Related Research Articles

Arianespace SA is a French company founded in March 1980 as the world's first commercial launch service provider. It operates two launch vehicles: Vega C, a small-lift rocket, and Ariane 6, a medium-to-heavy-lift rocket. Arianespace is a subsidiary of ArianeGroup, a joint venture between Airbus and Safran.

Galileo is a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) that went live in 2016, created by the European Union through the European Space Agency (ESA), operated by the European Union Agency for the Space Programme (EUSPA), headquartered in Prague, Czechia, with two ground operations centres in Oberpfaffenhofen, Germany, mostly responsible for the control of the satellites, and in Fucino, Italy, mostly responsible for providing the navigation data. The €10 billion project is named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei.

The BeiDou Navigation Satellite System is a satellite-based radio navigation system owned and operated by the China National Space Administration. It provides geolocation and time information to a BDS receiver anywhere on or near the Earth where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more BDS satellites. It does not require the user to transmit any data, and operates independently of any telephonic or Internet reception, though these technologies can enhance the usefulness of the BDS positioning information.

The State Space Agency of Ukraine is the Ukrainian government agency responsible for space policy and programs. It was formed on 29 February 1992, and was based on the Soviet space program infrastructure that remained in Ukraine following the dissolution of the Soviet Union. It was called the National Space Agency of Ukraine until 9 December 2010.

A satellite navigation or satnav system is a system that uses satellites to provide autonomous geopositioning. A satellite navigation system with global coverage is termed global navigation satellite system (GNSS). As of 2024, four global systems are operational: the United States's Global Positioning System (GPS), Russia's Global Navigation Satellite System (GLONASS), China's BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS), and the European Union's Galileo.
Surrey Satellite Technology Ltd, or SSTL, is a company involved in the manufacture and operation of small satellites. A spin-off company of the University of Surrey, it is presently wholly owned by Airbus Defence and Space.

OHB SE, headquartered in Bremen, is a European space and technology group specializing in the development and implementation of complete space systems, the production of components for various launcher programs as well as the operation of satellite systems and the processing and provision of the data collected. The company employs over 3,000 people at 15 locations in ten countries, most of them in Europe.
GIOVE, or Galileo In-Orbit Validation Element, is the name for two satellites built for the European Space Agency (ESA) to test technology in orbit for the Galileo positioning system.

The Quasi-Zenith Satellite System (QZSS), also known as Michibiki (みちびき), is a four-satellite regional satellite navigation system and a satellite-based augmentation system developed by the Japanese government to enhance the United States-operated Global Positioning System (GPS) in the Asia-Oceania regions, with a focus on Japan. The goal of QZSS is to provide highly precise and stable positioning services in the Asia-Oceania region, compatible with GPS. Four-satellite QZSS services were available on a trial basis as of 12 January 2018, and officially started on 1 November 2018. A satellite navigation system independent of GPS is planned for 2023 with seven satellites. In May 2023 it was announced that the system would expand to eleven satellites.
Launch Services Alliance is a "back-up" launch service provider. It is a joint venture between the multinational aerospace company Arianespace and Japanese conglomerate Mitsubishi Heavy Industries; initially, the American aerospace firm Boeing Launch Services was involved as well.
Telespazio Spa is a European spaceflight services company founded in 1961. It is a joint venture owned by Leonardo (67%) and Thales Group (33%) headquartered in Rome.
Astrium was an aerospace manufacturer subsidiary of the European Aeronautic Defence and Space Company (EADS) that provided civil and military space systems and services from 2006 to 2013. In 2012, Astrium had a turnover of €5.8 billion and 18,000 employees in France, Germany, the United Kingdom, Spain and the Netherlands. Astrium was a member of Institute of Space, its Applications and Technologies.

Thales Alenia Space is a joint venture between the French technology corporation Thales Group (67%) and Italian defense conglomerate Leonardo (33%). The company is headquartered in Cannes, France.
The European Union Space Programme is an EU funding programme established in 2021 along with its managing agency, the European Union Agency for the Space Programme, in order to implement the pre-existing European Space Policy established on 22 May 2007 when a joint and concomitant meeting at the ministerial level of the Council of the European Union and the Council of the European Space Agency, known collectively as the European Space Council, adopted a Resolution on the European Space Policy. The policy had been jointly drafted by the European Commission and the Director General of the European Space Agency. This was the first common political framework for space activities established by the European Union (EU).

GMV, founded in 1984, is a Spanish private capital business group with an international presence and more than 3300 workers. In its early days, it focused on the space and defense sectors, being the contract for the European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) the beginning of its growth. Over the years it has diversified its operations and expanded into other fields becoming today's technology group, which comprises 11 areas of specialization: Space, Aeronautics, Defense and Security, Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS), Automotive, Cybersecurity, Healthcare, and Digital Public Services, Industry, Financial sector, and Services.
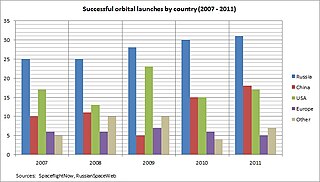
Russia's space industry comprises more than 100 companies and employs 250,000 people. Most of the companies are descendants of Soviet design bureaux and state production companies. The industry entered a deep crisis following the dissolution of the Soviet Union, with its fullest effect occurring in the last years of the 1990s. Funding of the space program declined by 80% and the industry lost a large part of its work force before recovery began in the early 2000s. Many companies survived by creating joint-ventures with foreign firms and marketing their products abroad.
Telespazio UK Ltd. is a British space company based in Luton, Bedfordshire. Founded in 1978 by a small group of engineers at the European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) in Darmstadt, Germany, VEGA presently works with various space agencies, satellite operators and manufacturers around the world. It works with the European Space Agency (ESA) and ESOC in Germany, European Space Research and Technology Centre (ESTEC) in Noordwijk, the Netherlands, ESA Centre for Earth Observation (ESRIN) in Rome, Italy, and European Space Astronomy Centre (ESAC) in Madrid, Spain.

Soyuz at the Guiana Space Centre was a European Space Agency (ESA) programme that operated Soyuz-2 launch vehicles at the Guiana Space Centre (CSG). It provided Arianespace with a medium-lift launch vehicle alongside the light-lift Vega and heavy-lift Ariane 5. The rocket was marketed by Starsem a joint venture of ArianeGroup, Arianespace, Progress Rocket Space Centre and Roscosmos.

The Directorate-General for Defence Industry and Space is a department of the European Commission.
The United Kingdom Global Navigation Satellite System was a United Kingdom Space Agency (UKSA) research programme which, between May 2018 and September 2020, developed outline proposals for a United Kingdom (UK) owned and operated conventional satellite navigation system, as a British alternative to the European Union (EU) owned and operated Galileo Global Navigation Satellite System. The main reason was to provide a national and independent system, to ensure UK security following its withdrawal from the EU as a result of Brexit. It was fully supported by the Ministry of Defence.
References
- ↑ GIOVE-A2 to secure the Galileo programme, European Space Agency press release, 5 March 2007.
- ↑ Galileo navigation satellite provider to be dismantled, Rob Coppinger, Flight International, 30 November 2007.