Related Research Articles

Al-Qaeda is a militant Sunni Islamist multi-national terrorist organization. It was founded in 1988 by Osama bin Laden, Abdullah Azzam, and several other Arab volunteers during the Soviet–Afghan War.

Ayman Mohammed Rabie al-Zawahiri is an Egyptian terrorist known for being the leader of terrorist group al-Qaeda since June 2011, succeeding Osama bin Laden following his death, and is a current or former member and senior official of Islamist organizations which have orchestrated attacks in Asia, Africa, and also some in North America and Europe. In 2012, he called on Muslims to kidnap Western tourists in Muslim countries.

Harkat-ul-Mujahideen- al-Islami is a Pakistan-based Islamic jihad group operating primarily in Kashmir. The group have been considered as having links to Osama bin Laden and al-Qaeda and the group has been designated as a terrorist organization by Bahrain, the United Nations, the United Kingdom and the United States. In response the organization changed its name to Harkat-ul-Mujahideen. The group splintered from Harkat-ul-Jihad-al-Islami (HuJI), a Pakistani group formed in 1980 to fight the Soviet military in Afghanistan. Government of India has declared and banned HuM as a jihad organisation.

Jaish-e-Mohammed is a Pakistan-based Deobandi Jihadist Mujahideen group active in Kashmir which is widely considered as a terrorist group. The group's primary motive is to separate Kashmir from India and merge it into Pakistan. Since its inception in 2000, the group has carried out several attacks in the state of Jammu and Kashmir. It portrays Kashmir as a "gateway" to the entire India, whose Muslims are also deemed to be in need of liberation. After liberating Kashmir, it aims to carry its 'Jihad' to other parts of India, with an intent to drive Hindus and other non-Muslims from the Indian subcontinent. It has carried out several attacks primarily in the Indian administered Jammu and Kashmir. It also maintained close relations with the Taliban and Al-Qaeda in Afghanistan and continues to be allied with these groups.

The insurgency in Jammu and Kashmir is against the Indian administration of Jammu and Kashmir, a region constituting the southern portion of the larger Kashmir region, which has been the subject of a dispute between India and Pakistan since 1947.
Mohammad Masood Azhar Alvi is a radical Islamist and terrorist, being the founder and leader of the Pakistan-based terrorist organisation Jaish-e-Mohammed, active mainly in the Pakistani-administered portion of the Kashmir region. His actions are not limited to the South Asian region, for instance BBC News describing him as "the man who brought jihad to Britain." On 1 May 2019, Masood Azhar was listed as an international terrorist by United Nations Security Council.
The United Jihad Council, also known as the Muttahida Jihad Council (MJC), is a terrorist organisation formed by the Pakistan Army for unified command and control over the anti-Indian militant groups operating in Jammu and Kashmir. It was formed in the summer of 1994 and is currently headed by Syed Salahuddin, the leader of Hizb-ul-Mujahideen. The organisation was created to unify and focus efforts of various armed militant groups fighting against the Indian rule in Kashmir. This made distribution of resources like arms, ammunition, propaganda materials and communications more streamlined. It also made it easier to coordinate and pool resources of various militant groups to collect information, plan operations and strike at targets of military importance inside Indian administered Kashmir.
Qari Saifullah Akhtar was an alleged member of Al-Qaeda who was in Pakistani custody a few times prior to his death. Akhtar, a graduate of Jamia Uloom-ul-Islamia in Karachi, had been the leader of Harkat-ul-Jihad-al-Islami (HUJI), a jihadi organization. He was a key figure and founder of HUJI and was involved in jihadi groups since the early 1980s. He was appointed the head of HUJI following the killing of Mawlana Irshad Ahmed at Sharana during clashes with Soviet forces in June 1985. He was reportedly involved in the 1995 coup attempt to topple the Pakistani government led by Benazir Bhutto. When HUJI merged with Harkat-ul-Mujahideen (HUM) around 1990 to form Harkat-ul-Ansar (HUA), Akhtar acted as deputy to former HUM leader and then amir Maulana Fazalur Rehman Khalil. HUA dissolved back into two separate groups in 1997, allowing Akhtar to become amir of HUJI. Since 1998 when Osama bin Laden released a fatwa under the banner World Islamic Front for Jihad Against the Jews and Crusaders, segments of HUJI have joined al-Qaeda. It has been reported that Akhtar was running a training camp at Rishkhor, Afghanistan before the US invaded Afghanistan in 2001, and had trained 3,500 persons in conventional and unconventional combat. He disappeared from Afghanistan but was apprehended in August 2004 in the United Arab Emirates. He was then handed over to Pakistan.
Harkat-ul-Jihad-al-Islami is a Pakistani Islamic fundamentalist organisation most active in South Asian countries of Pakistan, Bangladesh and India since the early 1990s. It was banned in Bangladesh in 2005. The operational commander of HuJI, Ilyas Kashmiri, was killed in a US drone strike in South Waziristan on 4 June 2011. He was linked to the 13 February 2010 bombing of a German bakery in Pune. A statement was released soon after the attack which claimed to be from Kashmiri; it threatened other cities and major sporting events in India. A local Taliban commander named Shah Sahib was named as Kashmiri's successor.
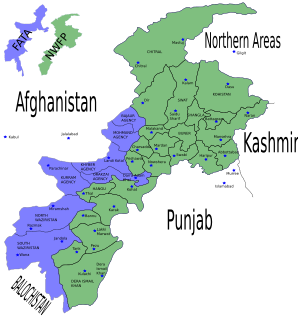
The insurgency in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, also known as the War in North-West Pakistan, is an ongoing armed conflict involving Pakistan, and Islamist militant groups such as the Tehrik-i-Taliban Pakistan (TTP), Jundallah, Lashkar-e-Islam (LeI), TNSM, al-Qaeda, and their Central Asian allies such as the ISIL–Khorasan (ISIL), Islamic Movement of Uzbekistan, East Turkistan Movement, Emirate of Caucasus, and elements of organized crime.
Mujahideen, or Mujahidin, is the plural form of mujahid, an Arabic term that broadly refers to Islamic guerrillas who engage in jihad, interpreted by most Muslims as the fight on behalf of God, religion or the community (ummah).

Tehrik-i-Taliban Pakistan, alternatively referred to as the Pakistani Taliban, is a Pashtun Islamist armed student group that is an umbrella organization of various student militant groups based along the Afghan–Pakistani border. Most Taliban groups in Pakistan coalesce under the TTP. In December 2007, about 13 groups united under the leadership of Baitullah Mehsud to form the TTP.
Pakistan and state-sponsored terrorism refers to the involvement of Pakistan in terrorism through the backing of various designated terrorist organizations. Pakistan has been frequently accused by various countries, including its neighbours Afghanistan, India, and Iran, as well as by the United States, the United Kingdom, Germany, and France, of involvement in a variety of terrorist activities in both its local region of South Asia and beyond. Pakistan's northwestern tribal regions along the Afghanistan–Pakistan border have been described as an effective safe haven for terrorists by Western media and the United States Secretary of Defense, while India has accused Pakistan of perpetuating the insurgency in Jammu and Kashmir by providing financial support and armaments to militant groups, as well as by sending state-trained terrorists across the Line of Control and de jure India–Pakistan border to launch attacks in Indian-administered Kashmir and India proper, respectively. According to an analysis published by the Saban Center for Middle East Policy at the Brookings Institution in 2008, Pakistan was reportedly, "with the possible exception of Iran, perhaps the world's most active sponsor of terrorist groups... aiding these groups that pose a direct threat to the United States. Pakistan's active participation has caused thousands of deaths in the region; all these years Pakistan has been supportive to several terrorist groups despite several stern warnings from the international community." Daniel Byman, a professor and senior analyst of terrorism and security at the Center For Middle East Policy, also wrote that, "Pakistan is probably 2008's most active sponsor of terrorism". In 2018, the former Prime Minister of Pakistan, Nawaz Sharif, suggested that the Pakistani government played a role in the 2008 Mumbai attacks that were carried out by Lashkar-e-Taiba, a Pakistan-based Islamist terrorist group. In July 2019, Pakistani Prime Minister Imran Khan, on an official visit to the United States, acknowledged the presence of some 30,000–40,000 armed terrorists operating on Pakistani soil. He further stated that previous administrations were hiding this truth, particularly from the United States, for the last 15 years during the War on Terror.

Ilyas Kashmiri, also referred to as Maulana Ilyas Kashmiri and Muhammad Ilyas Kashmiri, was a terrorist who fought against the state of India in Kashmir. NBC News reported that United States officials had mentioned him as a possible successor to Osama bin Laden as head of al-Qaeda, which was later found out to be a fake story. Prior to his death, a CNN News headline called him the "most dangerous man on Earth", while the late journalist Syed Saleem Shahzad said of him that "he is invariably described by the world intelligence agencies as the most effective, dangerous, and successful guerrilla leader in the world."
Jamia Uloom-ul-Islamia is an Islamic University situated in Banoori Town, Karachi, Pakistan. The university continues the tradition of the Darul Uloom system initiated by Darul Uloom Deoband. As of 2007, there are about twelve thousand students in different departments of the Jamiah and its branches, including a number of foreign students from over sixty countries.
Fazlur Rehman Khalil is a founder of Harkat-ul-Mujahideen (HuM) and current leader of Ansar-ul-Umma, which is accused of being a front organization of the banned HuM.

Al-Qaeda in the Indian Subcontinent usually abbreviated as AQIS, is an Islamist militant organization which aims to fight the governments of Pakistan, Afghanistan, India, Myanmar and Bangladesh in order to establish an Islamic state. The militant group has also stated its intentions to attack American targets in the Indian Subcontinent. This group is listed as a terrorist organization by the United Nations, United States, Canada, Pakistan and India.
Sana-ul-Haq, better known as Asim Umar, was an Indian militant and the leader of al-Qaeda in the Indian Subcontinent. al-Qaeda leader Ayman al-Zawahiri announced the creation of AQIS and introduced Asim Umar as its leader in a video posted online in September 2014.
Darsgah-Jihad-O-Shahadat is an Islamist group based in the southern Indian city of Hyderabad, with branches in the state of Kerala. The group claims to have trained about 50,000 people in self-defence techniques at its training camps in Hazrat Ujale Shah Idgah grounds at Saidabad and Purani Haveli.
Organizations designated as terrorist by Bahrain are organizations that have been designated by the Bahrain government as terrorist organisations. The Ministry of Foreign Affairs maintains a public list of designated terrorist individuals and entities.
References
- ↑ "Farman Shinwari, Qaeda's new Pak chief and Harkat's old associate". The Indian Express. May 2, 2012. Retrieved 8 January 2013.
- ↑ "Farman Shinwari named new al-Qaeda chief in Pakistan". The News International. April 30, 2012. Retrieved 8 January 2013.
- ↑ "Farman Shinwari: New Al Qaeda leader, Kashmir jihad expert". Rediff.com. July 18, 2012. Retrieved 8 January 2013.
- ↑ "Al-Qaida names Shinwari as its new chief in Pak". The Tribune. May 1, 2012. Retrieved 8 January 2013.
- ↑ https://web.archive.org/web/20130807142045/http://www.thenews.com.pk/Todays-News-7-194673-Well-wishers-in-police-prison-played-key-role-says-Taliban