
The Franco-British Aviation Model 290 was a French four-seat amphibian flying boat built by the Franco-British Aviation Company (FBA) as a replacement for the Model 17 in French naval service.

The FBA Type H was a French reconnaissance flying boat produced in large numbers in France and Italy during World War I by Franco-British Aviation.

The Macchi M.C.100 was an Italian commercial flying boat designed and built by Macchi.

The FBA 21 and 23 were small flying boat airliners built in France in the mid-1920s. Their development was an attempt by FBA to develop a commercial version of their FBA 19 bomber which had failed to attract orders from military buyers. Retaining the same basic design as their predecessor, the Model 21 added an enclosed cabin for four passengers. Unfortunately for FBA, they aroused as little interest as their military counterparts, and only a handful were built in a number of slight variations, including one example of a dedicated mail plane.

The Saro Cloud was a British passenger amphibian flying boat designed and built by Saunders-Roe as the A.19. It was later produced as the A.29 for the Royal Air Force for pilot and navigator training.
The Fokker B.I was a reconnaissance flying boat built in the Netherlands in 1922. The B.I was followed by an improved version, the B.III in 1926. It was a conventional biplane flying boat design, with staggered sesquiplane wings braced by struts arranged as a Warren truss. The engine was mounted pusher-wise on the top wing. The duralumin hull featured three open cockpits - one at the nose for a gunner, one in front of the lower wing for the pilot and engineer and one behind the wings for another gunner. The B.I was amphibious, equipped with main undercarriage that folded back along the hull, but this feature was omitted in the B.III. The B.I was flown in the Dutch East Indies by the Naval Air Service for a number of years, and although it gave good service, no further examples were ordered from Fokker.

The Saunders Kittiwake was a British amphibian flying-boat built by S.E. Saunders at East Cowes, Isle of Wight.
The Hiro H4H was a 1930s Japanese bomber or reconnaissance monoplane flying boat designed and built by the Hiro Naval Arsenal for the Imperial Japanese Navy.

The Eastman E-2 Sea Rover, also called the Beasley-Eastman E-2 Sea Rover, was a light seaplane built in the late 1920s for business and shuttle use.

The Curtiss CA-1 was an American five-seat biplane amphibian designed by Frank Courtney and built by Curtiss-Wright at St Louis, Missouri.
The Shavrov Sh-5 was a Soviet civil amphibian flying-boat designed by Vadim Borisovich Shavrov as a photographic platform for aerial mapping. By the time it flew it was an outdated design and the type did not enter production.
The SABCA S.11 or SABCA S.XI was a prototype Belgian airliner of the 1930s. It was a three-engined high-winged monoplane intended for service in the Belgian Congo, but only a single example was built.

The Guillemin JG.40 was designed and built to meet a French government requirement for a small air ambulance capable of operating in the colonies. Two were completed and performed well but the JG.40 did not reach production.
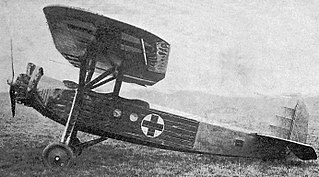
The Lorraine-Hanriot LH.21S was designed and built in 1930 to meet a French government requirement for a small air ambulance capable of operating in the colonies. It did not reach production.

The Nieuport-Delage NiD 940 was a French, tailless, pusher configuration touring aircraft first flown in 1934. It suffered from longitudinal instabilities and despite modifications and a more powerful engine, it did not receive its Certificate of Airworthiness.

The Aviaméta 92 was a French, all-metal, five seat monoplane built in the late 1920s. Three different engines were fitted, and one example flew the first non-stop Paris-Algiers flight in preparation for an abandoned trans-Atlantic attempt.

The Hanriot H.46 Styx was a French, single-engined, parasol wing aircraft which could equally be configured for training, liaison or ambulance roles; in the latter form it was able to accept a patient on a stretcher. Several different engines were fitted and flown but the type did not reach production.
The Bloch MB.60, initially known as the MB.VI, was a tri-motor mailplane designed and built in France from 1930 to 1931 to an order for an aircraft suitable for use as a postal, commercial or medical transport.

The Loening C-1 Air Yacht was an amphibious airliner produced in the United States at the end of the 1920s.

The Ireland Neptune was a four or five place pusher configuration biplane sold in flying boat and amphibian versions. Designed in the U.S. and first flown in 1927, well over 50 were built.















