Related Research Articles

Photoluminescence is light emission from any form of matter after the absorption of photons. It is one of many forms of luminescence and is initiated by photoexcitation, hence the prefix photo-. Following excitation, various relaxation processes typically occur in which other photons are re-radiated. Time periods between absorption and emission may vary: ranging from short femtosecond-regime for emission involving free-carrier plasma in inorganic semiconductors up to milliseconds for phosphoresence processes in molecular systems; and under special circumstances delay of emission may even span to minutes or hours.

In thermodynamics and fluid mechanics, the compressibility is a measure of the instantaneous relative volume change of a fluid or solid as a response to a pressure change. In its simple form, the compressibility may be expressed as

Thermionic emission is the liberation of charged particles from a hot electrode whose thermal energy gives some particles enough kinetic energy to escape the material's surface. The particles, sometimes called thermions in early literature, are now known to be ions or electrons. Thermal electron emission specifically refers to emission of electrons and occurs when thermal energy overcomes the material's work function.

Cadmium arsenide (Cd3As2) is an inorganic semimetal in the II-V family. It exhibits the Nernst effect.

Indium nitride is a small bandgap semiconductor material which has potential application in solar cells and high speed electronics.

Caesium iodide or cesium iodide is the ionic compound of caesium and iodine. It is often used as the input phosphor of an X-ray image intensifier tube found in fluoroscopy equipment. Caesium iodide photocathodes are highly efficient at extreme ultraviolet wavelengths.
Chalcogenide glass is a glass containing one or more chalcogens. Polonium is also a chalcogen but is not used because of its strong radioactivity. Chalcogenide materials behave rather differently from oxides, in particular their lower band gaps contribute to very dissimilar optical and electrical properties.

X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) is a widely used technique for determining the local geometric and/or electronic structure of matter. The experiment is usually performed at synchrotron radiation facilities, which provide intense and tunable X-ray beams. Samples can be in the gas phase, solutions, or solids.

Secondary electrons are electrons generated as ionization products. They are called 'secondary' because they are generated by other radiation. This radiation can be in the form of ions, electrons, or photons with sufficiently high energy, i.e. exceeding the ionization potential. Photoelectrons can be considered an example of secondary electrons where the primary radiation are photons; in some discussions photoelectrons with higher energy (>50 eV) are still considered "primary" while the electrons freed by the photoelectrons are "secondary".

Indium gallium nitride is a semiconductor material made of a mix of gallium nitride (GaN) and indium nitride (InN). It is a ternary group III/group V direct bandgap semiconductor. Its bandgap can be tuned by varying the amount of indium in the alloy. InxGa1−xN has a direct bandgap span from the infrared for InN to the ultraviolet of GaN. The ratio of In/Ga is usually between 0.02/0.98 and 0.3/0.7.
Aluminium gallium nitride (AlGaN) is a semiconductor material. It is any alloy of aluminium nitride and gallium nitride.
Superferromagnetism is the magnetism of an ensemble of magnetically interacting super-moment-bearing material particles that would be superparamagnetic if they were not interacting. Nanoparticles of iron oxides, such as ferrihydrite, often cluster and interact magnetically. These interactions change the magnetic behaviours of the nanoparticles and lead to an ordered low-temperature phase with non-randomly oriented particle super-moments.
In materials science, heavy fermion materials are a specific type of intermetallic compound, containing elements with 4f or 5f electrons in unfilled electron bands. Electrons are one type of fermion, and when they are found in such materials, they are sometimes referred to as heavy electrons. Heavy fermion materials have a low-temperature specific heat whose linear term is up to 1000 times larger than the value expected from the free electron model. The properties of the heavy fermion compounds often derive from the partly filled f-orbitals of rare-earth or actinide ions, which behave like localized magnetic moments.
In solid state physics the Ridley–Watkins–Hilsum theory (RWH) explains the mechanism by which differential negative resistance is developed in a bulk solid state semiconductor material when a voltage is applied to the terminals of the sample. It is the theory behind the operation of the Gunn diode as well as several other microwave semiconductor devices, which are used practically in electronic oscillators to produce microwave power. It is named for British physicists Brian Ridley, Tom Watkins and Cyril Hilsum who wrote theoretical papers on the effect in 1961.
Physica Status Solidi, often stylized physica status solidi or pss, is a family of international peer-reviewed, scientific journals, publishing research on all aspects of solid state physics, and materials science. It is owned and published by Wiley–VCH. These journals publish over 2000 articles per year, making it one of the largest international publications in condensed matter physics. The current editor in chief is Stefan Hildebrandt at the Editorial Office based in Berlin. This office also manages the peer-review process.
The piezooptic effect is manifest as a change in refractive index, n, of a material caused by a change in pressure on that material. Early demonstrations of the piezooptic effect were done on liquids. The effect has since been demonstrated in solid, crystalline materials.
He Yizhen was a Chinese physicist. She contributed to applying spectroscopy to the steel industry in China and to the research in amorphous state physics. Her research specialty in amorphous physics was metallic glass. She filled up the blank of spectroscopy research in China, and became the first person to measure the whole internal friction peak of metallic glass. He Yizhen was one of the founders of the Institute of Solid State Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Hefei. The research emphases of the institute are nuclear engineering, special metallic materials, and internal friction of solid.
Solar radio emission refers to radio waves that are naturally produced by the Sun, primarily from the lower and upper layers of the atmosphere called the chromosphere and corona, respectively. The Sun produces radio emissions through four known mechanisms, each of which operates primarily by converting the energy of moving electrons into electromagnetic radiation. The four emission mechanisms are thermal bremsstrahlung (braking) emission, gyromagnetic emission, plasma emission, and electron-cyclotron maser emission. The first two are incoherent mechanisms, which means that they are the summation of radiation generated independently by many individual particles. These mechanisms are primarily responsible for the persistent "background" emissions that slowly vary as structures in the atmosphere evolve. The latter two processes are coherent mechanisms, which refers to special cases where radiation is efficiently produced at a particular set of frequencies. Coherent mechanisms can produce much larger brightness temperatures (intensities) and are primarily responsible for the intense spikes of radiation called solar radio bursts, which are byproducts of the same processes that lead to other forms of solar activity like solar flares and coronal mass ejections.
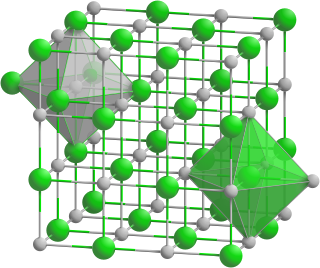
Europium(II) oxide (EuO) is a chemical compound which is one of the oxides of europium. In addition to europium(II) oxide, there is also europium(III) oxide and the mixed valence europium(II,III) oxide.
References
- ↑ Oster, L.; Yaskolko, V.; Haddad, J. (1999), "Classification of Exoelectron Emission Mechanisms", Physica Status Solidi A, 174 (2): 431, Bibcode:1999PSSAR.174..431O, doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-396X(199908)174:2<431::AID-PSSA431>3.0.CO;2-Z
- ↑ Gerasimov, A. B.; Dolidze, G. M.; Mizandari, L. A.; Tsertsvadze, A. A. (1976), "On the physical mechanism of exoelectron emission", Physica Status Solidi A, 35 (2): K131, Bibcode:1976PSSAR..35..131G, doi:10.1002/pssa.2210350256