Related Research Articles

The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of 27 member states that are located primarily in Europe. The Union has a total area of 4,233,255 km2 (1,634,469 sq mi) and an estimated total population of over 449 million. The EU has often been described as a sui generis political entity combining the characteristics of both a federation and a confederation.

A directive is a legal act of the European Union that requires member states to achieve particular goals without dictating how the member states achieve those goals. A directive's goals have to be made the goals of one or more new or changed national laws by the member states before this legislation applies to individuals residing in the member states. Directives normally leave member states with a certain amount of leeway as to the exact rules to be adopted. Directives can be adopted by means of a variety of legislative procedures depending on their subject matter.

Transport in Europe provides for the movement needs of over 700 million people and associated freight.

In the European Union, competition law promotes the maintenance of competition within the European Single Market by regulating anti-competitive conduct by companies to ensure that they do not create cartels and monopolies that would damage the interests of society.
The freedoms of the air, also called five freedoms of air transport, are a set of commercial aviation rights granting a country's airlines the privilege to enter and land in another country's airspace. They were formulated as a result of disagreements over the extent of aviation liberalisation in the Convention on International Civil Aviation of 1944, known as the Chicago Convention. The United States had called for a standardized set of separate air rights to be negotiated between states, but most other countries were concerned that the size of the U.S. airlines would dominate air travel if there were not strict rules. The freedoms of the air are the fundamental building blocks of the international commercial aviation route network. The use of the terms "freedom" and "right" confers entitlement to operate international air services only within the scope of the multilateral and bilateral treaties that allow them.

The Merchant Marine Act of 1920 is a United States federal statute that provides for the promotion and maintenance of the American merchant marine. Among other purposes, the law regulates maritime commerce in U.S. waters and between U.S. ports. Section 27 of the Merchant Marine Act is known as the Jones Act and deals with cabotage. It requires that all goods transported by water between U.S. ports be carried on ships that have been constructed in the United States and that fly the U.S. flag, are owned by U.S. citizens, and are crewed by U.S. citizens and U.S. permanent residents. The act was introduced by Senator Wesley Jones. The law also defines certain seaman's rights.
Cabotage is the transport of goods or passengers between two places in the same country. The term originally applied to shipping along coastal routes, port to port, but now applies to aviation, railways, and road transport as well.

The Bolkestein directive or Services Directive, officially Services in the Internal Market Directive2006/123/EC, is a European Union law aiming at establishing a single market for services within the European Union (EU). Drafted under the leadership of the former right-wing European Commissioner for Internal Market Frits Bolkestein, it has been popularly referred to by his name. It was seen as an important kick-start to the Lisbon Agenda which, launched in 2000, was an agreed strategy to make the EU "the world's most dynamic and competitive economy" by 2010.

The modern terms short-sea shipping, marine highway and motorways of the sea, as well as the more historical terms coastal trade, coastal shipping, coasting trade and coastwise trade, all encompass the movement of cargo and passengers mainly by sea along a coast, without crossing an ocean.
The European single market, also known as the European internal market or the European common market, is the single market comprising mainly the 27 member states of the European Union (EU). With certain exceptions, it also comprises Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway, and Switzerland. The single market seeks to guarantee the free movement of goods, capital, services, and people, known collectively as the "four freedoms". This is achieved through common rules and standards that all participating states are legally committed to follow.
The freedom of movement for workers is a policy chapter of the acquis communautaire of the European Union. The free movement of workers means that nationals of any member state of the European Union can take up an employment in another member state on the same conditions as the nationals of that particular member state. In particular, no discrimination based on nationality is allowed. It is part of the free movement of persons and one of the four economic freedoms: free movement of goods, services, labour and capital. Article 45 TFEU states that:
- Freedom of movement for workers shall be secured within the Community.
- Such freedom of movement shall entail the abolition of any discrimination based on nationality between workers of the Member States as regards employment, remuneration and other conditions of work and employment.
- It shall entail the right, subject to limitations justified on grounds of public policy, public security or public health:
- The provisions of this article shall not apply to employment in the public service.
Home state regulation is a principle in the law of the European Union for resolving conflict of laws between Member States when dealing with cross-border selling or marketing of goods and services. The principle states that, where an action or service is performed in one country but received in another, the applicable law is the law of the country where the action or service is performed. It is also called home country control, country of origin rule, or country of origin principle. It is one possible rule of EU law, specifically of European Single Market law, that determines which laws will apply to goods or services that cross the border of Member States.
Government procurement or public procurement is undertaken by the public authorities of the European Union (EU) and its member states in order to award contracts for public works and for the purchase of goods and services in accordance with principles derived from the Treaties of the European Union. Such procurement represents 13.6% of EU GDP as of March 2023, and has been the subject of increasing European regulation since the 1970s because of its importance to the European single market.
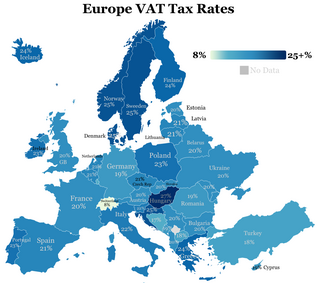
The European Union value-added tax is a value added tax on goods and services within the European Union (EU). The EU's institutions do not collect the tax, but EU member states are each required to adopt in national legislation a value added tax that complies with the EU VAT code. Different rates of VAT apply in different EU member states, ranging from 17% in Luxembourg to 27% in Hungary. The total VAT collected by member states is used as part of the calculation to determine what each state contributes to the EU's budget.
The Erika legislative packages of the European Union are maritime laws intended to improve safety in the shipping industry and thereby reduce environmental damage to the oceans.
European labour law regulates basic transnational standards of employment and partnership at work in the European Union and countries adhering to the European Convention on Human Rights. In setting regulatory floors to competition for job-creating investment within the Union, and in promoting a degree of employee consultation in the workplace, European labour law is viewed as a pillar of the "European social model". Despite wide variation in employment protection and related welfare provision between member states, a contrast is typically drawn with conditions in the United States.

The area of freedom, security and justice (AFSJ) of the European Union (EU) is a policy domain concerning home affairs and migration, justice as well as fundamental rights, developed to address the challenges posed to internal security by collateral effects of the free movement of people and goods in the absence of border controls or customs inspection throughout the Schengen Area, as well as to safeguard adherence to the common European values through ensuring that the fundamental rights of people are respected across the EU.

The Maritime Labour Convention (MLC) is an International Labour Organization (ILO) convention, number 186, established in 2006 as the fourth pillar of international maritime law and embodies "all up-to-date standards of existing international maritime labour Conventions and Recommendations, as well as the fundamental principles to be found in other international labour Conventions". The other pillars are the SOLAS, STCW and MARPOL. The treaties applies to all ships entering the harbours of parties to the treaty (port states), as well as to all ships flying the flag of state party (flag states, as of 2021: over 97 per cent).
Philip Ruttley is an Anglo-Swiss lawyer and published expert in European Union competition (anti-trust) law and international trade law. He has been described as "one of Europe's foremost maritime competition experts".

Directive 2010/63/EU is the European Union (EU) legislation "on the protection of animals used for scientific purposes" and is one of the most stringent ethical and welfare standards worldwide.