
Citizen participation or public participation in social science refers to different mechanisms for the public to express opinions—and ideally exert influence—regarding political, economic, management or other social decisions. Participatory decision-making can take place along any realm of human social activity, including economic, political, management, cultural or familial.
Governance is the overall complex system or framework of processes, functions, structures, rules, laws and norms born out of the relationships, interactions, powerdynamics, cultures and communication within an organized group of individuals which not only sets the boundaries of acceptable conduct and practices of different actors of the group and controls their decision-making processes through the creation and enforcement of rules and guidelines, but also manages, allocates and mobilizes relevant resources and capacities of different members and sets the overall direction of the group in order to effectively address its specific collective needs, problems and challenges. The concept of governance can be applied to social, political or economic entities such as a state and its government, a governed territory, a society, a community, a social group, a formal or informal organization, a corporation, a non-governmental organization, a non-profit organization, a project team, a market, a network or even the global stage. "Governance" can also pertain to a specific sector of activities such as land, environment, health, internet, security, etc. The degree of formality in governance depends on the internal rules of a given entity and its external interactions with similar entities. As such, governance may take many forms, driven by many different motivations and with many different results.

The AEGEE, or Association des États Généraux des Étudiants de l'Europe, known as European Students' Forum in English, is the largest transnational, interdisciplinary student organisation in Europe.
A supranational union is a type of international organization and political union that is empowered to directly exercise some of the powers and functions otherwise reserved to states. A supranational organization involves a greater transfer of or limitation of state sovereignty than other kinds of international organizations.

The European Trade Union Confederation (ETUC) is the major trade union organisation representing workers at the European level. In its role as a European social partner, the ETUC works both in a consulting role with the European Commission and negotiates agreements and work programmes with European employers. It coordinates the national and sectoral policies of its affiliates on social and economic matters, particularly in the framework of the EU institutional processes, including European economic governance and the EU Semester.
Public participation, also known as citizen participation or patient and public involvement, is the inclusion of the public in the activities of any organization or project. Public participation is similar to but more inclusive than stakeholder engagement.

The Council of European Municipalities and Regions (CEMR) is the largest organisation of local and regional governments in Europe. Its members are 60 national associations of towns, municipalities and regions from 41 countries that are part of the Council of Europe. Together these associations represent about 130,000 local and regional authorities.

The Congress of Local and Regional Authorities is the pan-European political assembly representing local and regional authorities from the forty-six member states of the Council of Europe. Its role is to promote local and regional democracy, improve local and regional governance and strengthen authorities' self-government, according to the principles laid down in the European Charter of Local Self-Government. It is made up of two chambers, the Chamber of Local Authorities and the Chamber of Regions and holds its plenary sessions twice a year at the Palace of Europe in Strasbourg, where its permanent Secretariat is located.

The Directorate-General for International Partnerships is the European Commission department responsible for international development policy. It operates under the authority of the European Commissioner for International Partnerships, currently Jutta Urpilainen.

The North–South Centre, officially the European Centre for Global Interdependence and Solidarity, is a Partial Agreement of the Council of Europe, the oldest political organisation of European states.

The Eastern Partnership (EaP) is a joint initiative of the European Union, together with its member states, and six Eastern European countries. The EaP framework governs the EU's relationship with the post-Soviet states of Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belarus, Georgia, Moldova, and Ukraine. The EaP is intended to provide a forum for discussions regarding trade, economic strategy, travel agreements, and other issues between the EU and its Eastern European neighbours. It also aims at building a common area of shared values of democracy, prosperity, stability, and increased cooperation. The project was initiated by Poland and a subsequent proposal was prepared in co-operation with Sweden. It was presented by the foreign ministers of Poland and Sweden at the EU's General Affairs and External Relations Council in Brussels on 26 May 2008. The Eastern Partnership was inaugurated by the EU in Prague, Czech Republic on 7 May 2009.
A resident welfare association is a Non-governmental organization that represents the interests of the residents of a specific urban or suburban locality, particularly in Indian cities.
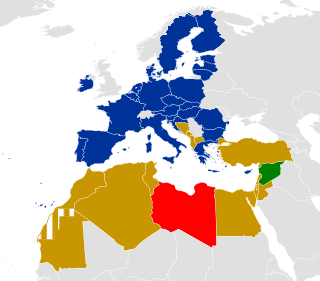
The Union for the Mediterranean is an intergovernmental organization of 43 member states from Europe and the Mediterranean Basin: the 27 EU member states and 16 Mediterranean partner countries from North Africa, Western Asia and Southern Europe. It was founded on 13 July 2008 at the Paris Summit for the Mediterranean, with an aim of reinforcing the Euro-Mediterranean Partnership (Euromed) that was set up in 1995 as the Barcelona Process. Its general secretariat is located in Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain.
The Network of Associations of Local Authorities of South-East Europe or (NALAS) was created in 2001 to enhance the process of democratization and decentralization in south-east Europe. It is currently made up of national associations of local authorities in the region.
Type II partnerships were developed at the Johannesburg World Summit on Sustainable Development in 2002. Arising in opposition to the state-centred eco-governmentality of previous approaches to sustainable development policy, the partnerships facilitate the inclusion of private and civil actors into the management of sustainable development. The partnerships are employed alongside traditional intergovernmental mechanisms in order to effectively implement the United Nations' Agenda 21 and Millennium Development Goals, particularly at sub-national level. Although widely acknowledged as one of the most innovative and effective developments in global environmental governance in recent years, the partnerships have faced criticism due to fears of a lack of accountability, and the risk that they may exacerbate inequalities of power between Northern and Southern states. Despite these reservations, there is a general consensus among state and non-governmental actors that Type II partnerships are a significantly progressive step in global environmental governance in general, and sustainable development discourse in particular.
Multistakeholder governance is a practice of governance that employs bringing multiple stakeholders together to participate in dialogue, decision making, and implementation of responses to jointly perceived problems. The principle behind such a structure is that if enough input is provided by multiple types of actors involved in a question, the eventual consensual decision gains more legitimacy, and can be more effectively implemented than a traditional state-based response. While the evolution of multistakeholder governance is occurring principally at the international level, public-private partnerships (PPPs) are domestic analogues.

The community-led local development (CLLD) funding approach is a European Union initiative to support the decentralised management of development projects, primarily in rural, but also in coastal and urban areas, by involving relevant local actors, including local organizations and associations, as well as individual citizens. At first it was limited to the rural areas under the name LEADER. The approach is regularly evaluated, and also discussed widely in academic literature on local economic and social development.
The Local Authorities as Drivers for Development Education and Raising-Awareness Project or LADDER Project, was launched by the European Association for Local Democracy, in 2015 with the objective of develop and increase the action of Local Authorities in European Union policies of Development Education and Awareness Raising (DEAR). The associates of this project work with education and awareness raising as a tool to trigger and foster the process of a resilient, sustainable development through a peaceful and democratic way.

The European Partnership for Democracy (EPD) is a membership-based network of not-for-profit organisations that describes its aim as "supporting democracy around the world".

Nataša Vučković is a Serbian politician. She has led Serbia's Center for Democracy Foundation since 1994 and was a Democratic Party (DS) member of the Serbian parliament from 2007 to 2020. She left the DS in September 2020 and is no longer active with any political party.













