
Guru Gobind Singh was the tenth and last human Sikh Guru. He was a warrior, poet, and philosopher. In 1675, at the age of nine he was formally installed as the leader of the Sikhs after his father Guru Tegh Bahadur was executed by Emperor Aurangzeb. His father was the ninth Sikh Guru. His four biological sons died during his lifetime – two in battle and two executed by the Mughal governor Wazir Khan.

The Takht Sri Darbar Sahib Damdama Sahib, is one of the five takhts or Seat of Temporal Authority of Sikhism, located in Talwandi Sabo, near the city of Bathinda in Bathinda district of Punjab, India. At this place Guru Gobind Singh, the tenth Sikh Guru, prepared the full version of the Sikh scriptures called Sri Guru Granth Sahib in 1705. The other four Takhts are the Akal Takht, Takht Sri Keshgarh Sahib, Takht Sri Patna Sahib and Takht Sri Hazur Sahib.

Fatehgarh Sahib is a city and a sacred pilgrimage site of Sikhism in the north west Indian state of Punjab. It is the headquarters of Fatehgarh Sahib district, located about 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) north of Sirhind. Fatehgarh Sahib is named after Fateh Singh, the 7-year-old son of Guru Gobind Singh, who was seized and buried alive, along with his 9-year-old brother Zoravar Singh, by the Mughals under the orders of governor Wazir Khan during the ongoing Mughal-Sikh wars of the early 18th century. The town experienced major historical events after the martyrdom of the sons in 1705, with frequent changes of control between the Sikhs and Mughals.
Sadhaura is a town, near Yamunanagar city with Municipal Committee in Yamunanagar district in the Indian state of Haryana. The city of Yamunanagar, it is of great historic significance. Sadhaura is very old town many historical temples/Dargah are there like Manokamna Temple, Laxmi narayan Temple, Roza Peer Dargah are some famous places in Sadhaura.
Samana is a town and a municipal council, nearby Patiala City in Patiala district in the Indian state of Punjab.
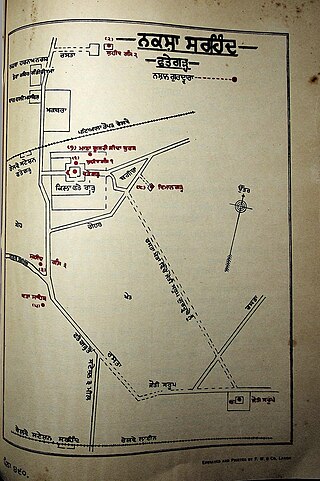
Sirhind is the older name of Fatehgarh Sahib, a city and Sikh pilgrimage site in Punjab, India. It is situated on the Delhi to Lahore Highway. It has a population of about 60,851 . It is now a district headquarters in the state of Punjab; the name of the district is Fatehgarh Sahib.

Gurdwara Fatehgarh Sahib is a Sikh gurdwara or place of worship in the city of Fatehgarh Sahib in the Indian state of Punjab. The gurdwara marks the 1710 conquest of the city by the Sikhs under the leadership of Banda Singh Bahadur. Sikhs captured the area and razed the fort built by Ferozshah Tughlaq to the ground.

The Fateh Burj, a prominent tourist site in Punjab and the tallest victory tower in India, is situated in the historical village of Chappar Chiri in the SAS Nagar district of Punjab state. It was completed in 2011. The 328-foot (100 m) tower is dedicated to establishment of the Sikh Misls in a large part of Punjab in 1711. It is situated in Banda Singh Bahadur Road. It is situated just outside Mohali, 140 kilometres from Amritsar and 20 km from Sirhind. It was here that Banda Singh Bahadur, one of the most respected and great Sikh warriors, won a decisive battle against Wazir Khan, commander of the Mughal army.

Mirza Askari, better known by his title Wazir Khan, He was the Moghul Faujdar of Sirhind region and (Deputy-Governor) Sarkar of Sirhind under Delhi Subah in the present-day state of Punjab, and administered the territory that lay between the Sutlej and Yamuna rivers, he official notable for his conflicts with the Sikhs, he was the descendant of of Persian descent who was the Courtrian to the third Moghol Emperor Akbar I.

Banda Singh Bahadur; born Lachman Dev;, was a Sikh warrior and a general of the Khalsa Army. At age 15, he left home to become an ascetic, and was given the name Madho Das Bairagi. He established a monastery at Nānded, on the bank of the river Godāvarī. In 1707, Guru Gobind Singh accepted an invitation to meet Mughal Emperor Bahadur Shah I in southern India, he visited Banda Singh Bahadur in 1708. Banda became disciple of Guru Gobind Singh and was given a new name, Gurbaksh Singh(as written in Mahan Kosh), after the baptism ceremony. He is popularly known as Banda Singh Bahadur. He was given five arrows by the Guru as a blessing for the battles ahead. He came to Khanda, Sonipat and assembled a fighting force and led the struggle against the Mughal Empire.
Lohgarh is a historic town in Bilaspur tehsil of Yamunanagar district of Haryana in India. It was the capital of First Sikh State under Baba Banda Singh Bahadur from 1710 to 1716.

Binod Singh, a Trehan Khatri and a descendant of Guru Angad, was an army man and disciple of Guru Gobind Singh and was among few Sikhs who accompanied him to Nanded in 1706. In Budha Dal Chronicles, Guru Gobind Singh made Baba Binod Singh the head of the Khalsa.

Baba Baj Singh, also known as Baj Bahadur, was a Sikh general, governor, scholar and martyr from present-day India.
The siege of Sirhind was fought between the Mughal Empire and Sikh forces in 1710. The Sikhs besieged, stormed, captured, plundered and razed the city of Sirhind after defeating and beheading Wazir Khan in the Battle of Chappar Chiri.
The Battle of Samana was fought between the Khalsa under the leadership of Banda Singh Bahadur and the Mughal Government of Samana in 1709. Following the battle, Banda Singh Bahadur shook the administration of Delhi.

The Battle of Chappar Chiri, also called Battle of Sirhind, was fought between Mughal Empire and the Sikhs on 12 May 1710 at Chappar Chiri, located 20 kilometers from Sirhind.

The Battle of Rahon was fought between Sikhs and Mughal Empire on 11 October 1710.

Chaar Sahibzaade 2: Rise of Banda Singh Bahadur is a 2016 Indian Punjabi-language animated film, directed and produced by Harry Baweja. It is the sequel to the 2014 film Chaar Sahibzaade. The film was released on 11 November 2016.

Chapar Chiri is a small village located in the Mohali district of Punjab, India. It is near Mohali city and is 14 km west of Chandigarh.
The Khalsa Fauj were the military forces of the Khalsa order of the Sikhs, established by the tenth guru, Guru Gobind Singh, in 1699. It replaced the Akal Sena that had been established by the sixth guru, Guru Hargobind.















