Related Research Articles

An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope that is specific for one particular epitope on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can tag a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly.
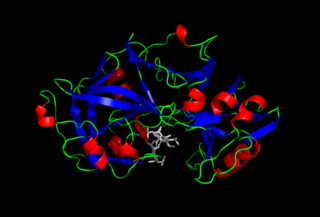
Pepsin is an endopeptidase that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides. It is produced in the gastric chief cells of the stomach lining and is one of the main digestive enzymes in the digestive systems of humans and many other animals, where it helps digest the proteins in food. Pepsin is an aspartic protease, using a catalytic aspartate in its active site.
Opsonins are extracellular proteins that, when bound to substances or cells, induce phagocytes to phagocytose the substances or cells with the opsonins bound. Thus, opsonins act as tags to label things in the body that should be phagocytosed by phagocytes. Different types of things ("targets") can be tagged by opsonins for phagocytosis, including: pathogens, cancer cells, aged cells, dead or dying cells, excess synapses, or protein aggregates. Opsonins help clear pathogens, as well as dead, dying and diseased cells.
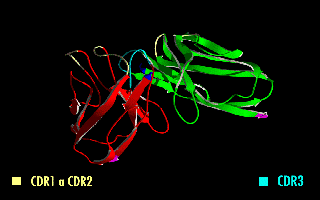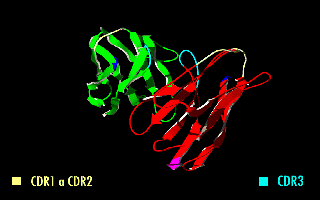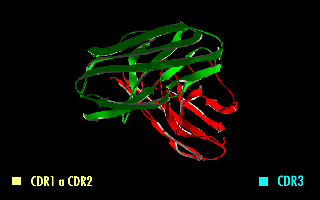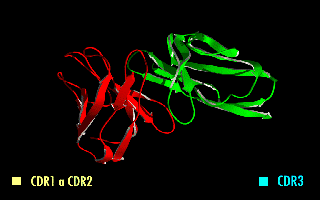
A single-chain variable fragment (scFv) is not actually a fragment of an antibody, but instead is a fusion protein of the variable regions of the heavy (VH) and light chains (VL) of immunoglobulins, connected with a short linker peptide of ten to about 25 amino acids. The linker is usually rich in glycine for flexibility, as well as serine or threonine for solubility, and can either connect the N-terminus of the VH with the C-terminus of the VL, or vice versa. This protein retains the specificity of the original immunoglobulin, despite removal of the constant regions and the introduction of the linker. The image to the right shows how this modification usually leaves the specificity unaltered.

Protein A is a 42 kDa surface protein originally found in the cell wall of the bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. It is encoded by the spa gene and its regulation is controlled by DNA topology, cellular osmolarity, and a two-component system called ArlS-ArlR. It has found use in biochemical research because of its ability to bind immunoglobulins. It is composed of five homologous Ig-binding domains that fold into a three-helix bundle. Each domain is able to bind proteins from many mammalian species, most notably IgGs. It binds the heavy chain within the Fc region of most immunoglobulins and also within the Fab region in the case of the human VH3 family. Through these interactions in serum, where IgG molecules are bound in the wrong orientation, the bacteria disrupts opsonization and phagocytosis.
In biochemistry, avidity refers to the accumulated strength of multiple affinities of individual non-covalent binding interactions, such as between a protein receptor and its ligand, and is commonly referred to as functional affinity. Avidity differs from affinity, which describes the strength of a single interaction. However, because individual binding events increase the likelihood of occurrence of other interactions, avidity should not be thought of as the mere sum of its constituent affinities but as the combined effect of all affinities participating in the biomolecular interaction. A particular important aspect relates to the phenomenon of 'avidity entropy'. Biomolecules often form heterogenous complexes or homogeneous oligomers and multimers or polymers. If clustered proteins form an organized matrix, such as the clathrin-coat, the interaction is described as a matricity.
The fragment antigen-binding region is a region on an antibody that binds to antigens. It is composed of one constant and one variable domain of each of the heavy and the light chain. The variable domain contains the paratope, comprising a set of complementarity-determining regions, at the amino terminal end of the monomer. Each arm of the Y thus binds an epitope on the antigen.
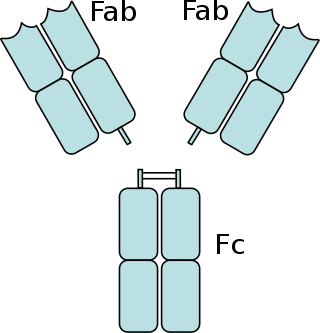
The fragment crystallizable region is the tail region of an antibody that interacts with cell surface receptors called Fc receptors and some proteins of the complement system. This property allows antibodies to activate the immune system. In IgG, IgA and IgD antibody isotypes, the Fc region is composed of two identical protein fragments, derived from the second and third constant domains of the antibody's two heavy chains; IgM and IgE Fc regions contain three heavy chain constant domains in each polypeptide chain. The Fc regions of IgGs bear a highly conserved N-glycosylation site. Glycosylation of the Fc fragment is essential for Fc receptor-mediated activity. The N-glycans attached to this site are predominantly core-fucosylated diantennary structures of the complex type. In addition, small amounts of these N-glycans also bear bisecting GlcNAc and α-2,6 linked sialic acid residues.
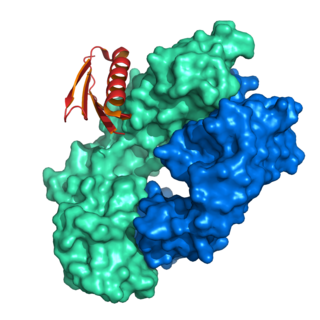
Protein L was first isolated from the surface of bacterial species Peptostreptococcus magnus and was found to bind immunoglobulins through L chain interaction, from which the name was suggested. It consists of 719 amino acid residues. The molecular weight of Protein L purified from the cell walls of Peptostreptoccus magnus was first estimated as 95kD by SDS-PAGE in the presence of reducing agent 2-mercaptoethanol, while the molecular weight was determined to 76kD by gel chromotography in the presence of 6 M guanidine HCl. Protein L does not contain any interchain disulfide loops, nor does it consist of disulfide-linked subunits. It is an acidic molecule with a pI of 4.0. Unlike Protein A and Protein G, which bind to the Fc region of immunoglobulins (antibodies), Protein L binds antibodies through light chain interactions. Since no part of the heavy chain is involved in the binding interaction, Protein L binds a wider range of antibody classes than Protein A or G. Protein L binds to representatives of all antibody classes, including IgG, IgM, IgA, IgE and IgD. Single chain variable fragments (scFv) and Fab fragments also bind to Protein L.
Small modular immunopharmaceuticals, or SMIPs for short, are artificial proteins that are intended for use as pharmaceutical drugs. They are largely built from parts of antibodies (immunoglobulins), and like them have a binding site for antigens that could be used for monoclonal antibody therapy. SMIPs have similar biological half-life and, being smaller than antibodies, are reasoned to have better tissue penetration properties. They were invented by Trubion and are now being developed by Emergent BioSolutions, which acquired Trubion in 2010.
A bispecific monoclonal antibody is an artificial protein that can simultaneously bind to two different types of antigen or two different epitopes on the same antigen. Naturally occurring antibodies typically only target one antigen. BsAbs can be manufactured in several structural formats. BsAbs can be designed to recruit and activate immune cells, to interfere with receptor signaling and inactivate signaling ligands, and to force association of protein complexes. BsAbs have been explored for cancer immunotherapy, drug delivery, and Alzeimer's disease.

Immunoglobulin heavy constant alpha 1 is a immunoglobulin gene with symbol IGHA1. It encodes a constant (C) segment of Immunoglobulin A heavy chain. Immunoglobulin A is an antibody that plays a critical role in immune function in the mucous membranes. IgA shows the same typical structure of other antibody classes, with two heavy chains and two light chains, and four distinct domains: one variable region, and three variable regions. As a major class of immunoglobulin in body secretions, IgA plays a role in defending against infection, as well as preventing the access of foreign antigens to the immunologic system.
Monospecific antibodies are antibodies whose specificity to antigens is singular in any of several ways: antibodies that all have affinity for the same antigen; antibodies that are specific to one antigen or one epitope; or antibodies specific to one type of cell or tissue. Monoclonal antibodies are monospecific, but monospecific antibodies may also be produced by other means than producing them from a common germ cell. Regarding antibodies, monospecific and monovalent overlap in meaning; both can indicate specificity to one antigen, one epitope, or one cell type. However, antibodies that are monospecific to a certain tissue, or all monospecific to the same tissue because clones, can be polyvalent in their epitope binding.
A heavy-chain antibody is an antibody which consists only of two heavy chains and lacks the two light chains usually found in antibodies.
Primary and secondary antibodies are two groups of antibodies that are classified based on whether they bind to antigens or proteins directly or target another (primary) antibody that, in turn, is bound to an antigen or protein.

Two chemically linked fragments antigen-binding form an artificial antibody that binds to two different antigens, making it a type of bispecific antibody. They are fragments antigen-binding of two different monoclonal antibodies and are linked by chemical means like a thioether. Typically, one of the Fabs binds to a tumour antigen and the other to a protein on the surface of an immune cell, for example an Fc receptor on a macrophage. In this way, tumour cells are attached to immune cells, which destroy them.
Snake antivenom is a medication made up of antibodies used to treat snake bites by venomous snakes. It is a type of antivenom.
In molecular biology, the domain B, refers to the immunoglobulin-binding domain found in the Staphylococcus aureus virulence factor protein A (SpA). Hence, it is abbreviated to SpAB.
F-star Biotechnology Ltd. is a biotechnology company, founded in Vienna in 2006, with a current main research site in Cambridge, UK. The company is focused in developing bispecific monoclonal antibodies using a modular combinatorial approach that engineers the Fc constant region of an immunoglobulin into a novel antigen-binding site.
Recombinant antibodies are antibody fragments produced by using recombinant antibody coding genes. They mostly consist of a heavy and light chain of the variable region of immunoglobulin. Recombinant antibodies have many advantages in both medical and research applications, which make them a popular subject of exploration and new production against specific targets. The most commonly used form is the single chain variable fragment (scFv), which has shown the most promising traits exploitable in human medicine and research. In contrast to monoclonal antibodies produced by hybridoma technology, which may lose the capacity to produce the desired antibody over time or the antibody may undergo unwanted changes, which affect its functionality, recombinant antibodies produced in phage display maintain high standard of specificity and low immunogenicity.
References
- ↑ Wozniak-Knopp G, Bartl S, Bauer A, Mostageer M, Woisetschläger M, Antes B, Ettl K, Kainer M, Weberhofer G, Wiederkum S, Himmler G, Mudde GC, Rüker F (2010). "Introducing antigen-binding sites in structural loops of immunoglobulin constant domains: Fc fragments with engineered HER2/neu-binding sites and antibody properties". Protein Eng Des. 23 (4): 289–297. doi: 10.1093/protein/gzq005 . PMID 20150180.