Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an Internet Standard protocol for collecting and organizing information about managed devices on IP networks and for modifying that information to change device behavior. Devices that typically support SNMP include cable modems, routers, switches, servers, workstations, printers, and more.
FCAPS is the ISO Telecommunications Management Network model and framework for network management. FCAPS is an acronym for fault, configuration, accounting, performance, security, the management categories into which the ISO model defines network management tasks. In non-billing organizations accounting is sometimes replaced with administration.
Nagios Core, formerly known as Nagios, is a free and open-source computer-software application that monitors systems, networks and infrastructure. Nagios offers monitoring and alerting services for servers, switches, applications and services. It alerts users when things go wrong and alerts them a second time when the problem has been resolved.
The Common Management Information Protocol (CMIP) is the OSI specified network management protocol.
In computing, syslog is a standard for message logging. It allows separation of the software that generates messages, the system that stores them, and the software that reports and analyzes them. Each message is labeled with a facility code, indicating the software type generating the message, and assigned a severity level.
Network monitoring is the use of a system that constantly monitors a computer network for slow or failing components and that notifies the network administrator in case of outages or other trouble. Network monitoring is part of network management.
A network tap is a system that monitors events on a local network. A tap is typically a dedicated hardware device, which provides a way to access the data flowing across a computer network. In many cases, it is desirable for a third party to monitor the traffic between two points in the network. If the network between points A and B consists of a physical cable, a "network tap" may be the best way to accomplish this monitoring. The network tap has three ports: an A port, a B port, and a monitor port. A tap inserted between A and B passes all traffic through unimpeded in real time, but also copies that same data to its monitor port, enabling a third party to listen. Network taps are commonly used for network intrusion detection systems, VoIP recording, network probes, RMON probes, packet sniffers, and other monitoring and collection devices and software that require access to a network segment. Taps are used in security applications because they are non-obtrusive, are not detectable on the network, can deal with full-duplex and non-shared networks, and will usually pass through or bypass traffic even if the tap stops working or loses power.
Security event management (SEM), and the related SIM and SIEM, are computer security disciplines that use data inspection tools to centralize the storage and interpretation of logs or events generated by other software running on a network.
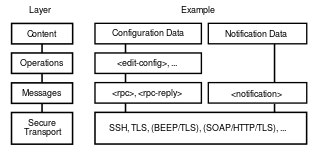
The Network Configuration Protocol (NETCONF) is a network management protocol developed and standardized by the IETF. It was developed in the NETCONF working group and published in December 2006 as RFC 4741 and later revised in June 2011 and published as RFC 6241. The NETCONF protocol specification is an Internet Standards Track document.
OpenNMS is a free and open-source enterprise grade network monitoring and network management platform. It is developed and supported by a community of users and developers and by the OpenNMS Group, offering commercial services, training and support.
The Remote Network MONitoring (RMON) MIB was developed by the IETF to support monitoring and protocol analysis of LANs. The original version focused on OSI Layer 1 and Layer 2 information in Ethernet and Token Ring networks. It has been extended by RMON2 which adds support for Network- and Application-layer monitoring and by SMON which adds support for switched networks. It is an industry standard specification that provides much of the functionality offered by proprietary network analyzers. RMON agents are built into many high-end switches and routers.
The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of network monitoring systems. Please see the individual products' articles for further information.
Avaya Unified Communications Management in computer networking is the name of a collection of GUI software programs from Avaya utilizing a service-oriented architecture (SOA) that serves as a foundation for unifying configuration and monitoring of Avaya Unified Communications Servers and data systems.
OTP is a collection of useful middleware, libraries, and tools written in the Erlang programming language. It is an integral part of the open-source distribution of Erlang. The name OTP was originally an acronym for Open Telecom Platform, which was a branding attempt before Ericsson released Erlang/OTP as open source. However neither Erlang nor OTP is specific to telecom applications.

Shinken is an open source computer system and network monitoring software application compatible with Nagios. It watches hosts and services, gathers performance data and alerts users when error conditions occur and again when the conditions clear.

Extromatica Network Monitor is a network monitoring application created and maintained by Extromatica company. It is designed to monitor network hardware, servers and network services for faults and performance degradation. It alerts users when things go wrong and again when they get better. The software supports a variety of real-time notification mechanisms, including Short Message Service (SMS).
Event Management, as defined by ITIL, is the process that monitors all events that occur through the IT infrastructure. It allows for normal operation and also detects and escalates exception conditions.

SNAMP is an open-source, cross-platform software platform for telemetry, tracing and elasticity management of distributed applications.

Octopussy, also known as 8Pussy, is a free and open-source computer-software which monitors systems, by constantly analyzing the syslog data they generate and transmit to such a central Octopussy server. Therefore, software like Octopussy plays an important role in maintaining an ISMS within ISO/IEC 27001-compliant environments.
NXLog is a multi-platform log management tool that helps to easily identify security risks, policy breaches or analyze operational problems in server logs, operation system logs and application logs. In concept NXLog is similar to syslog-ng or Rsyslog but it is not limited to UNIX and syslog only. It supports different platforms, log sources and formats, so NXLog can be used to implement a centralized, scalable logging system. NXLog Community Edition is proprietary and can be downloaded free of charge with no license costs or limitations.




