Related Research Articles

Scabies is a contagious skin infestation by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei. The most common symptoms are severe itchiness and a pimple-like rash. Occasionally, tiny burrows may appear on the skin. In a first-ever infection, the infected person will usually develop symptoms within two to six weeks. During a second infection, symptoms may begin within 24 hours. These symptoms can be present across most of the body or just certain areas such as the wrists, between fingers, or along the waistline. The head may be affected, but this is typically only in young children. The itch is often worse at night. Scratching may cause skin breakdown and an additional bacterial infection in the skin.

Leprosy, also known as Hansen's disease (HD), is a long-term infection by the bacteria Mycobacterium leprae or Mycobacterium lepromatosis. Infection can lead to damage of the nerves, respiratory tract, skin, and eyes. This nerve damage may result in a lack of ability to feel pain, which can lead to the loss of parts of a person's extremities from repeated injuries or infection through unnoticed wounds. An infected person may also experience muscle weakness and poor eyesight. Leprosy symptoms may begin within one year, but, for some people, symptoms may take 20 years or more to occur.

Skin cancers are cancers that arise from the skin. They are due to the development of abnormal cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. There are three main types of skin cancers: basal-cell skin cancer (BCC), squamous-cell skin cancer (SCC) and melanoma. The first two, along with a number of less common skin cancers, are known as nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC). Basal-cell cancer grows slowly and can damage the tissue around it but is unlikely to spread to distant areas or result in death. It often appears as a painless raised area of skin that may be shiny with small blood vessels running over it or may present as a raised area with an ulcer. Squamous-cell skin cancer is more likely to spread. It usually presents as a hard lump with a scaly top but may also form an ulcer. Melanomas are the most aggressive. Signs include a mole that has changed in size, shape, color, has irregular edges, has more than one color, is itchy or bleeds.

Vitiligo, also called leucoderma, is a long-term skin condition characterized by patches of the skin losing their pigment. The patches of skin affected become white and usually have sharp margins. The hair from the skin may also become white. The inside of the mouth and nose may also be involved. Typically both sides of the body are affected. Often the patches begin on areas of skin that are exposed to the sun. It is more noticeable in people with dark skin. Vitiligo may result in psychological stress and those affected are sometimes stigmatized.
Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the skin. It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A dermatologist is a specialist medical doctor who manages diseases related to skin, hair, nails, and some cosmetic problems.
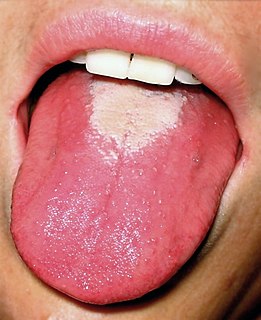
Scarlet fever is an infectious disease resulting from a group A streptococcus infection, also known as Streptococcus pyogenes. The signs and symptoms include a sore throat, fever, headaches, swollen lymph nodes, and a characteristic rash. The rash is red and feels like sandpaper and the tongue may be red and bumpy. It most commonly affects children between five and 15 years of age.

Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by raised areas of abnormal skin. These areas are red, or purple on some people with darker skin, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small, localized patches to complete body coverage. Injury to the skin can trigger psoriatic skin changes at that spot, which is known as the Koebner phenomenon.

A blister is a small pocket of body fluid within the upper layers of the skin, usually caused by forceful rubbing (friction), burning, freezing, chemical exposure or infection. Most blisters are filled with a clear fluid, either serum or plasma. However, blisters can be filled with blood or with pus.

Onchocerciasis, also known as river blindness, is a disease caused by infection with the parasitic worm Onchocerca volvulus. Symptoms include severe itching, bumps under the skin, and blindness. It is the second-most common cause of blindness due to infection, after trachoma.

A rash is a change of the human skin which affects its color, appearance, or texture.

Cellulitis is a bacterial infection involving the inner layers of the skin. It specifically affects the dermis and subcutaneous fat. Signs and symptoms include an area of redness which increases in size over a few days. The borders of the area of redness are generally not sharp and the skin may be swollen. While the redness often turns white when pressure is applied, this is not always the case. The area of infection is usually painful. Lymphatic vessels may occasionally be involved, and the person may have a fever and feel tired.

A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment.

Athlete's foot, known medically as tinea pedis, is a common skin infection of the feet caused by fungus. Signs and symptoms often include itching, scaling, cracking and redness. In rare cases the skin may blister. Athlete's foot fungus may infect any part of the foot, but most often grows between the toes. The next most common area is the bottom of the foot. The same fungus may also affect the nails or the hands. It is a member of the group of diseases known as tinea.

Darier's disease (DAR) is an inherited skin disorder that presents with multiple greasy, crusting, thick brown bumps that merge into patches.

Pemphigus is a rare group of blistering autoimmune diseases that affect the skin and mucous membranes. The name is derived from the Greek root pemphix, meaning "pustule".

Fungal infection, also known as mycosis, is disease caused by fungi. Different types are traditionally divided according to the part of the body affected; superficial, subcutaneous, and systemic. Superficial fungal infections include common tinea of the skin, such as tinea of the body, groin, hands, feet and beard, and yeast infections such as pityriasis versicolor. Subcutaneous types include eumycetoma and chromoblastomycosis, which generally affect tissues in and beneath the skin. Systemic fungal infections are more serious and include cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, pneumocystis pneumonia, aspergillosis and mucormycosis. Signs and symptoms range widely. There is usually a rash with superficial infection. Fungal infection within the skin or under the skin may present with a lump and skin changes. Pneumonia-like symptoms or meningitis may occur with a deeper or systemic infection.
An occupational disease is any chronic ailment that occurs as a result of work or occupational activity. It is an aspect of occupational safety and health. An occupational disease is typically identified when it is shown that it is more prevalent in a given body of workers than in the general population, or in other worker populations. The first such disease to be recognised, squamous-cell carcinoma of the scrotum, was identified in chimney sweep boys by Sir Percival Pott in 1775. Occupational hazards that are of a traumatic nature are not considered to be occupational diseases.

Meleda disease (MDM) or "mal de Meleda", also called Mljet disease, keratosis palmoplantaris and transgradiens of Siemens, is an extremely rare autosomal recessive congenital skin disorder in which dry, thick patches of skin develop on the soles of the hands and feet, a condition known as palmoplantar hyperkeratosis. Meleda Disease is a skin condition which usually can be identified not long after birth. This is a genetic condition but it is very rare. The hands and feet usually are the first to show signs of the disease but the disease can advance to other parts of the body. Signs of the disease include thickening of the skin, on hands and soles of feet, which can turn red in color. There currently is no cure and treatment is limited, but Acitretin can be used in severe cases.

Schamberg's disease, is a chronic discoloration of the skin found in people of all ages, usually only affecting the feet, legs or thighs or a combination. It may occur as a single event or subsequent bouts may cause further spread. It is most common in males. It is named after Jay Frank Schamberg, who described it in 1901. There is no known cure for this disease but it is not a life-threatening condition and is mainly of cosmetic concern, although, because it can appear so suddenly, so extensively and because it usually leaves permanent discoloration of the skin, it can cause understandable psychological concern. The skin lesions sometimes cause itching, which can be treated by applying cortisone cream. The cortisone cream will only help with the itching and does not improve the discoloration of the skin. Schamberg's disease causes no other symptoms beside skin discoloration and itching. The condition is caused by inflammation of capillaries near the surface of skin and subsequent leaking of red blood cells into surrounding tissues. As the red blood cells break down and get mostly resorbed, some of the iron released by the red blood cells remains in the skin and causes the characteristic rust-colored appearance. The cause of the capillary inflammation is usually unknown.
References
- ↑ Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelso; Abbas, Abul (2004) Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease (7th ed.). Saunders. Page 1230. ISBN 0-7216-0187-1.