
A monorail is a railway in which the track consists of a single rail or beam. Colloquially, the term "monorail" is often used to describe any form of elevated rail or people mover. More accurately, the term refers to the style of track. Monorail systems are most frequently implemented in large cities, airports, and theme parks.

A rubber-tyred metro or rubber-tired metro is a form of rapid transit system that uses a mix of road and rail technology. The vehicles have wheels with rubber tires that run on a roll way inside guide bars for traction. Traditional, flanged steel wheels running on rail tracks provide guidance through switches and act as backup if tyres fail. Most rubber-tyred trains are purpose-built and designed for the system on which they operate. Guided buses are sometimes referred to as 'trams on tyres', and compared to rubber-tyred metros.

A railroad switch (AE), turnout, or [set of] points (CE) is a mechanical installation enabling railway trains to be guided from one track to another, such as at a railway junction or where a spur or siding branches off.

In rail transport, a derailment is a type of train wreck that occurs when a rail vehicle such as a train comes off its rails. Although many derailments are minor, all result in temporary disruption of the proper operation of the railway system and they are a potentially serious hazard.
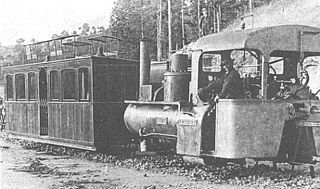
The Lartigue Monorail system was developed by the French engineer Charles Lartigue (1834–1907). He further developed a horse drawn monorail system, which had been invented by Henry Robinson Palmer in 1821.

The Meigs Elevated Railway was an experimental but unsuccessful 19th century elevated steam-powered urban rapid transit system, often described as a monorail but technically pre-electric third rail. It was invented in the US by Josiah Vincent Meigs, of Lowell, Massachusetts, and was demonstrated from 1886 to 1894 in a suburb of Boston called East Cambridge.

An adhesion railway relies on adhesion traction to move the train, and is the most widespread and common type of railway in the world. Adhesion traction is the friction between the drive wheels and the steel rail. Since the vast majority of railways are adhesion railways, the term adhesion railway is used only when it is necessary to distinguish adhesion railways from railways moved by other means, such as by a stationary engine pulling on a cable attached to the cars or by a pinion meshing with a rack.
The term monorail or industrial monorail is used to describe any number of transport systems in which a chair or carrier is suspended from, or rides on, an overhead rail structure. Unlike the well-known duo-rail system, there are many rail-guided transport options which have been described as monorails, so that tracing the history presents a demarcation problem regarding what should be included and what should be omitted.

The National Rail Museum in Chanakyapuri, New Delhi, displays exhibits on the history of rail transport in India. The museum was inaugurated on 1 February 1977. The museum spans over an area of over 4.4 hectares and the indoor gallery comprises an octagonal building which houses six display galleries and a large open area is laid out to simulate the atmosphere of a railway yard. It is open every day except Mondays and national holidays.

A wheelset is a pair of railroad vehicle wheels mounted rigidly on an axle allowing both wheels to rotate together. Wheelsets are often mounted in a bogie – a pivoted frame assembly holding at least two wheelsets – at each end of the vehicle. Most modern freight cars and passenger cars have bogies each with two wheelsets, but three wheelsets are used in bogies of freight cars that carry heavy loads, and three-wheelset bogies are under some passenger cars. Four-wheeled goods wagons that were once near-universal in Europe and Great Britain and their colonies have only two wheelsets; in recent decades such vehicles have become less common as trainloads have become heavier.
William Thorold was a 19th-century millwright, architect and civil engineer in Norwich, Norfolk, England.
0-3-0 is a type of wheel arrangement for a monorail steam locomotive.

In railway engineering, curve resistance is a part of train resistance, namely the additional rolling resistance a train must overcome when travelling on a curved section of track. Curve resistance is typically measured in per mille, with the correct physical unit being Newton per kilo-Newton (N/kN). Older texts still use the wrong unit of kilogram-force per tonne (kgf/t).

Patiala State Monorail Trainways (PSMT) was a unique rail-guided, partially road-borne railway system running in Patiala from 1907 to 1927. PSMT was the second monorail system in India, after the Kundala Valley Railway, near Munnar in Kerala, and the only operational locomotive-hauled railway system built using the Ewing System in the world. The Kundala Valley Railway pre-dated this, also using the Ewing system between 1902 and 1908, although this only used bullocks for haulage. Following the conversion of the Kundala Valley Railway from a monorail to a narrow gauge railway in 1908, PSMT was the only monorail system in India until its closure in 1927. These were the only instances of a monorail train system in India, until the Mumbai Monorail was opened on 2 February 2014.

The minimum railway curve radius is the shortest allowable design radius for the centerline of railway tracks under a particular set of conditions. It has an important bearing on construction costs and operating costs and, in combination with superelevation in the case of train tracks, determines the maximum safe speed of a curve. The minimum radius of a curve is one parameter in the design of railway vehicles as well as trams; monorails and automated guideways are also subject to a minimum radius.

On a roller coaster, the wheel assemblies are the point of contact between the cars carrying the riders and the track rails. They often consist of at least 3 wheels per assembly, but can contain more.
Kundala Valley Railway was the first monorail system in India, later converted to a 2 ft narrow-gauge railway, that operated in Kundala Valley, Munnar of Idukki district in Kerala, India. The railway line had 35 km length.

A railway or railroad is a track on which the vehicle travels over two parallel steel bars, called rails. The rails support and guide the wheels of the vehicles, which are traditionally either trains or trams. Modern light rail is a relatively new innovation which combines aspects of those two modes of transport. However fundamental differences in the track and wheel design are important, especially where trams or light railways and trains have to share a section of track, as sometimes happens in congested areas.

Track geometry is concerned with the properties and relations of points, lines, curves, and surfaces in the three-dimensional positioning of railroad track. The term is also applied to measurements used in design, construction and maintenance of track. Track geometry involves standards, speed limits and other regulations in the areas of track gauge, alignment, elevation, curvature and track surface. Standards are usually separately expressed for horizontal and vertical layouts although track geometry is three-dimensional.

A train wheel or rail wheel is a type of wheel specially designed for use on railway tracks. The wheel acts as a rolling component, typically press fitted onto an axle and mounted directly on a railway carriage or locomotive, or indirectly on a bogie, also called a truck. The powered wheels under the locomotive are called driving wheels. Wheels are initially cast or forged and then heat-treated to have a specific hardness. New wheels are machined using a lathe to a standardized shape, called a profile, before being installed onto an axle. All wheel profiles are regularly checked to ensure proper interaction between the wheel and the rail. Incorrectly profiled wheels and worn wheels can increase rolling resistance, reduce energy efficiency and may even cause a derailment. The International Union of Railways has defined a standard wheel diameter of 920 mm (36 in), although smaller sizes are used in some rapid transit railway systems and on ro-ro carriages.
















