The Advanced Maryland Automatic Network Disk Archiver (Amanda) is an open source computer archiving tool that is able to back up data residing on multiple computers on a network. It uses a client–server model, where the server contacts each client to perform a backup at a scheduled time.

The system utility fsck is a tool for checking the consistency of a file system in Unix and Unix-like operating systems, such as Linux, macOS, and FreeBSD. The equivalent programs on MS-DOS and Microsoft Windows are CHKDSK, SFC, and SCANDISK.

tcpdump is a data-network packet analyzer computer program that runs under a command line interface. It allows the user to display TCP/IP and other packets being transmitted or received over a network to which the computer is attached. Distributed under the BSD license, tcpdump is free software.

Squid is a caching and forwarding HTTP web proxy. It has a wide variety of uses, including speeding up a web server by caching repeated requests, caching World Wide Web (WWW), Domain Name System (DNS), and other network lookups for a group of people sharing network resources, and aiding security by filtering traffic. Although used for mainly HTTP and File Transfer Protocol (FTP), Squid includes limited support for several other protocols including Internet Gopher, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), Transport Layer Security (TLS), and Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS). Squid does not support the SOCKS protocol, unlike Privoxy, with which Squid can be used in order to provide SOCKS support.
The Unix file system (UFS) is a family of file systems supported by many Unix and Unix-like operating systems. It is a distant descendant of the original filesystem used by Version 7 Unix.
PF is a BSD licensed stateful packet filter, a central piece of software for firewalling. It is comparable to netfilter (iptables), ipfw, and ipfilter.
This is a list of operating systems specifically focused on security. Similar concepts include security-evaluated operating systems that have achieved certification from an auditing organization, and trusted operating systems that provide sufficient support for multilevel security and evidence of correctness to meet a particular set of requirements.

The file command is a standard program of Unix and Unix-like operating systems for recognizing the type of data contained in a computer file.

The history of Unix dates back to the mid-1960s, when the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, AT&T Bell Labs, and General Electric were jointly developing an experimental time-sharing operating system called Multics for the GE-645 mainframe. Multics introduced many innovations, but also had many problems. Bell Labs, frustrated by the size and complexity of Multics but not its aims, slowly pulled out of the project. Their last researchers to leave Multics – among them Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, Doug McIlroy, and Joe Ossanna – decided to redo the work, but on a much smaller scale.
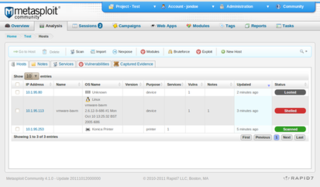
The Metasploit Project is a computer security project that provides information about security vulnerabilities and aids in penetration testing and IDS signature development. It is owned by Boston, Massachusetts-based security company, Rapid7.

Argus – the Audit Record Generation and Utilization System is the first implementation of network flow monitoring, and is an ongoing open source network flow monitor project. Started by Carter Bullard in 1984 at Georgia Tech, and developed for cyber security at Carnegie Mellon University in the early 1990s, Argus has been an important contributor to Internet cyber security technology over its 30 years..

Wireshark is a free and open-source packet analyzer. It is used for network troubleshooting, analysis, software and communications protocol development, and education. Originally named Ethereal, the project was renamed Wireshark in May 2006 due to trademark issues.
Omnipeek is a packet analyzer software tool from Savvius, a LiveAction company, for network troubleshooting and protocol analysis. It supports an application programming interface (API) for plugins.
The LAIM Working Group is a NSF and ONR funded research group at the National Center for Supercomputing Applications under the direction of Adam SlagellArchived 2007-02-22 at the Wayback Machine. Work from this group focuses upon log anonymization and Internet privacy. The LAIM group, established in 2005, has released 3 different log anonymization tools: CANINE, Scrub-PA, and FLAIM. FLAIM is their only tool still under active development.
syslog-ng is a free and open-source implementation of the syslog protocol for Unix and Unix-like systems. It extends the original syslogd model with content-based filtering, rich filtering capabilities, flexible configuration options and adds important features to syslog, like using TCP for transport. As of today, syslog-ng is developed by Balabit IT Security Ltd. It has three editions with a common codebase. The first is called syslog-ng Open Source Edition (OSE) with the license LGPL. The second is called Premium Edition (PE) and has additional plugins (modules) under a proprietary license. The third is called Storebox (SSB), which comes as an appliance with a Web-based UI as well as additional features including ultra-fast-text search, unified search, content-based alerting and a premier tier support.

The Berkeley Software Distribution or Berkeley Standard Distribution (BSD) is a discontinued operating system based on Research Unix, developed and distributed by the Computer Systems Research Group (CSRG) at the University of California, Berkeley. The term "BSD" commonly refers to its open-source descendants, including FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, and DragonFly BSD.

Unix is a family of multitasking, multi-user computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others.
Tiger is a security software for Unix-like computer operating systems. It can be used both as a security audit tool and a host-based intrusion detection system and supports multiple UNIX platforms. Tiger is free under the GPL license and unlike other tools, it needs only of POSIX tools, and is written entirely in shell language.
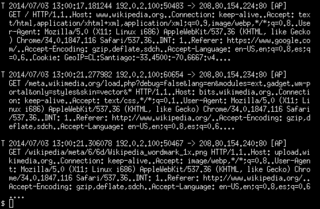
ngrep is a network packet analyzer written by Jordan Ritter. It has a command-line interface, and relies upon the pcap library and the GNU regex library.
Super Dimension Fortress is a non-profit public access UNIX shell provider on the Internet. It has been in continual operation since 1987 as a non-profit social club. The name is derived from the Japanese anime series Super Dimension Fortress Macross; the original SDF server was a Bulletin board system created by Ted Uhlemann for fellow Japanese anime fans. From its BBS roots, which have been well documented as part of the BBS: The Documentary project, SDF has grown into a feature-rich provider serving members around the world.












