See also
| Sovereign states |
|
|---|---|
| States with limited recognition | |
| Dependencies and other entities | |
Fauna of Greece may refer to:
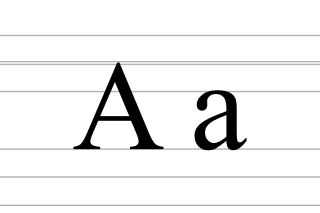
A or a is the first letter and the first vowel letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, and others worldwide. Its name in English is a, plural aes.

Cyprus, officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Although it is geographically located in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical make-up are overwhelmingly Southeast European. It is the third largest and third most populous island in the Mediterranean. It is located southeast of Greece, south of Turkey, west of Syria and Lebanon, northwest of Israel and Palestine, and north of Egypt. Its capital and largest city is Nicosia. Cyprus hosts the British-controlled military bases Akrotiri and Dhekelia, whilst the northeast portion of the island is de facto governed by the self-declared Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus, which is separated from the Republic of Cyprus by the United Nations Buffer Zone.

Greek is an Indo-European language, constituting an independent Hellenic branch within the Indo-European language family. It is native to Greece, Cyprus, Italy, southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, Caucasus, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems.

Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, Greece shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to the east. The Aegean Sea lies to the east of the mainland, the Ionian Sea to the west, and the Sea of Crete and the Mediterranean Sea to the south. Greece has the longest coastline on the Mediterranean Basin, featuring thousands of islands. The country comprises nine traditional geographic regions, and has a population of over 10.4 million. Athens is the nation's capital and largest city, followed by Thessaloniki and Patras.

Ancient Greece was a northeastern Mediterranean civilisation, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity, that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically related city-states and communities. Prior to the Roman period, most of these regions were officially unified only once under the Kingdom of Macedon from 338 to 323 BC. In Western history, the era of classical antiquity was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine period.

Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek, Dark Ages, the Archaic or Homeric period, and the Classical period.

The Aegean Islands are the group of islands in the Aegean Sea, with mainland Greece to the west and north and Turkey to the east; the island of Crete delimits the sea to the south, those of Rhodes, Karpathos and Kasos to the southeast. The ancient Greek name of the Aegean Sea, Archipelago, was later applied to the islands it contains and is now used more generally, to refer to any island group.

In ancient Greek religion and mythology, the twelve Olympians are the major deities of the Greek pantheon, commonly considered to be Zeus, Poseidon, Hera, Demeter, Aphrodite, Athena, Artemis, Apollo, Ares, Hephaestus, Hermes, and either Hestia or Dionysus. They were called Olympians because, according to tradition, they resided on Mount Olympus.
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BC. It was derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and is the earliest known alphabetic script to have developed distinct letters for consonants as well as vowels. In Archaic and early Classical times, the Greek alphabet existed in many local variants, but, by the end of the 4th century BC, the Ionic-based Euclidean alphabet, with 24 letters, ordered from alpha to omega, had become standard throughout the Greek-speaking world and is the version that is still used for Greek writing today.
Romanization of Greek is the transliteration (letter-mapping) or transcription (sound-mapping) of text from the Greek alphabet into the Latin alphabet.

The Super League Greece 1, or Stoiximan Super League for sponsorship reasons, is the highest professional association football league in Greece. The league was formed on 16 July 2006 and replaced Alpha Ethniki at the top of the Greek football league system. The members of the cooperative are the Football Limited Companies (P.A.E.) that have the right to participate in the Super League 1 championship. The president of Super League 1 is Vangelis Marinakis, who has been re-elected for the third time.

The Greece national under-21 football team is the national under-21 football team of Greece and is controlled by the Hellenic Football Federation, the governing body for football in Greece. The team competes in the European Under-21 Football Championship, held every two years.

The Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, also known as the Seven Wonders of the World or simply the Seven Wonders, is a list of seven notable structures present during classical antiquity. The first known list of seven wonders dates back to the 2nd–1st century BC.