Related Research Articles
In object-oriented programming, a class is an extensible program-code-template for creating objects, providing initial values for state and implementations of behavior.
Multiple inheritance is a feature of some object-oriented computer programming languages in which an object or class can inherit features from more than one parent object or parent class. It is distinct from single inheritance, where an object or class may only inherit from one particular object or class.
In software engineering and computer science, abstraction is the process of generalizing concrete details, such as attributes, away from the study of objects and systems to focus attention on details of greater importance. Abstraction is a fundamental concept in computer science and software engineering, especially within the object-oriented programming paradigm. Examples of this include:
In computing, aspect-oriented programming (AOP) is a programming paradigm that aims to increase modularity by allowing the separation of cross-cutting concerns. It does so by adding behavior to existing code without modifying the code, instead separately specifying which code is modified via a "pointcut" specification, such as "log all function calls when the function's name begins with 'set'". This allows behaviors that are not central to the business logic to be added to a program without cluttering the code of core functions.
In software engineering, a software design pattern is a general, reusable solution to a commonly occurring problem within a given context in software design. It is not a finished design that can be transformed directly into source or machine code. Rather, it is a description or template for how to solve a problem that can be used in many different situations. Design patterns are formalized best practices that the programmer can use to solve common problems when designing an application or system.
Software design is the process of conceptualizing how a software system will work before it is implemented or modified. Software design also refers to the direct result of the design process – the concepts of how the software will work which consists of both design documentation and undocumented concepts.
The Law of Demeter (LoD) or principle of least knowledge is a design guideline for developing software, particularly object-oriented programs. In its general form, the LoD is a specific case of loose coupling. The guideline was proposed by Ian Holland at Northeastern University towards the end of 1987, and the following three recommendations serve as a succinct summary:
In computer science, separation of concerns is a design principle for separating a computer program into distinct sections. Each section addresses a separate concern, a set of information that affects the code of a computer program. A concern can be as general as "the details of the hardware for an application", or as specific as "the name of which class to instantiate". A program that embodies SoC well is called a modular program. Modularity, and hence separation of concerns, is achieved by encapsulating information inside a section of code that has a well-defined interface. Encapsulation is a means of information hiding. Layered designs in information systems are another embodiment of separation of concerns.
In object-oriented programming languages, a mixin is a class that contains methods for use by other classes without having to be the parent class of those other classes. How those other classes gain access to the mixin's methods depends on the language. Mixins are sometimes described as being "included" rather than "inherited".
Modular programming is a software design technique that emphasizes separating the functionality of a program into independent, interchangeable modules, such that each contains everything necessary to execute only one aspect of the desired functionality.

Modern C++ Design: Generic Programming and Design Patterns Applied is a book written by Andrei Alexandrescu, published in 2001 by Addison-Wesley. It has been regarded as "one of the most important C++ books" by Scott Meyers.
Object-oriented analysis and design (OOAD) is a technical approach for analyzing and designing an application, system, or business by applying object-oriented programming, as well as using visual modeling throughout the software development process to guide stakeholder communication and product quality.
In object-oriented programming, inheritance is the mechanism of basing an object or class upon another object or class, retaining similar implementation. Also defined as deriving new classes from existing ones such as super class or base class and then forming them into a hierarchy of classes. In most class-based object-oriented languages like C++, an object created through inheritance, a "child object", acquires all the properties and behaviors of the "parent object", with the exception of: constructors, destructors, overloaded operators and friend functions of the base class. Inheritance allows programmers to create classes that are built upon existing classes, to specify a new implementation while maintaining the same behaviors, to reuse code and to independently extend original software via public classes and interfaces. The relationships of objects or classes through inheritance give rise to a directed acyclic graph.
In computer programming, a trait is a concept used in programming languages which represents a set of methods that can be used to extend the functionality of a class.
Matthew Flatt is an American computer scientist and professor at the University of Utah School of Computing in Salt Lake City. He is also the leader of the core development team for the Racket programming language.
In computer programming, feature-oriented programming (FOP) or feature-oriented software development (FOSD) is a programming paradigm for program generation in software product lines (SPLs) and for incremental development of programs.
In computer science, information hiding is the principle of segregation of the design decisions in a computer program that are most likely to change, thus protecting other parts of the program from extensive modification if the design decision is changed. The protection involves providing a stable interface which protects the remainder of the program from the implementation. Written in another way, information hiding is the ability to prevent certain aspects of a class or software component from being accessible to its clients, using either programming language features or an explicit exporting policy.

Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of objects, which can contain data and code: data in the form of fields, and code in the form of procedures. In OOP, computer programs are designed by making them out of objects that interact with one another.
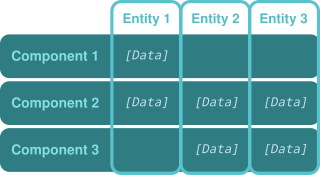
Entity component system (ECS) is a software architectural pattern mostly used in video game development for the representation of game world objects. An ECS comprises entities composed from components of data, with systems which operate on the components.
The composition filters model denotes a modular extension to the conventional object model. It provides a solution for a wide range of problems in the construction of large and complex applications. Most notably, one implementation of composition filters provides an abstraction layer for message-passing systems.
References
- ↑ "Implementing Layered Designs with Mixin Layers" (PDF).
- ↑ "Object Oriented Frameworks and Product Lines" (PDF).
- ↑ "Mixin Layers: An Object Oriented Implementation Technique for Refinements and Collaboration-Based Designs" (PDF).
- ↑ "Aspectual Mixin Layers: Aspects and Features in Concert" (PDF).
- ↑ "Aspectual Feature Modules".