| Original author(s) | Collabora |
|---|---|
| Initial release | 2006 |
| Stable release | 0.2.8.1 [1] / 10 March 2016 |
| Written in | C GLib |
| Platform | Cross-platform |
| Type | telecommunication technology |
| License | GNU Lesser General Public License |
| Website | www |
Farstream (previously known as Farsight) is an audio/video conferencing framework based on GStreamer. The project provides audio/video conferencing for as many instant messengers as possible through a modular design. Telepathy and Farsight constitute the first implementation of the Jingle XMPP protocol.
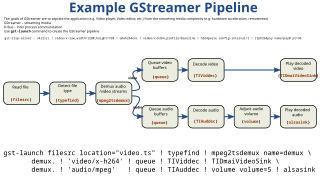
GStreamer is a pipeline-based multimedia framework that links together a wide variety of media processing systems to complete complex workflows. For instance, GStreamer can be used to build a system that reads files in one format, processes them, and exports them in another. The formats and processes can be changed in a plug and play fashion.
Telepathy is a software framework which can be used to make software for interpersonal communications such as instant messaging, Voice over IP or videoconferencing. Telepathy enables the creation of communications applications using components via the D-Bus inter-process communication mechanism. Through this it aims to simplify development of communications applications and promote code reuse within the free software and open source communities by defining a logical boundary between the applications and underlying network protocols.

Jingle is an extension to the Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP) which adds peer-to-peer (P2P) session control (signaling) for multimedia interactions such as in Voice over IP (VoIP) or videoconferencing communications. It was designed by Google and the XMPP Standards Foundation. The multimedia streams are delivered using the Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP). If needed, NAT traversal is assisted using Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE).
The software is open-source, being distributed under the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) and is intended to run on POSIX-compliant operating systems, including Linux but also Windows and Mac OS X. It is being used for audio/video conferencing on the Nokia 770, [2] N800, [3] N810 and N900. It is also the VoIP framework used by Meego.

Open-source software (OSS) is a type of computer software in which source code is released under a license in which the copyright holder grants users the rights to study, change, and distribute the software to anyone and for any purpose. Open-source software may be developed in a collaborative public manner. Open-source software is a prominent example of open collaboration.

The GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) is a free-software license published by the Free Software Foundation (FSF). The license allows developers and companies to use and integrate a software component released under the LGPL into their own software without being required by the terms of a strong copyleft license to release the source code of their own components. However, any developer who modifies an LGPL-covered component is required to make their modified version available under the same LGPL license. For proprietary software, code under the LGPL is usually used in the form of a shared library, so that there is a clear separation between the proprietary and LGPL components. The LGPL is primarily used for software libraries, although it is also used by some stand-alone applications.
The Portable Operating System Interface (POSIX) is a family of standards specified by the IEEE Computer Society for maintaining compatibility between operating systems. POSIX defines the application programming interface (API), along with command line shells and utility interfaces, for software compatibility with variants of Unix and other operating systems.
Farsight is under development in the Farsight 2 series. The maintainer is Olivier Crête.
Examples of applications using Farstream: