Fail Monastery, occasionally known as Failford Abbey, had a dedication to 'Saint Mary', and was located at Fail on the bank of the Water of Fail, Parish of Tarbolton near the town of Tarbolton, South Ayrshire. Most of the remaining monastery ruins were removed in 1952. The official and rarely used title was House of the Holy Trinity of Failford or the Ministry of Failford.

The old Barony and castle, fortalice, or tower house of Hill of Beith lay in the feudal Regality of Kilwinning, within the Baillerie of Cunninghame, and the Sherrifdom of Ayr, now the Parish of Beith, North Ayrshire, Scotland.

Lambroughton Loch or Wheatrig Loch was situated in a low-lying area between the farms and dwellings of Hillhead, Lambroughton, Wheatrig, Titwood and Lochridge mainly in the Parish of Dreghorn, North Ayrshire. The loch was mainly fed by the Lochridge Burn, the Garrier Burn and surface runoff, such as from the old rig and furrows indicated by Roy's maps of the mid-18th century. The loch outflow was via the Lochridge Burn that runs into the Garrier Burn, passes the site of the old Lochend habitation and into the Bracken Burn near Little Alton. The rivulet or watercourse is known as the Garrier Burn beyond this point.

Lochlea or Lochlie was situated in a low-lying area between the farms and dwellings of Lochlea and Lochside in the Parish of Tarbolton, South Ayrshire, Scotland. The loch was natural, sitting in a hollow created by glaciation. The loch waters ultimately drained via Fail Loch, the Mill Burn, and the Water of Fail. It is well-documented due to the presence of a crannog that was excavated and documented circa 1878, and its association with the poet Robert Burns, who lived here for several years whilst his father was the tenant. Lochlea lies 2+1⁄2 miles northeast of Tarbolton, and just over three miles northwest of Mauchline.

Buiston Loch, also known as Buston, Biston, and Mid Buiston was situated in the mid-Ayrshire clayland at an altitude of 90 m OD. The loch was natural, sitting in a hollow created by glaciation. The loch waters drained via the Garrier Burn that joins the Bracken and Lochridge Burns before joining the River Irvine.

Halket Loch' also known as Halkhead or Halketh, was situated in the mid-Ayrshire clayland near Lugton. It is visible as a surface depression in pastureland, sometimes partially flooded, situated in a low-lying area close to farms and dwellings of East, North and Middle Halket and Craighead in the Parish of Dunlop, East Ayrshire, Scotland. The loch was natural, sitting in a hollow created by glaciation. The loch waters drained via the Glazert Water that joins the Annick Water.

Loch Brown, also known in Scots as Loch Broun, Broon or Broom, was situated in a kettle hole in the mid-Ayrshire clayland near Crosshands. It is nowadays (2011) visible as a surface depression in pastureland, partially flooded, situated in a low-lying area close to farms and dwellings of Skeoch, Dalsangan, Ladebrae, Lochhill, and Crosshands, mainly in the Parish of Mauchline and partly in Craigie, East Ayrshire, Scotland. Duveloch is an old name for the loch and this may derive from the Gaelic Dubh, meaning black or dark loch.

Littlestane Loch, was situated in the mid-Ayrshire clayland near Stanecastle, Irvine, North Ayrshire, Scotland. It is nowadays (2011) only visible as an area of permanent water in the Scottish Wildlife Trust Sourlie Nature Reserve. The loch was natural, sitting in a hollow created by glaciation. The loch waters outflow was via the Red Burn that flows into the River Garnock. The site of Littlestane Loch site is partly built over and much of the site is now public open space lying within the Parish of Girdle Toll.
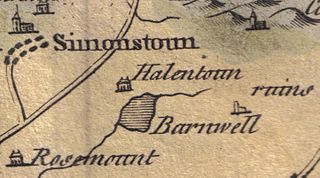
Helenton Loch was situated in a low lying area between the farms and dwellings of Helentongate, Mains, and Burnbank in the Parish of Symington, South Ayrshire, Scotland. The loch was natural, sitting in a hollow, a kettle hole, created by glaciation. The loch waters ultimately drained via the Pow Burn. Helenton Hill is a prominent landmark to the west of the old loch site. The nearby lands of Rosemount were in 1549 known as 'Goldring' and were the property of the Schaws of Sornbeg.

Hessilhead Loch or Hazelhead Loch was situated in a low-lying area near the old Castle of Hessilhead in the Parish of Beith, North Ayrshire, Scotland. The old loch, used in the defence of the castle, was probably infilled when the castle ruins were landscaped in the 19th century.

The Blae Loch is a small freshwater loch situated in a hollow in a low-lying area beneath Blaelochhead Hill in the Parish of Beith, North Ayrshire, Scotland.

The Galrigs Loch was a substantial freshwater loch situated in low lying area between Newfield and Dundonald in South Ayrshire, Scotland. It was drained in the early 18th century.

Clevens Loch was a substantial freshwater loch situated in a low-lying area below Clevance Farm and Langholm Farm in Dundonald parish, South Ayrshire, Scotland.

The Loch of Trabboch or Dalrympleston Loch (NS440211) was situated in a low-lying area below the old Castle of Trabboch, once held by the Boyd family in the Parish of Stair, East Ayrshire, Scotland.

The Loch of Stair was a typical Ayrshire post-glacial 'Kettle Hole', situated in a low-lying area below the farm of Loch Hill, in the Parish of Stair, East Ayrshire, Scotland. This freshwater loch was drained in the 19th century, leaving a wetland area which still periodically floods.

Martnaham Loch is a freshwater loch lying across the border between East and South Ayrshire Council Areas, two kilometres from Coylton, in the parishes of Coylton and Dalrymple, three miles from Ayr. The loch lies along an axis from northeast to southwest. The remains of a castle lie on a possibly artificial islet within the loch. The Campbells of Loudoun once held the lands, followed by the Kennedys of Cassillis.

Lindston Loch was a small freshwater loch situated within a glacial 'kettle hole.' The loch lies in the South Ayrshire Council Area, Parish of Dalrymple, Scotland.

Whitehill Loch, previously known as Hillhouse Loch was a freshwater loch in the East Ayrshire Council Area, now drained, near Galston, in the Parish of Riccarton, lying in a glacial Kettle Hole.

Black Loch is a freshwater loch, named from its dark waters, situated in the East Ayrshire Council Area, between Cumnock and New Cumnock, lying in a glacial Kettle Hole mainly within the Parish of New Cumnock, a small portion protruding into Old Cumnock Parish. It is said to be one of only two lochs or lakes in the world that have outflows running to two separate destinations. The 'Runner' is a deep and broad ditch that was dug many years back to link the three lochs of Lowes, Black, and Creoch.

Haugh or The Haugh is a small village or hamlet in East Ayrshire, Parish of Mauchline, Scotland. The habitation is situated about two and a half miles downstream from Catrine, on the north bank of the River Ayr. The River Ayr Way runs through the village.