
Metrology is the scientific study of measurement. It establishes a common understanding of units, crucial in linking human activities. Modern metrology has its roots in the French Revolution's political motivation to standardise units in France when a length standard taken from a natural source was proposed. This led to the creation of the decimal-based metric system in 1795, establishing a set of standards for other types of measurements. Several other countries adopted the metric system between 1795 and 1875; to ensure conformity between the countries, the Bureau International des Poids et Mesures (BIPM) was established by the Metre Convention. This has evolved into the International System of Units (SI) as a result of a resolution at the 11th General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) in 1960.
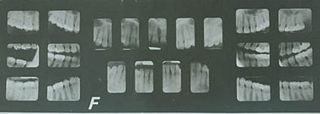
Forensic dentistry or forensic odontology involves the handling, examination, and evaluation of dental evidence in a criminal justice context. Forensic dentistry is used in both criminal and civil law. Forensic dentists assist investigative agencies in identifying human remains, particularly in cases when identifying information is otherwise scarce or nonexistent—for instance, identifying burn victims by consulting the victim's dental records. Forensic dentists may also be asked to assist in determining the age, race, occupation, previous dental history, and socioeconomic status of unidentified human beings.

In forensic science, questioned document examination (QDE) is the examination of documents potentially disputed in a court of law. Its primary purpose is to provide evidence about a suspicious or questionable document using scientific processes and methods. Evidence might include alterations, the chain of possession, damage to the document, forgery, origin, authenticity, or other questions that come up when a document is challenged in court.

Trace evidence occurs when objects make contact, and material is transferred. This type of evidence is usually not visible to the naked eye and requires specific tools and techniques to be located and obtained. Due to this, trace evidence is often overlooked, and investigators must be trained to detect it. When it comes to an investigation trace evidence can come in many different forms and is found in a wide variety of cases. This evidence can link a victim to suspects and a victim or suspect to the crime scene.
Since the early 1990s, American and International forensic science laboratories and practitioners have collaborated in Scientific Working Groups (SWGs) to improve discipline practices and build consensus standards. In 2014, the SWGs are being reorganized under the NIST Organization for Scientific Area Committees (OSAC).

Gunshot residue (GSR), also known as cartridge discharge residue (CDR), gunfire residue (GFR), or firearm discharge residue (FDR), consists of all of the particles that are expelled from the muzzle of a gun following the discharge of a bullet. It is principally composed of burnt and unburnt particles from the explosive primer, the propellant (gunpowder), stabilisers and other additives. The act of firing a bullet incites a highly pressurised, explosive reaction that is contained within the barrel of the firearm, which expels the bullet. This can cause the bullet, the barrel, or the cartridge to become damaged, meaning gunshot residue may also included metallic particles from the cartridge casing, the bullet jacket, as well as any other dirt or residue contained within the barrel that could have become dislodged.

The Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences (CIOMS) is an international non-governmental organization of 40 international, national, and associate member groups representing the biomedical science community. It was jointly established by the World Health Organization (WHO) and United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) in 1949 as a successor to the International Medical Congress that organized 17 conferences from 1867 until the 1913 outbreak of World War One.

Digital forensics is a branch of forensic science encompassing the recovery, investigation, examination, and analysis of material found in digital devices, often in relation to mobile devices and computer crime. The term "digital forensics" was originally used as a synonym for computer forensics but has expanded to cover investigation of all devices capable of storing digital data. With roots in the personal computing revolution of the late 1970s and early 1980s, the discipline evolved in a haphazard manner during the 1990s, and it was not until the early 21st century that national policies emerged.

Forensic video analysis is the scientific examination, comparison and/or evaluation of video in legal matters.

Fire investigation, sometimes referred to as origin and cause investigation, is the analysis of fire-related incidents. After firefighters extinguish a fire, an investigation is launched to determine the origin and cause of the fire or explosion. These investigations can occur in two stages. The first stage is an investigation of the scene of the fire to establish its origin and cause. The second step is to conduct laboratory examination on the retrieved samples. Investigations of such incidents require a systematic approach and knowledge of fire science.

The Health Sciences Authority (HSA) is a statutory board under the Ministry of Health of the Government of Singapore. It is a multi-disciplinary agency responsible for applying medical, pharmaceutical, and scientific expertise to protect and advance public health and safety.
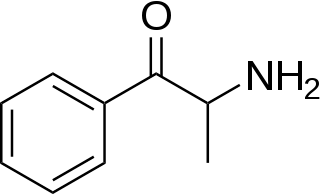
Substituted cathinones, which include some stimulants and entactogens, are derivatives of cathinone. They feature a phenethylamine core with an alkyl group attached to the alpha carbon, and a ketone group attached to the beta carbon, along with additional substitutions. Cathinone occurs naturally in the plant khat whose leaves are chewed as a recreational drug.
The Scientific Working Group on Imaging Technology was convened by the Federal Bureau of Investigation in 1997 to provide guidance to law enforcement agencies and others in the criminal justice system regarding the best practices for photography, videography, and video and image analysis. This group was terminated in 2015.
Forensic metrology is a branch of metrology applied to forensic sciences. Metrology has evolved various techniques for assessing the margin of error or uncertainty associated with measurements. Forensic laboratories and criminalistic laboratories perform numerous measurements and tests to support criminal prosecution and civil legal actions. Examples of forensic metrology include the measurement of alcohol content in blood using breathalyzers, quantification of controlled substances, and length measurements of firearm barrels. The results of forensic measurements are used to determine if a person is charged with a crime or may be used to determine a statutory sentencing enhancement. Other examples of forensic metrology includes tests that measure if there is a presence of a substance, latent print examination, questioned documents examination, and DNA analysis.

Hugh Berryman is a U.S. forensic anthropologist with areas of expertise in blunt force trauma, skeletal remains, and osteology. He is one of only three forensic anthropologists in the state of Tennessee and seventy-four in the nation certified by the American Board of Forensic Anthropology. Additionally, he has received two awards offered by the American Academy of Forensic Sciences (AAFS): the Ellis R. Kerley Award in 2008 and the T. Dale Stewart lifetime achievement award in 2012. Due to his areas of expertise and qualifications, his assistance has been sought by local, state, and federal authorities as well as private interests.

The Harris County Institute of Forensic Sciences is a science-based, independent operation consisting of two distinct forensic services for the Harris County community – the Medical Examiner Service and the Crime Laboratory Service. The institute is located in Houston, Texas. The institute is a part of the Texas Medical Center.

The International Society for Forensic Genetics – ISFG is an international non-profit scientific society founded in 1968. The main goal of the society is to advance the field of forensic genetics, also termed DNA profiling, through dissemination of scientific results and opinions, communication amongst scientists and education. The bi-annual international ISFG congresses, international workshops and seminars, the society’s scientific journal, and the scientific recommendations on current topics all work towards this goal. The society’s website contains up to date information on all activities.
The Scientific Working Group on Digital Evidence (SWGDE) is a group that brings together law enforcement, academic, and commercial organizations actively engaged in the field of digital forensics to develop cross-disciplinary guidelines and standards for the recovery, preservation, and examination of digital evidence. It was supported by the United States Federal Bureau of Investigation, but after 2014 is under the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
The European Federation of Organisations for Medical Physics (EFOMP) was founded in May 1980 in London to serve as an umbrella organisation representing the national Medical Physics societies in Europe. The office moved to Utrecht in January 2021. It is a non-profit organisation and aims to foster and coordinate the activities of its national member organisations, encourage exchange and dissemination of professional and scientific information, develop guidelines for education, training and accreditation programmes and to make recommendations on the responsibilities, organisational relationships and roles of medical physicists.

Forensic colorimetry, or forensic color analysis, is the examination of specimen color for purposes of forensic investigation. Typical specimens involved in color analyses include pigments, dyes, or other objects that are distinguishable by their intrinsic color. Analyses may be conducted by-eye or by computational methods, both by matching specimen colors to a standardised chart or database.













