Related Research Articles

Bioinformatics is an interdisciplinary field of science that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data, especially when the data sets are large and complex. Bioinformatics uses biology, chemistry, physics, computer science, computer programming, information engineering, mathematics and statistics to analyze and interpret biological data. The subsequent process of analyzing and interpreting data is referred to as computational biology.
A mathematical model is an abstract description of a concrete system using mathematical concepts and language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed mathematical modeling. Mathematical models are used in applied mathematics and in the natural sciences and engineering disciplines, as well as in non-physical systems such as the social sciences. It can also be taught as a subject in its own right.
Data mining is the process of extracting and discovering patterns in large data sets involving methods at the intersection of machine learning, statistics, and database systems. Data mining is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and statistics with an overall goal of extracting information from a data set and transforming the information into a comprehensible structure for further use. Data mining is the analysis step of the "knowledge discovery in databases" process, or KDD. Aside from the raw analysis step, it also involves database and data management aspects, data pre-processing, model and inference considerations, interestingness metrics, complexity considerations, post-processing of discovered structures, visualization, and online updating.

Computational biology refers to the use of data analysis, mathematical modeling and computational simulations to understand biological systems and relationships. An intersection of computer science, biology, and big data, the field also has foundations in applied mathematics, chemistry, and genetics. It differs from biological computing, a subfield of computer science and engineering which uses bioengineering to build computers.
Computer science is the study of the theoretical foundations of information and computation and their implementation and application in computer systems. One well known subject classification system for computer science is the ACM Computing Classification System devised by the Association for Computing Machinery.

SPSS Statistics is a statistical software suite developed by IBM for data management, advanced analytics, multivariate analysis, business intelligence, and criminal investigation. Long produced by SPSS Inc., it was acquired by IBM in 2009. Versions of the software released since 2015 have the brand name IBM SPSS Statistics.
A scientific theory is an explanation of an aspect of the natural world and universe that can be repeatedly tested and corroborated in accordance with the scientific method, using accepted protocols of observation, measurement, and evaluation of results. Where possible, some theories are tested under controlled conditions in an experiment. In circumstances not amenable to experimental testing, theories are evaluated through principles of abductive reasoning. Established scientific theories have withstood rigorous scrutiny and embody scientific knowledge.

Computer simulation is the process of mathematical modelling, performed on a computer, which is designed to predict the behaviour of, or the outcome of, a real-world or physical system. The reliability of some mathematical models can be determined by comparing their results to the real-world outcomes they aim to predict. Computer simulations have become a useful tool for the mathematical modeling of many natural systems in physics, astrophysics, climatology, chemistry, biology and manufacturing, as well as human systems in economics, psychology, social science, health care and engineering. Simulation of a system is represented as the running of the system's model. It can be used to explore and gain new insights into new technology and to estimate the performance of systems too complex for analytical solutions.
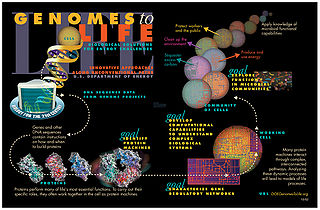
Systems biology is the computational and mathematical analysis and modeling of complex biological systems. It is a biology-based interdisciplinary field of study that focuses on complex interactions within biological systems, using a holistic approach to biological research.
Mathematical and theoretical biology, or biomathematics, is a branch of biology which employs theoretical analysis, mathematical models and abstractions of living organisms to investigate the principles that govern the structure, development and behavior of the systems, as opposed to experimental biology which deals with the conduction of experiments to test scientific theories. The field is sometimes called mathematical biology or biomathematics to stress the mathematical side, or theoretical biology to stress the biological side. Theoretical biology focuses more on the development of theoretical principles for biology while mathematical biology focuses on the use of mathematical tools to study biological systems, even though the two terms are sometimes interchanged.
Computational science, also known as scientific computing, technical computing or scientific computation (SC), is a division of science that uses advanced computing capabilities to understand and solve complex physical problems. This includes
Mathematical software is software used to model, analyze or calculate numeric, symbolic or geometric data.
JMP is a suite of computer programs for statistical analysis and machine learning developed by JMP, a subsidiary of SAS Institute. The program was launched in 1989 to take advantage of the graphical user interface introduced by the Macintosh operating systems. It has since been significantly rewritten and made available for the Windows operating system.

RapidMiner is a data science platform that analyses the collective impact of an organization's data. It was acquired by Altair Engineering in September 2022.
Systems immunology is a research field under systems biology that uses mathematical approaches and computational methods to examine the interactions within cellular and molecular networks of the immune system. The immune system has been thoroughly analyzed as regards to its components and function by using a "reductionist" approach, but its overall function can't be easily predicted by studying the characteristics of its isolated components because they strongly rely on the interactions among these numerous constituents. It focuses on in silico experiments rather than in vivo.

Hod Lipson is an Israeli - American robotics engineer. He is the director of Columbia University's Creative Machines Lab. Lipson's work focuses on evolutionary robotics, design automation, rapid prototyping, artificial life, and creating machines that can demonstrate some aspects of human creativity. His publications have been cited more than 43,000 times, and he has an h-index of 86, as of 12 April 2023. Lipson is interviewed in the 2018 documentary on artificial intelligence Do You Trust This Computer?

A cellular model is a mathematical model of aspects of a biological cell, for the purposes of in silico research.
Rexer Analytics’s Annual Data Miner Survey is the largest survey of data mining, data science, and analytics professionals in the industry. It consists of approximately 50 multiple choice and open-ended questions that cover seven general areas of data mining science and practice: (1) Field and goals, (2) Algorithms, (3) Models, (4) Tools, (5) Technology, (6) Challenges, and (7) Future. It is conducted as a service to the data mining community, and the results are usually announced at the PAW conferences and shared via freely available summary reports. In the 2013 survey, 1259 data miners from 75 countries participated. After 2011, Rexer Analytics moved to a biannual schedule.
Virtual Cell (VCell) is an open-source software platform for modeling and simulation of living organisms, primarily cells. It has been designed to be a tool for a wide range of scientists, from experimental cell biologists to theoretical biophysicists.

Symbolic regression (SR) is a type of regression analysis that searches the space of mathematical expressions to find the model that best fits a given dataset, both in terms of accuracy and simplicity.
References
- ↑ Piatetsky, Gregory. "Four main languages for Analytics, Data Mining, Data Science". www.kdnuggets.com. KDnuggets. Retrieved 19 May 2016.
- ↑ Keohane, Dennis. "Nutonian - At the Cutting Edge of Technology, Science, and Data Analysis". www.venturefizz.com. VentureFizz. Archived from the original on 2017-01-04. Retrieved 2016-05-19.
- ↑ Regalado, Antonio (August 19, 2014). "35 Innovators Under 35". MIT Technology Review. Retrieved 19 May 2016.
- 1 2 Keim, Brandon (December 3, 2009). "Download Your Own Robot Scientist". Wired Magazine . Retrieved April 22, 2013.
- 1 2 Chang, Kenneth (April 2, 2009). "Hal, Call Your Office: Computers That Act Like Physicists". The New York Times . Retrieved April 22, 2013.
- 1 2 Ehrenberg, Rachel (January 14, 2012). "Software Scientist". Science News Digital. Retrieved April 22, 2013.
- ↑ Manjoo, Farhad (September 30, 2009). "Will Robots Steal Your Job?". Slate . Retrieved April 20, 2013.
- ↑ Shtull-Trauring, Asaf (February 3, 2012). "An Israeli professor's 'Eureqa' moment". Haaretz. Retrieved April 20, 2013.
- ↑ "DataRobot Acquires Nutonian". DataRobot. May 25, 2017. Retrieved December 9, 2023.