Related Research Articles

Algebraic notation is the standard method for recording and describing the moves in a game of chess. It is based on a system of coordinates to uniquely identify each square on the board. It is used by most books, magazines, and newspapers.

Fischer random chess, also known as Chess960, is a variation of the game of chess invented by the former world chess champion Bobby Fischer. Fischer announced this variation on June 19, 1996, in Buenos Aires, Argentina. Fischer random chess employs the same board and pieces as classical chess, but the starting position of the pieces on the players' home ranks is randomized, following certain rules. The random setup makes gaining an advantage through the memorization of openings impracticable; players instead must rely more on their skill and creativity over the board.

A newline is a control character or sequence of control characters in character encoding specifications such as ASCII, EBCDIC, Unicode, etc. This character, or a sequence of characters, is used to signify the end of a line of text and the start of a new one.
Portable Game Notation (PGN) is a standard plain text format for recording chess games, which can be read by humans and is also supported by most chess software.
Forsyth–Edwards Notation (FEN) is a standard notation for describing a particular board position of a chess game. The purpose of FEN is to provide all the necessary information to restart a game from a particular position.

A filename or file name is a name used to uniquely identify a computer file in a file system. Different file systems impose different restrictions on filename lengths.
In linguistics and semiotics, a notation system is a system of graphics or symbols, characters and abbreviated expressions, used in artistic and scientific disciplines to represent technical facts and quantities by convention. Therefore, a notation is a collection of related symbols that are each given an arbitrary meaning, created to facilitate structured communication within a domain knowledge or field of study.

In computer chess, a chess engine is a computer program that analyzes chess or chess variant positions, and generates a move or list of moves that it regards as strongest.
PGN may refer to:
Chess notation systems are used to record either the moves made or the position of the pieces in a game of chess. Chess notation is used in chess literature, and by players keeping a record of an ongoing game. The earliest systems of notation used lengthy narratives to describe each move; these gradually evolved into more compact notation systems. Algebraic notation is now the accepted international standard, with several variants. Descriptive chess notation was used in English- and Spanish-language literature until the late 20th century, but is now obsolescent. Portable Game Notation (PGN) is a text file format based on English algebraic notation which can be processed by most chess software. Other notation systems include ICCF numeric notation, used for international correspondence chess, and systems for transmission using Morse code over telegraph or radio. The standard system for recording chess positions is Forsyth–Edwards Notation (FEN).
ICCF numeric notation is the official chess notation system of the International Correspondence Chess Federation. The system was devised for use in international correspondence chess to avoid the potential confusion of using algebraic notation, as the chess pieces have different abbreviations depending on language.
EPD may refer to:
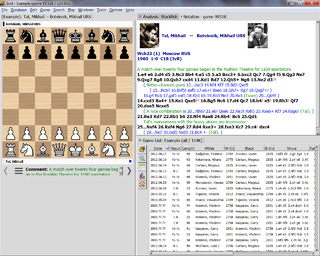
Shane's Chess Information Database (Scid) is a free and open source UNIX, Windows, Linux, and Mac application for viewing and maintaining large databases of chess games. It has features comparable to popular commercial chess software. Scid is written in Tcl/Tk and C++.
X-FEN is an extension of Forsyth–Edwards Notation (FEN) introduced by Reinhard Scharnagl in 2003. It was designed to be able to represent all possible positions in Fischer random chess (FRC) and Capablanca random chess (CRC). It is fully backward compatible with FEN.
David Forsyth (1854–1909), a Scotsman who emigrated to New Zealand, served as chess editor of the Glasgow Weekly Herald. Forsyth invented a method for recording chess positions, which he published in the Glasgow Weekly Herald in 1883, now known as Forsyth notation. He won the New Zealand Chess Championship in 1901.

Clan Forsyth is a Scottish clan.

MChess Pro is the name given to a chess playing computer program written by Marty Hirsch which won the World Microcomputer Chess Championship in 1995. The program is no longer under development and is no longer commercially available and therefore has largely historical significance only.
Numeric Annotation Glyphs or NAGs are used to annotate chess games when using a computer, typically providing an assessment of a chess move or a chess position. NAGs exist to indicate a simple annotation in a language independent manner.
A chess diagram is graphic representation of a position in a chess game, using standardised symbols. Chess diagrams are widely used in chess publications as an aid to visualisation, or to aid the readers to verify that they are looking at the correct position on their chessboard or computer. The symbols used generally resemble the pieces of the standard Staunton chess set, although a number of different fonts have been used over the centuries.
Steven James Edwards was an American computer scientist and computer programmer who specialized in chess. He specified the Portable Game Notation, the Forsyth–Edwards Notation - expanding on previous work by David Forsyth, and Extended Position Description with John Stanback. In 1994, he introduced a distance to mate endgame tablebase format, called the Edwards' tablebases. He authored chess programs and tools, such as Spector, Symbolic, the Chess in Lisp (CIL) package, and several others.