some can be used as water-in-oil emulsifiers, and some as oil-in-water emulsifiers. Sucrose esters are used in cosmetics, food preservatives, food additives, and other products. A class of sucrose esters with highly substituted hydroxyl groups, olestra, is also used as a fat replacer in food.











