Related Research Articles

The Basques are a Southwestern European ethnic group, characterised by the Basque language, a common culture and shared genetic ancestry to the ancient Vascones and Aquitanians. Basques are indigenous to, and primarily inhabit, an area traditionally known as the Basque Country —a region that is located around the western end of the Pyrenees on the coast of the Bay of Biscay and straddles parts of north-central Spain and south-western France.

ETA, an acronym for Euskadi Ta Askatasuna, was an armed Basque nationalist and far-left separatist organization in the Basque Country between 1959 and 2018, with its goal being independence for the region. The group was founded in 1959 during the era of Francoist Spain, and later evolved from a pacifist group promoting traditional Basque culture to a violent paramilitary group. It engaged in a campaign of bombings, assassinations, and kidnappings throughout Spain and especially the Southern Basque Country against the regime, which was highly centralised and hostile to the expression of non-Castilian minority identities. ETA was the main group within the Basque National Liberation Movement and was the most important Basque participant in the Basque conflict.

In Spain, an autonomous community is the first sub-national level of political and administrative division, created in accordance with the Spanish Constitution of 1978, with the aim of guaranteeing limited autonomy of the nationalities and regions that make up Spain.

Navarre, officially the Chartered Community of Navarre, is a landlocked foral autonomous community and province in northern Spain, bordering the Basque Autonomous Community, La Rioja, and Aragon in Spain and Nouvelle-Aquitaine in France. The capital city is Pamplona. The present-day province makes up the majority of the territory of the medieval Kingdom of Navarre, a long-standing Pyrenean kingdom that occupied lands on both sides of the western Pyrenees, with its northernmost part, Lower Navarre, located in the southwest corner of France.

The Spanish language has two names: español and castellano. Spanish speakers from different countries or backgrounds can show a preference for one term or the other, or use them indiscriminately, but political issues or common usage might lead speakers to prefer one term over the other. This article identifies the differences between those terms, the countries or backgrounds that show a preference for one or the other, and the implications the choice of words might have for a native Spanish speaker.
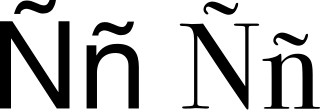
Ñ, or ñ, is a letter of the modern Latin alphabet, formed by placing a tilde on top of an upper- or lower-case N. It became part of the Spanish alphabet in the eighteenth century when it was first formally defined, but it has subsequently been used in other languages, such as Galician, Asturian, the Aragonese Grafía de Uesca, Basque, Chavacano, some Philippine languages, Chamorro, Guarani, Quechua, Mapudungun, Mandinka, Papiamento, and Tetum alphabets, as well as in Latin transliteration of Tocharian and many Indian languages, where it represents or. It represents in Crimean Tatar, Kazakh, ALA-LC romanization for Turkic languages, the Common Turkic Alphabet, Nauruan and romanized Quenya. In Breton and in Rohingya, it denotes nasalization of the preceding vowel.

The Basque Nationalist Party, officially Basque National Party in English, is a Basque nationalist and regionalist political party. The party is located in the centre of the political spectrum.

The Basque Country is the name given to the home of the Basque people. The Basque country is located in the western Pyrenees, straddling the border between France and Spain on the coast of the Bay of Biscay. Euskal Herria is the oldest documented Basque name for the area they inhabit, dating from the 16th century.

The Aquitanian language was the language of the ancient Aquitani, spoken on both sides of the western Pyrenees in ancient Aquitaine and in the areas south of the Pyrenees in the valleys of the Basque Country before the Roman conquest. It probably survived in Aquitania north of the Pyrenees until the Early Middle Ages.

The Basque Country national football team represents the Basque Country in football. It selects players from the Basque Country autonomous community, Navarre and the French Basque Country and is organised by the Basque Football Federation. It is not affiliated with FIFA or UEFA and therefore only allowed to play friendly matches against FIFA or non-FIFA affiliated teams.
Education in Spain is regulated by the Ley Orgánica 8/2013, de 9 de diciembre, para la mejora de la calidad educativa that expands upon Article 27 of the Spanish Constitution of 1978. The Spanish education system is compulsory and free for all children aged between 6 and 16 years and is supported by the national government together with the governments of each of the country's 17 autonomous communities.

Euskal Irrati Telebista is the Basque Autonomous Community's public broadcast service, which broadcasts throughout the Basque Country. Its main brand is Euskal Telebista.

The majority of languages of Spain belong to the Romance language family, of which Spanish is the only language which has official status for the whole country. Those also include Catalan and Galician as well as an additional number of languages and dialects belonging to the Romance language continuum.

Standard Basque is a standardised version of the Basque language, developed by the Basque Language Academy in the late 1960s, which nowadays is the most widely and commonly spoken Basque-language version throughout the Basque Country. Heavily based on the literary tradition of the central areas, it is the version of the language that is commonly used in education at all levels, from elementary school to university, on television and radio, and in the vast majority of all written production in Basque.

Both the perceived nationhood of Spain, and the perceived distinctions between different parts of its territory derive from historical, geographical, linguistic, economic, political, ethnic and social factors.
An ikastola is a type of primary and secondary school in the Basque Autonomous Community, Navarre and the French Basque Country in which pupils are taught either entirely or predominantly in the Basque language. Ikastolak can be nowadays either private or public, divided into different networks.

The Basque Country, also called Basque Autonomous Community, is an autonomous community in northern Spain. It includes the Basque provinces of Álava, Biscay, and Gipuzkoa.

A baserri is a traditional half-timbered or stone-built type of housebarn farmhouse found in the Basque Country in northern Spain and Southwestern France. The baserris, with their gently sloping roofs and entrance portals, are highly characteristic of the region and form a vital part in traditional Basque societal structures. They are also seen to have played an important role in protecting the Basque language in periods of persecution by providing the language with a very dispersed but substantial speaker base.

The Basque conflict, also known as the Spain–ETA conflict, was an armed and political conflict from 1959 to 2011 between Spain and the Basque National Liberation Movement, a group of social and political Basque organizations which sought independence from Spain and France. The movement was built around the separatist organization ETA, which had launched a campaign of attacks against Spanish administrations since 1959. ETA had been proscribed as a terrorist organization by the Spanish, British, French and American authorities at different moments. The conflict took place mostly on Spanish soil, although to a smaller degree it was also present in France, which was primarily used as a safe haven by ETA members. It was the longest running violent conflict in modern Western Europe. It has been sometimes referred to as "Europe's longest war".

Elkarrekin Podemos is a left-wing electoral alliance in the Basque Country formed by Podemos, Ezker Anitza and Equo in August 2016 ahead of the 2016 Basque regional election. The alliance was renewed ahead of the 2020 Basque regional election with the exclusion of Equo, after the party had broken up with the Unidas Podemos nationwide alliance to join Más País in the lead up to the November 2019 Spanish general election.
References
- ↑ Kintana y otros, Xabier (1991). Hiztegia bi mila. San Sebastián: Elkar S.A. ISBN 84-7529-983-0
- ↑ Fernández Vallejo, Marta (12 February 2020). "El aprendizaje del euskera hasta el B2 ya es gratuito en todo Euskadi" (in Spanish). El Correo. Retrieved 5 April 2020.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link)