Related Research Articles

Amplitude modulation (AM) is a modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In amplitude modulation, the amplitude of the wave is varied in proportion to that of the message signal, such as an audio signal. This technique contrasts with angle modulation, in which either the frequency of the carrier wave is varied, as in frequency modulation, or its phase, as in phase modulation.

Frequency modulation (FM) is the encoding of information in a carrier wave by varying the instantaneous frequency of the wave. The technology is used in telecommunications, radio broadcasting, signal processing, and computing.
In electronics and telecommunications, modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform, called the carrier signal, with a separate signal called the modulation signal that typically contains information to be transmitted. For example, the modulation signal might be an audio signal representing sound from a microphone, a video signal representing moving images from a video camera, or a digital signal representing a sequence of binary digits, a bitstream from a computer.
Quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) is the name of a family of digital modulation methods and a related family of analog modulation methods widely used in modern telecommunications to transmit information. It conveys two analog message signals, or two digital bit streams, by changing (modulating) the amplitudes of two carrier waves, using the amplitude-shift keying (ASK) digital modulation scheme or amplitude modulation (AM) analog modulation scheme. The two carrier waves are of the same frequency and are out of phase with each other by 90°, a condition known as orthogonality or quadrature. The transmitted signal is created by adding the two carrier waves together. At the receiver, the two waves can be coherently separated (demodulated) because of their orthogonality. Another key property is that the modulations are low-frequency/low-bandwidth waveforms compared to the carrier frequency, which is known as the narrowband assumption.

Frequency-shift keying (FSK) is a frequency modulation scheme in which digital information is encoded on a carrier signal by periodically shifting the frequency of the carrier between several discrete frequencies. The technology is used for communication systems such as telemetry, weather balloon radiosondes, caller ID, garage door openers, and low frequency radio transmission in the VLF and ELF bands. The simplest FSK is binary FSK, in which the carrier is shifted between two discrete frequencies to transmit binary information.

In electronics and telecommunications, a radio transmitter or just transmitter is an electronic device which produces radio waves with an antenna with the purpose of signal transmission up to a radio receiver. The transmitter itself generates a radio frequency alternating current, which is applied to the antenna. When excited by this alternating current, the antenna radiates radio waves.
Demodulation is extracting the original information-bearing signal from a carrier wave. A demodulator is an electronic circuit that is used to recover the information content from the modulated carrier wave. There are many types of modulation so there are many types of demodulators. The signal output from a demodulator may represent sound, images or binary data.
Angle modulation is a class of carrier modulation that is used in telecommunications transmission systems. The class comprises frequency modulation (FM) and phase modulation (PM), and is based on altering the frequency or the phase, respectively, of a carrier signal to encode the message signal. This contrasts with varying the amplitude of the carrier, practiced in amplitude modulation (AM) transmission, the earliest of the major modulation methods used widely in early radio broadcasting.

Very low frequency or VLF is the ITU designation for radio frequencies (RF) in the range of 3–30 kHz, corresponding to wavelengths from 100 to 10 km, respectively. The band is also known as the myriameter band or myriameter wave as the wavelengths range from one to ten myriameters. Due to its limited bandwidth, audio (voice) transmission is highly impractical in this band, and therefore only low data rate coded signals are used. The VLF band is used for a few radio navigation services, government time radio stations and for secure military communication. Since VLF waves can penetrate at least 40 meters (131 ft) into saltwater, they are used for military communication with submarines.
Pulse-position modulation (PPM) is a form of signal modulation in which M message bits are encoded by transmitting a single pulse in one of possible required time shifts. This is repeated every T seconds, such that the transmitted bit rate is bits per second. It is primarily useful for optical communications systems, which tend to have little or no multipath interference.
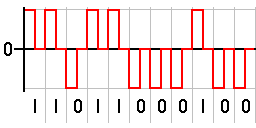
Return-to-zero describes a line code used in telecommunications signals in which the signal drops (returns) to zero between each pulse. This takes place even if a number of consecutive 0s or 1s occur in the signal. The signal is self-clocking. This means that a separate clock does not need to be sent alongside the signal, but suffers from using twice the bandwidth to achieve the same data-rate as compared to non-return-to-zero format.
The International Telecommunication Union uses an internationally agreed system for classifying radio frequency signals. Each type of radio emission is classified according to its bandwidth, method of modulation, nature of the modulating signal, and type of information transmitted on the carrier signal. It is based on characteristics of the signal, not on the transmitter used.
The Hellschreiber, Feldhellschreiber or Typenbildfeldfernschreiber is a facsimile-based teleprinter invented by Rudolf Hell. Compared to contemporary teleprinters that were based on typewriter systems and were mechanically complex and expensive, the Hellschreiber was much simpler and more robust, with far fewer moving parts. It has the added advantage of being capable of providing intelligible communication even over very poor quality radio or cable links, where voice or other teledata would be unintelligible.
Continuous phase modulation (CPM) is a method for modulation of data commonly used in wireless modems. In contrast to other coherent digital phase modulation techniques where the carrier phase abruptly resets to zero at the start of every symbol, with CPM the carrier phase is modulated in a continuous manner. For instance, with QPSK the carrier instantaneously jumps from a sine to a cosine whenever one of the two message bits of the current symbol differs from the two message bits of the previous symbol. This discontinuity requires a relatively large percentage of the power to occur outside of the intended band, leading to poor spectral efficiency. Furthermore, CPM is typically implemented as a constant-envelope waveform, i.e., the transmitted carrier power is constant. Therefore, CPM is attractive because the phase continuity yields high spectral efficiency, and the constant envelope yields excellent power efficiency. The primary drawback is the high implementation complexity required for an optimal receiver.
Amplitude-shift keying (ASK) is a form of amplitude modulation that represents digital data as variations in the amplitude of a carrier wave. In an ASK system, a symbol, representing one or more bits, is sent by transmitting a fixed-amplitude carrier wave at a fixed frequency for a specific time duration. For example, if each symbol represents a single bit, then the carrier signal could be transmitted at nominal amplitude when the input value is 1, but transmitted at reduced amplitude or not at all when the input value is 0.
On–off keying (OOK) denotes the simplest form of amplitude-shift keying (ASK) modulation that represents digital data as the presence or absence of a carrier wave. In its simplest form, the presence of a carrier for a specific duration represents a binary one, while its absence for the same duration represents a binary zero. Some more sophisticated schemes vary these durations to convey additional information. It is analogous to unipolar encoding line code.
In a digitally modulated signal or a line code, symbol rate, modulation rate or baud rate is the number of symbol changes, waveform changes, or signaling events across the transmission medium per unit of time. The symbol rate is measured in baud (Bd) or symbols per second. In the case of a line code, the symbol rate is the pulse rate in pulses per second. Each symbol can represent or convey one or several bits of data. The symbol rate is related to the gross bit rate, expressed in bits per second.

Underwater acoustic communication is a technique of sending and receiving messages in water. There are several ways of employing such communication but the most common is by using hydrophones. Underwater communication is difficult due to factors such as multi-path propagation, time variations of the channel, small available bandwidth and strong signal attenuation, especially over long ranges. Compared to terrestrial communication, underwater communication has low data rates because it uses acoustic waves instead of electromagnetic waves.
IEC 61334, known as Distribution automation using distribution line carrier systems, is a standard for low-speed reliable power line communications by electricity meters, water meters and SCADA. It is also known as spread frequency-shift keying (S-FSK) and was formerly known as IEC 1334 before IEC's most recent renumbering. It is actually a series of standards describing the researched physical environment of power lines, a well-adapted physical layer, a workable low-power media access layer, and a management interface. Related standards use the physical layer, but not the higher layers.
References
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22. (in support of MIL-STD-188).
This article incorporates public domain material from Federal Standard 1037C. General Services Administration. Archived from the original on 2022-01-22. (in support of MIL-STD-188).