Related Research Articles

The economy of Denmark is a modern high-income and mixed economy.

Transport economics is a branch of economics founded in 1959 by American economist John R. Meyer that deals with the allocation of resources within the transport sector. It has strong links to civil engineering. Transport economics differs from some other branches of economics in that the assumption of a spaceless, instantaneous economy does not hold. People and goods flow over networks at certain speeds. Demands peak. Advance ticket purchase is often induced by lower fares. The networks themselves may or may not be competitive. A single trip may require the bundling of services provided by several firms, agencies and modes.

The economy of the European Union is the joint economy of the member states of the European Union (EU). It is the third largest economy in the world in nominal terms, after the United States and China, and the third one in purchasing power parity (PPP) terms, after China and the United States. The European Union's GDP estimated to be around $16.6 trillion (nominal) in 2022 representing around one sixth of the global economy. Germany has by far the biggest national GDP of all EU countries, followed by France and Italy.
Microsimulation is a category of computerized analytical tools that perform analysis of activities such as highway traffic flowing through an intersection, financial transactions, or pathogens spreading disease through a population on the granularity level of individuals. Synonyms include microanalytic simulation and microscopic simulation. Microsimulation, with its emphasis on stochastic or rule-based structures, should not be confused with the similar complementary technique of multi-agent simulation, which focuses more on the behaviour of individuals.

Environmental policy is the commitment of an organization or government to the laws, regulations, and other policy mechanisms concerning environmental issues. These issues generally include air and water pollution, waste management, ecosystem management, maintenance of biodiversity, the management of natural resources, wildlife and endangered species. For example, concerning environmental policy, the implementation of an eco-energy-oriented policy at a global level to address the issues of global warming and climate changes could be addressed. Policies concerning energy or regulation of toxic substances including pesticides and many types of industrial waste are part of the topic of environmental policy. This policy can be deliberately taken to influence human activities and thereby prevent undesirable effects on the biophysical environment and natural resources, as well as to make sure that changes in the environment do not have unacceptable effects on humans.

Poverty is measured in different ways by different bodies, both governmental and nongovernmental. Measurements can be absolute, which references a single standard, or relative, which is dependent on context. Poverty is widely understood to be multidimensional, comprising social, natural and economic factors situated within wider socio-political processes. The capabilities approach argues that capturing the perceptions of poor people is fundamental to understanding poverty.
A tax-benefit model is a form of microsimulation model. It is usually based on a representative or administrative data set and certain policy rules. These models are used to cost certain policy reforms and to determine the winners and losers of reform. One example is EUROMOD, which models taxes and benefits for 27 EU states, and its post-Brexit offshoot, UKMOD.
The Policy Simulation Model (PSM) is a static microsimulation model which encapsulates the tax and benefits system, and population, of Great Britain. It is based on survey data from the Family Resources Survey (FRS) which is uprated to simulate the current year, together with several years into the future through a process of static uprating. The uprating process covers a complex range of processes, ranging from simple numerical uprating of financial values, to modelling the draw-down of old benefits through to the implications of the rising state pension age.
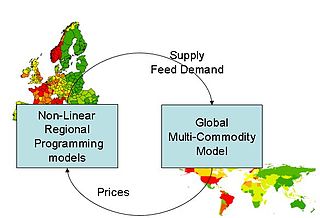
The CAPRI model is a tool for ex-ante impact assessment of agricultural and international trade policies with a focus on the European Union. As an economic partial comparative static equilibrium model for agriculture, its core consists of two interlinked modules: the supply module, covering about 280 regional aggregate programming models covering the EU27, Norway and Western Balkans at the NUTS 2 level and the market module, a global spatial multi-commodity model for about 50 agricultural commodities, which together allow calculation of a wide range of economic and environmental indicators. A spatial downscaling component allows impact assessment at the 1x1 km grid level for EU27. CAPRI is written in GAMS and steered by a Graphical User Interface realized in Java.
The European social model is a concept that emerged in the discussion of economic globalization and typically contrasts the degree of employment regulation and social protection in European countries to conditions in the United States. It is commonly cited in policy debates in the European Union, including by representatives of both labour unions and employers, to connote broadly "the conviction that economic progress and social progress are inseparable" and that "[c]ompetitiveness and solidarity have both been taken into account in building a successful Europe for the future".

Redistribution of income and wealth is the transfer of income and wealth from some individuals to others through a social mechanism such as taxation, welfare, public services, land reform, monetary policies, confiscation, divorce or tort law. The term typically refers to redistribution on an economy-wide basis rather than between selected individuals.
Wainer Lusoli is an Italian academic, trained as a political scientist and policy analyst. He has worked on policy areas including science policy, open science, science in society, political participation, electronic democracy, digital identity, social computing and cloud computing.
The Survey on Household Income and Wealth (SHIW) is a statistical survey conducted by the Sample Surveys Division of the Banca d'Italia . The main objective of the SHIW is to study the economic behaviours of Italian households. In recent years the survey has been integrated in international research projects such as the Luxembourg Income Study and the Luxembourg Wealth Study, whose aim is to produce a comparable cross-national Data Archive on household income and wealth. Starting from 2008, the survey has also been part of a project conducted by the European Central Bank to produce a harmonized survey on household finances and consumption in the Euro area.
TARKI Social Research Institute is an independent research centre located in Budapest, Hungary. TARKI conducts applied socioeconomic research in social stratification, labour markets, income distribution, intergenerational transfers, tax-benefit systems, consumption and lifestyle patterns and attitudes in Hungary and, in the majority of its projects, in Europe. TARKI is closely embedded in international collaborations with major European academic partners in various research projects. Senior staff at TARKI all have PhDs with substantive and methodological interests and many hold professorial appointments at major universities. TARKI has its own fieldwork apparatus, capable of carrying out regular empirical surveys on social structure and on attitudes and of managing large scale international research. TARKI also carries out the Hungarian fieldwork of various high-quality international surveys.
Joachim Merz is a German economist. His research involves welfare economics, income and income distribution, wealth, time utilization, time and income need, taxes, the job market, consumption and socioeconomics, with emphasis on freelancing, self-employment and salaried employment
For pensions, a reliable Pension model is necessary for system simulations and projections, so it is important to have a sound database for pension system analyses. For an example of a complex pension model see e.g..

The Center for Distributive, Labor and Social Studies (CEDLAS) is a research center specialising in distribution, labor and social issues in Latin America.
On 6 May 2015, the European Commission, led at the time by Jean-Claude Juncker, established the Digital Single Market strategy, intended to remove virtual borders, boost digital connectivity, and make it easier for consumers to access cross-border online content across the European Union. The Digital Single Market, which is one of the Commission's 10 political priorities, aims to fit the EU's single market for the digital age, moving from 28 national digital markets to a single one, and then opening up digital services to all citizens and strengthen business competitiveness in the digital economy. In other words, the Digital Single Market is a market characterized by ensuring the free movement of people, services and capital and allowing individuals and businesses to seamlessly access and engage in online activities irrespective of their nationality or place of residence. Fair competition conditions and a high level of protection of personal and consumer data are applied.
The Microdata Information System (MISSY) is a database-driven online system that provides structured metadata about selected research data of official statistics free of charge as part of the service infrastructure of the German Microdata Lab (GML) at GESIS – Leibniz Institute for the Social Sciences. MISSY is targeted at empirically working scientists who use official microdata for their research.

SOUTHMOD is a collection of tax-benefit models for countries in the Global South, maintained and managed by the United Nations University World Institute for Development Economics Research (UNU-WIDER) and partners. It belongs to the class of static microsimulation models and currently has modules for seven countries in Africa, four in Latin America, and one in Southeast Asia (Vietnam). The models are freely available for non-commercial research use.
References
- ↑ "Institute for Social and Economic Research (ISER)". Iser.essex.ac.uk. Retrieved 2023-01-02.
- ↑ "Welcome to EUROMOD Website | EUROMOD - Tax-benefit microsimulation model for the European Union". Euromod-web.jrc.ec.europa.eu. 2022-12-14. Retrieved 2023-01-02.
- ↑ "Extended functionalities | EUROMOD - Tax-benefit microsimulation model for the European Union".
- ↑ "What is EUROMOD? | EUROMOD - Tax-benefit microsimulation model for the European Union".
- ↑ "What is EUROMOD? | EUROMOD - Tax-benefit microsimulation model for the European Union".
- ↑ "Access EUROMOD | EUROMOD - Tax-benefit microsimulation model for the European Union".
- ↑ "Access EUROMOD | EUROMOD - Tax-benefit microsimulation model for the European Union".
- ↑ "EUROMOD-JRC Interface | EUROMOD - Tax-benefit microsimulation model for the European Union".
- ↑ "Home".
- ↑ "Home".
- ↑ "Home".
- ↑ "Home".