
A monorail is a railway in which the track consists of a single rail or a beam.

Rail transport is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface.

A train is a series of connected vehicles that run along a railway track and transport people or freight. Trains are typically pulled or pushed by locomotives, though some are self-propelled, such as multiple units. Passengers and cargo are carried in railroad cars, also known as wagons. Trains are designed to a certain gauge, or distance between rails. Most trains operate on steel tracks with steel wheels, the low friction of which makes them more efficient than other forms of transport.

Rail transport in India is an important mode of conveyance for people and goods in India. Indian Railways (IR) is the primary operator of rail operations throughout the country. IR is a state-owned organisation of the Ministry of Railways, which historically had its own government budget. Between 2019 and 2020, 22.15 million passengers used the Indian Railways network daily. In the same period, 3.32 million metric tons of freight was also shipped daily on the IR network.

The history of rail transport began in the BCE times. It can be divided into several discrete periods defined by the principal means of track material and motive power used.
Rail terminology is a form of technical terminology. The difference between the American term railroad and the international term railway is the most significant difference in rail terminology. These and other terms have often originated from the parallel development of rail transport systems in different parts of the world. In English-speaking countries outside the United Kingdom, a mixture of US and UK terms may exist.

Indian Railways (IR) is a statutory body under the ownership of the Ministry of Railways, Government of India that operates India's national railway system. It manages the fourth largest national railway system in the world by size, with a total route length of 68,103 km (42,317 mi) as of 31 March 2022. 52,247 km (32,465 mi) or 83% of all the broad-gauge routes are electrified with 25 kV 50 Hz AC electric traction as of 1 April 2022.
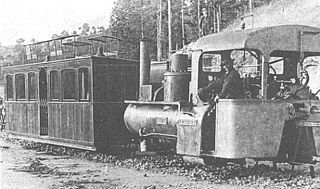
The Lartigue Monorail system was developed by the French engineer Charles Lartigue (1834–1907). He further developed a horse drawn monorail system, which had been invented by Henry Robinson Palmer in 1821.

A transfer table or traverser is a piece of railway equipment. It functions similarly to a turntable, although it cannot be used to turn vehicles around.
The term monorail or industrial monorail is used to describe any number of transport systems in which a chair or carrier is suspended from, or rides on, an overhead rail structure. Unlike the well-known duo-rail system, there are many rail-guided transport options which have been described as monorails, so that tracing the history presents a demarcation problem regarding what should be included and what should be omitted.

The Kalka–Shimla Railway is a 2 ft 6 in narrow-gauge railway in North India which traverses a mostly mountainous route from Kalka to Shimla. It is known for dramatic views of the hills and surrounding villages. The railway was built under the direction of Herbert Septimus Harington between 1898 and 1903 to connect Shimla, the summer capital of India during the British Raj, with the rest of the Indian rail system.
The Indian Railway Service of Mechanical Engineering, abbreviated as IRSME, is one of the group 'A' central engineering services of the Indian railways. The officers of this service are responsible for managing the Mechanical Engineering Division of the Indian Railways. Till 2019, IRSME officers were drawn from the Combined Engineering Service Examination (ESE) conducted by Union Public Service Commission. All appointments to the Group 'A' services are made by the president of India.

The National Rail Museum in Chanakyapuri, New Delhi, displays exhibits on the history of rail transport in India. The museum was inaugurated on 1 February 1977. The museum spans over an area of over 11 acres and the indoor gallery comprises an octagonal building which houses six display galleries and a large open area is laid out to simulate the atmosphere of a railway yard. It is open every day except Mondays and national holidays.
William Thorold was an eminent 19th-century millwright, architect and civil engineer in Norwich, Norfolk, England.
0-3-0 is a type of wheel arrangement for a monorail steam locomotive.

The Ewing System is a balancing monorail system developed in the late 19th century by British inventor W. J. Ewing. It is not to be confused with the much later system patented by Robert W. Ewing.
Colonel Charles William Bowles was a British civil engineer for Patiala State Monorail Trainways commissioned by Maharaja Bhupinder Singh of Patiala.
Kundala Valley Railway was the first monorail system in India, later converted to a 2 ft narrow-gauge railway, that operated in Kundala Valley, Munnar of Idukki district in Kerala, India. The railway line had 35 km length.

The North Western State Railway (NWR) was formed in January 1886 from the merger of the Scinde, Punjab & Delhi Railway, the Indus Valley State Railway, the Punjab Northern State Railway, the eastern section of the Sind–Sagar Railway and the southern section of the Sind–Pishin State Railway and the Kandahar State Railway.

The South African Railways Dutton road-rail tractors of 1923 were road-rail steam tractors.





















